A blood sugar chart shows a person's ideal blood sugar level throughout the day, including before and after meals. It can help a person manage their blood sugar if they need to keep their blood sugar levels within normal limits, such as people with diabetes. Another blood sugar level that people should pay attention to is the blood sugar level 2 hours after eating.
1. What is a 2-hour postprandial blood sugar level?
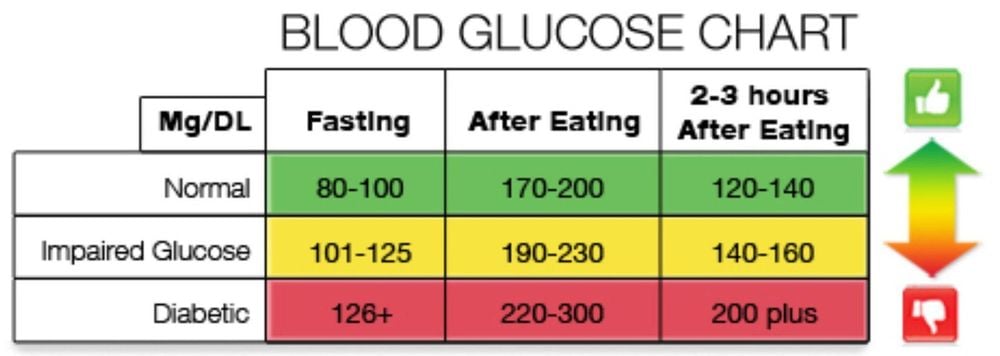
A normal blood sugar level is less than 100 mg/dL after not eating (fasting) for at least 8 hours. This number is less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating.
Blood sugar levels tend to be lowest during the day just before meals. Pre-meal blood sugar levels in people without diabetes range from 70 to 80 mg/dL. For some people, 60 mg/dL is normal; for others, 90 mg/dL is standard.
However, in addition to the 2-hour postprandial blood sugar level, there are other blood sugar levels used to assess whether a person has diabetes and to monitor blood sugar control in people who already have diabetes.
2. Assessing Blood Sugar
2.1. Normal Blood Sugar Ranges and Diabetes
For most healthy people, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
When fasting: 4.0 -5.4 mmol / L (72 to 99 mg / dL).
2 hours after eating: Up to 7.8 mmol / L (140 mg / dL).
Blood sugar levels in people with diabetes are as follows:
Before meals: 4 to 7 mmol / L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
After meals: Less than 9 mmol / L for people with type 1 diabetes and less than 8.5 mmol / L for people with type 2 diabetes.
2.2. Blood sugar levels in diabetes diagnosis
| Plasma glucose test | Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
| Random | Below 11.1 mmol/l.Below 200 mg/dl. | 11.1 mmol/l or higher.200 mg/dl or higher. | |
| Fasting | Below 5.5 mmol/l.Below 100 mg/dl. | 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l.100 to 125 mg/dl. | 7.0 mmol/l or higher.126 mg/dl or higher. |
| 2 hours after performing the tolerance test | Below 7.8 mmol/l.Below 140 mg/dl. | 7.8 to 11.0 mmol/l.140 to 199 mg/dl. | 11.1 mmol/l or higher.200 mg/dl or higher. |
Random plasma glucose test: A blood sample for a blood glucose test can be taken at any time. This is not planned and is therefore used in the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes when time is of the essence.
Fasting plasma glucose test: A fasting plasma glucose test is performed after fasting for at least 8 hours and is therefore usually performed in the morning.
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): An oral glucose tolerance test is performed after a fasting plasma glucose test and then drinking a glass of water containing 75g of very sweet glucose. After drinking this glass of water, you need to rest until another blood sample is taken 2 hours later.
HbA1c test for diabetes diagnosis: The HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of glucose in the blood.
Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol (6.0%).
Prediabetes when HbA1c level is 42 to 47 mmol/mol (6.0 to 6.4%). Diabetes when HbA1c level is 48 mmol/mol (6.5%) or higher.
3. Why is it important to keep your blood sugar levels in check?
You must control your blood sugar levels because high blood sugar levels over a long period of time increase your risk of developing diabetes complications.
Complications of diabetes include:
- Kidney disease.
- Nerve damage.
- Retinopathy.
- Heart disease.
- Stroke.
The risk of these problems can be reduced by keeping your blood sugar levels under control. Small changes can make a big difference if you are dedicated and maintain them most days.
4. What is the target blood sugar level for everyone?
Doctors use blood sugar charts to set goals and monitor their diabetes treatment plans. Blood sugar charts also help people with diabetes evaluate and self-monitor their blood sugar test results. An individual's ideal blood sugar level depends on when they test their blood sugar during the day, as well as when they ate their last meal before testing.
Most diabetes treatment plans involve keeping blood sugar levels as close to normal or target as possible. This requires regular testing at home and as prescribed by your doctor, along with the ability to compare results to target levels.
To help interpret and evaluate blood sugar results, the following charts outline normal and abnormal blood sugar levels for people with and without diabetes.
| Test time | Target Blood Sugar Levels for People Without Diabetes | Target Blood Sugar Levels for People with Diabetes |
| Before meals | Below 100 mg / dl. | 80–130 mg / dl. |
| 1 – 2 hours after starting a meal | Below 140 mg / dl. | Below 180 mg / dl. |
| Over a 3-month period, the amount of HbA1C in the blood | Less than 5,7%. | Less than 7%. |
Blood sugar levels vary throughout the day and from person to person. Blood sugar levels are typically lowest before breakfast and before other meals. Blood sugar levels are typically highest immediately after meals. People with diabetes will typically have higher blood sugar goals or a higher tolerance range than people without diabetes.
Blood sugar goals vary from person to person depending on many factors, some of which include:
- Age.
- How long you have had diabetes.
- Previously diagnosed with cardiovascular disease.
- Problems with the body's smallest arteries.
- Any known damage to the eyes, kidneys, blood vessels, brain, or heart.
- Individual lifestyle habits and factors.
- Not recognizing low blood sugar.
- Stress.
- Other health conditions.
Most blood sugar charts display recommended levels as a range, allowing for variation within that range among individuals. Some temporary forms of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes, also have separate blood sugar recommendations.
| Test time | Blood sugar level |
| Fast for 8 hours or before breakfast | 60 – 90 mg / dl |
| Before meals | 60 – 90 mg / dl |
| 1 hour after meal | 100 – 120 mg / dl |
Recommendations for fasting blood sugar levels:
| Fasting blood sugar level | Risk Level and Recommended Action |
| Below 50 mg / dl | Danger Level: Seek medical attention. |
| 70 – 90 mg / dl | May be too low: Supplement with sugar if symptoms of low blood sugar occur or seek medical attention. |
| 90 – 120 mg / dl | Normal level. |
| 120 – 160 mg / dl | Seek medical attention. |
| 160 – 240 mg / dl | Too high: Find ways to lower your blood sugar. |
| 240 – 300 mg / dl | Too high: This can be a sign of poor blood sugar management, so see your doctor. |
| 300 mg/dl or more | Very High: Seek immediate medical attention |
As long as your blood sugar levels are not severely high, there are ways to bring them back into the normal range when they become too high.
Some ways to help lower your blood sugar include:
- Limiting your carbohydrate intake without fasting.
- Increasing your water intake to stay hydrated and dilute excess sugar in your blood.
- Increasing physical activity, such as walking after meals, to burn off excess sugar in your blood.
- Eating plenty of fiber.
These methods are not a substitute for medical treatment, but they are a useful addition to any diabetes treatment plan. Managing your blood sugar is an important step in preventing complications from diabetes. Keeping your blood sugar levels within normal ranges can also be a sign that your treatment is working.
Each person will have their own unique needs and characteristics that determine their own target blood sugar levels. Your doctor will set these goals using a blood sugar chart at the beginning of your treatment. Your doctor may adjust these goals as your treatment progresses. If you notice any symptoms of extremely low or high blood sugar, you should seek medical attention.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is implementing a Diabetes and Dyslipidemia Screening Package performed by a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors and supported by modern technological equipment, which will help provide the most accurate diabetes test results, thereby proposing an appropriate treatment regimen.
References: webmd.com, diabetes.co.uk, medicalnewstoday.com
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.