The article was professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Thi Duyen - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Prediabetes is a health condition that can be improved and returned to normal through early intervention in lifestyle and daily activities. Drug intervention to treat prediabetes can be indicated for certain conditions when dietary and lifestyle adjustments are ineffective or ineffective. So when is prediabetes prescribed medication and what are the oral medications?
1. Overview of prediabetes
In the prediabetes stage, blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. All patients with type 2 diabetes first go through the prediabetes stage. The rise in blood sugar during prediabetes occurs when the body develops "insulin resistance." Insulin "s a vital hormone that helps the body regulate glucose levels. Insulin resistance develops if insulin can’t effectively control glucose in the blood and cells.
Insulin resistance can worsen over time if not managed properly. During the prediabetes stage, the body responds by generating extra insulin to keep blood sugar levels near normal. This resistance worsens with age and becomes exacerbated by variables including weight gain and lipid abnormalities. If insulin resistance worsens to the point that the body is unable to create enough insulin to compensate, blood sugar levels rise, resulting in prediabetes.
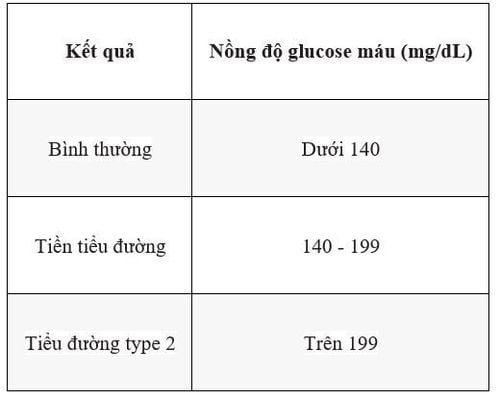
Depending on the results of blood sugar tests, prediabetes may be more precisely diagnosed as "impaired glucose tolerance" or "impaired fasting glucose." Impaired fasting glucose means your blood sugar levels rise after not eating for a while.
Impaired glucose tolerance means your blood sugar levels become unexpectedly high after consuming sugar. To diagnose impaired glucose tolerance, an endocrinologist will typically conduct a test called the 75g oral glucose tolerance test. During this test, the patient drinks a solution containing 75g of sugar, and blood samples are taken after 1 hour and 2 hours for analysis.
Not all cases of prediabetes will progress to type 2 diabetes, but prediabetes increases the likelihood of developing the disease. Prediabetes is also a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Just like people with type 2 diabetes, those with prediabetes often tend to be overweight, have high blood pressure, and have unhealthy cholesterol levels.
2. Can prediabetes be treated with medication?
Currently, some patients with prediabetes take medication along with changes in their diet and daily exercise routine. The only medication currently recognized by the Ministry of Health as beneficial for treating prediabetes is Metformin. Medication is prescribed to prediabetes patients who have one or more of the following risk factors: failure to adjust diet and lifestyle over a long period, low HDL cholesterol, high triglycerides, or a family history of diabetes or obesity. This medication should only be prescribed by an endocrinologist, who will provide guidance on its proper use. Patients should not purchase or use it on their own.
3. Some Notes on Using Metformin for Prediabetes Patients
For prediabetic patients prescribed Metformin, the effective dosage ranges from 1,000mg to 2,000mg daily. However, starting with a low dose is crucial for the body to adapt gradually. The recommended approach is to begin with 500mg/day for the first week, increase by 500mg/day in the second week, and, if necessary, add another 500mg/day in the third week until reaching the desired effect.
Metformin has proven to be highly effective for prediabetes management. Compared to newer drugs, it offers several advantages: it is cost-effective, safer, and does not cause hypoglycemia, a common complication in diabetes patients.

Prediabetes is a reversible condition, often manageable without medication through improved lifestyle modifications alone. The primary goal of prediabetes treatment is to prevent it from progressing into diabetes mellitus. Nevertheless, preventive measures for prediabetes also serve as one of the treatment strategies.
The most effective way to manage prediabetes is by making lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and exercising for at least 30 minutes daily. These activities can improve insulin resistance, lower elevated blood sugar levels, and help prevent progression to diabetes. Metformin (commonly known as Glucophage) can also reduce the risk of developing diabetes. It may enhance the benefits of weight loss and exercise, making it a valuable complementary option for patients.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
References: webmd.com, mayoclinic.org, healthline.com,drugs.com