Collagen plays a vital role in maintaining the elasticity and firmness of connective tissues in the body. Taking collagen supplements orally is a simple yet highly effective way to unlock significant benefits for both health and beauty, especially for women. However, many people remain concerned about whether consuming collagen could potentially harm the kidneys and stomach.
1. What is Collagen?
Collagen is a protein with a specialized structure that contains a full range of essential amino acids. In fact, it is the most abundant protein in our bodies, helping to bind cells and tissues together. Collagen is found in our bones, teeth, muscles, ligaments, and skin. It constitutes 90% of connective tissues and bone mass, and nearly 70% of the skin.
As we get older, our bodies produce less collagen, leading to visible signs of aging such as wrinkles, sagging skin, weakened joints and bones,… Therefore, supplementing with oral collagen or consuming collagen-rich foods (such as bone broth, avocados, salmon,…) is crucial to replenish the collagen levels that naturally decline as we age.
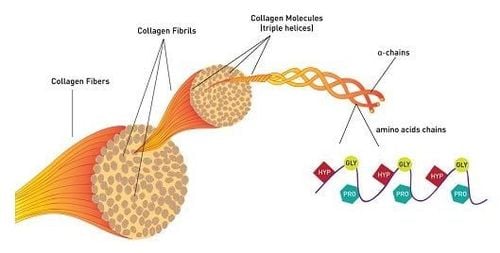
2. What is collagen peptide?
2.1. Structure of collagen peptide
Most oral collagen supplements are in the form of collagen peptides, also known as hydrolyzed collagen. This is a hydrolyzed form of collagen, a fibrous protein found in the extracellular matrix, connective tissues, and the outer membranes of living cells. After hydrolysis, collagen loses its gel-forming ability and becomes soluble in both hot and cold water. Collagen peptides have a low molecular weight and significantly smaller size, making them easier to digest and absorb.
Collagen peptides are rich in amino acids, including glycine, glutamine, proline, and hydroxyproline, which are 10 to 20 times higher than in regular proteins. Protein content can account for 90% to 97% of collagen peptide.

2.2. Absorption
When taken orally, collagen peptides reach the small intestine, where they are absorbed into the bloodstream as small collagen peptides and free amino acids. Through the vascular network, these collagen peptides and free amino acids are distributed throughout the body to target tissues, where they perform their biological functions. Additionally, using collagen in liquid form will result in better absorption than tablet and powder form.
2.3. Benefits
As a dietary supplement, collagen peptides have been shown to play a significant physiological role with positive effects on health. Numerous studies have highlighted the benefits of collagen peptides in improving skin elasticity, supporting digestive health, restoring lost cartilage tissue, reducing activity-related joint pain, strengthening tendons and ligaments, increasing lean muscle mass in older men and premenopausal women, enhancing bone mineral density in postmenopausal women, and protecting the body from UVA radiation,…
3. Oral collagen and kidney function
3.1. What is kidney function?
Essentially, our kidneys filter waste products, excess nutrients and fluids from the blood, which are then excreted through urine. Approximately 20% of the blood from the heart passes through the kidneys. In adults, the kidneys can filter up to 180 liters of blood per day. A test used to measure the kidney's ability to filter blood and eliminate waste is known as the Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) test (“glomerular” relates to the kidney filtering unit). The creatinine clearance rate, which measures the volume of plasma that can be cleared of creatinine per unit of time, is a useful method for calculating the GFR.
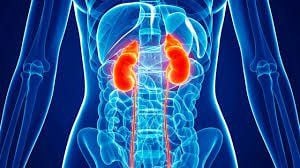
3.2. Use of collagen for individuals without kidney disease
According to a study published in 2005 in the journal Nutrition and Metabolism in London on dietary protein intake and kidney function, it was found that:
There is no substantial evidence of adverse effects from high protein intake on kidney function in healthy individuals over decades of high protein diets typical in Western countries.
Although high protein diets are seen to alter glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and related endocrine changes that may be harmful to individuals with kidney disease, there is insufficient evidence of adverse effects on healthy individuals.
Recently, a series of preliminary studies have been published regulating the use of extremely high protein levels (# 3.4 - 4.4 g/kg/day) and consistently reported no harmful effects, including the following key points:
Therefore, it can be concluded that:
In adults without kidney disease, a high-protein diet may increase glomerular filtration rate (GFR), serum urea and urinary calcium excretion. However, it does not cause the excretion of albumin in the urine, which is the most sensitive marker of kidney damage. These changes may be normal physiological adaptations to higher protein intake. (This conclusion was shared by the World Health Organization WHO in its 2002 report on Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in human nutrition).
So, is it safe to consume hydrolyzed collagen for the kidneys?
Most hydrolyzed collagen contains about 90 - 97% protein. Therefore, a high-protein diet (>1.2g/kg/day) or even supplementing extremely high doses of hydrolyzed collagen does not harm the kidneys in healthy individuals.

3.3. Collagen for chronic kidney disease (CKD)
For individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD), consuming a high-protein diet or taking high-protein supplements can lead to increased intraglomerular pressure and glomerular filtration (“chronic” refers to a condition or disease that lasts for a long time, typically longer than three months, and often persists for the person's lifetime). This can cause further damage to the glomerular structures, leading to or worsening chronic kidney disease (CKD). Therefore, a low-protein diet (LPD) of 0.6-0.8g/kg/day is often recommended for managing chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Conclusion: For individuals with chronic kidney disease or kidney-related issues, careful consideration is needed when consuming or supplementing with high-protein foods.
4. Is taking collagen harmful to the stomach?
While rare cases of gastrointestinal (digestive) symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal (belly) cramps have been reported with collagen intake, there is currently no reliable evidence to confirm whether collagen consumption is harmful to the stomach. However, alongside these concerns, collagen offers numerous benefits specifically for the stomach and the digestive tract in general.
For centuries, the benefits of bone broth and gelatin in treating digestive issues have been well recognized. Recently, scientists have identified that Collagen is the key nutritional factor behind the effectiveness of these foods. The amino acid properties of collagen allow this particular protein to provide numerous remarkable benefits, particularly for gut health. These benefits include reducing intestinal (gut) inflammation, healing stomach ulcers, aiding in digestion, and regulating stomach acid secretion.
5. The effects of Collagen on gastrointestinal health
5.1. Collagen regulation of gastric acid secretion
Collagen has been identified to play a role in regulating gastric (stomach) acid secretion by ensuring the release of an adequate amount of acid for optimal digestion. It also prevents excess gastric acid, thereby helping to prevent heartburn, acid reflux, stomach ulcers, and other digestive issues caused by hyperacidity.
5.2. Supporting stomach ulcer recovery
The two main amino acids in collagen Peptides, Glycine and Proline, can help heal the stomach lining and prevent stress-induced ulcers due to their positive effects on the central nervous system. Studies have shown that Glycine in collagen has the ability to inhibit harmful gastric secretions, effectively preventing stomach ulcers.
5.3. Improving digestion
For gastrointestinal health, Collagen aids in better digestion. As a hydrophilic molecule, collagen attracts water and acidic molecules. When ingested, water and stomach acids surround collagen molecules as they move through the digestive tract, assisting in the breakdown of other proteins and carbohydrates. By being hydrophilic and retaining water within the intestines, collagen helps ensure smoother movement of food through the gut.
5.4. Collagen supports the healing of the intestinal and gastric linings
Collagen is a crucial component in the repair and healing process of the intestinal lining. When there is damage or inflammation in the gastric and intestinal linings, new smooth muscle cells are created to repair the damaged mucosa. Scientists have discovered that a significant amount of collagen is produced in the intestine during the creation of these new smooth muscle cells. Therefore, collagen is the key ingredient that helps heal damage to the intestinal wall and gastric linings.
5.5. Aiding in the treatment of Leaky Gut Syndrome (1) and IBS (2)
Glutamine, a vital amino acid found in Collagen, has been recognized for its role in preventing intestinal inflammation and aiding in the treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Studies have shown that digestive imbalance can lower serum collagen levels, particularly in cases of intestinal inflammation. Therefore, supplementing with collagen is crucial in minimizing gastrointestinal diseases.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: collagenx.com.au, healthcentral.com, kidney.org, furtherfood.com, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov












