The article was professionally consulted by Master. Specialist Level 2 Doctor Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.
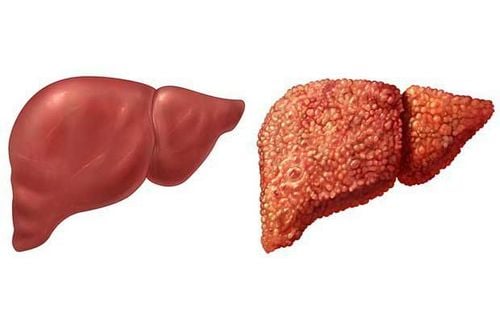
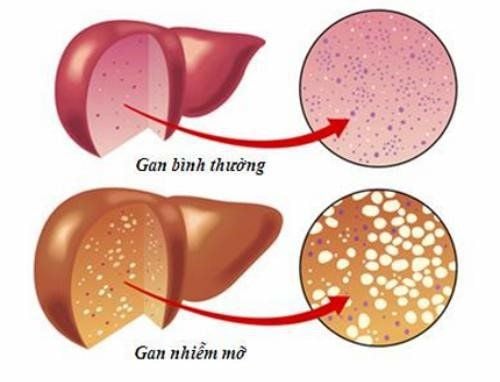
Cirrhosis is when liver cells and tissues are fibrotic and no longer secrete hormones that regulate the body. Cirrhosis increases portal vein pressure, causing many dangerous symptoms and complications, including edema due to cirrhosis.
1. What is edema?
Edema is a symptom that appears when fluid in the blood vessels escapes due to some abnormal cause or mechanism, stagnates in surrounding tissues, and causes edema.
Common locations for edema are the lower limbs (instep, ankle, front of the leg), upper limbs, eyelids, or whole-body edema.
Edema can be a manifestation of many different diseases, the most common of which are heart failure (especially right heart failure), kidney failure, cirrhosis, malnutrition, or diseases of the venous system…
2. Mechanism of edema due to cirrhosis
2.1 Main mechanism
2.1.1 Portal hypertension
Portal vein pressure increases when liver cells are fibrotic, scarred, and lose normal function. At that time, the pressure from the veins of the small intestine and splenic vein also gradually increases because these are the veins that drain into the portal vein. The consequence is the appearance of ascites (edema in the abdomen), prominent veins under the skin, and edema of the lower limbs.
2.1.2 Due to decreased plasma colloid osmotic pressure
The liver is the place where several important proteins for the body are synthesized, including Albumin. This is a substance that helps form colloidal pressure, whose main function is to retain water in the blood vessels. When liver function is impaired due to fibrosis, albumin synthesis is reduced, colloidal pressure is reduced, and water in the blood vessels easily escapes, causing symptoms of edema due to cirrhosis.
2.2 Secondary mechanisms
Cirrhosis will cause dilation of the splanchnic vessels and peripheral arteries, reducing blood supply to organs, including the kidneys. Thereby activating the RAA system (Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone); increasing the reabsorption of salt and water in the renal tubules, increasing the volume of fluid in the blood vessels, and causing more edema and ascites.
The liver is also the place where many hormones are excreted and degraded, including Aldosterone,. Excess of this substance inadvertently increases the reabsorption of salt and water and contributes to fluid retention in the body, combined with other mechanisms, making edema due to cirrhosis more severe.
2.1.2 Due to decrease in plasma colloidal pressure
3. Recognize edema due to cirrhosis
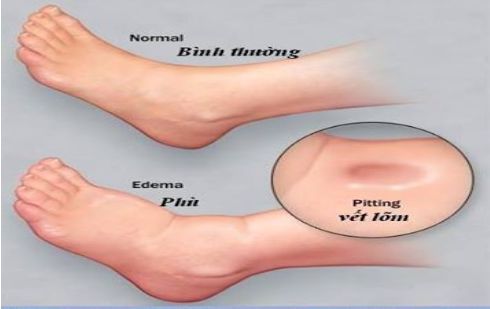
Edema due to cirrhosis is soft, concave edema (when pressed, it leaves a concave and the skin stretches again after 1-2 minutes), there is white blood, and no pain when pressed.
The onset of edema is usually in the legs, often occurring in locations close to the bones such as the ankles and the front of the calves. In the final stage, there may be edema all the body, abdominal edema forming ascites, which is very specific in patients with cirrhosis.
In addition to edema, patients with cirrhosis also have other symptoms such as Jaundice, yellow eyes, collateral circulation, hemorrhoids, and gastrointestinal bleeding due to ruptured esophageal veins…

4. What should be done to reduce edema due to cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is a serious disease, and treatment is also difficult. Current radical treatment for cirrhosis includes: Liver transplantation and stem cell culture.
Some solutions to help patients feel more comfortable when suffering from edema due to cirrhosis:
- Limit salt intake: Eat bland foods, limit foods that are too salty such as canned foods, and processed foods, or use several spices when seasoning.
- Balance water input and output: Based on the amount of urine and the amount of invisible water loss (about 500ml per day) to maintain water intake, do not drink too much or too little water.
- Raise legs when lying down or sleeping to increase the amount of venous blood flow to the heart, and avoid blood stasis for too long causing edema.
- Exercise moderately, to increase circulation in the body.
- Avoid standing or sitting in one place for too long.
- Limit the use of some drugs that cause fluid retention such as anti-inflammatory corticosteroids, some non-steroidal pain relievers...
To arrange an appointment, please call the HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
Vinmec successfully treats cirrhosis with stem cell transplantation.