Diagnostic challenges arise in certain disease entities due to the presence of numerous non-specific symptoms and inter-individual variability in clinical presentation. Moreover, necessary tests to make a definitive diagnosis are not always available. These hard-to-diagnose diseases often include digestive and autoimmune disorders.
1. Irritable Bowel Syndrome
This condition is characterized by abdominal pain and altered bowel habits persisting for at least 3 months. It is also one of the diseases with unknown causes. For differential diagnosis, doctors will need to rule out other conditions such as lactose intolerance, celiac disease, bacterial or parasitic infections, etc. Only then can they conclude that the patient has irritable bowel syndrome.
2. Celiac disease
In celiac disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the small intestine upon ingestion of gluten—a protein present in wheat, barley, and rye. The disease often causes diarrhea, fatigue, and weight loss. In addition, patients may also experience joint pain, rash, headache, depression, and seizures. However, many other medical conditions can cause similar symptoms, such as ulcers, Crohn's disease, and irritable bowel syndrome. Consequently, serological testing and small bowel biopsy are typically required to establish a definitive diagnosis of celiac disease.
3. Appendicitis
The appendix is a small, finger-like appendage that extends from the cecum. In cases of appendicitis, you may experience pain around your navel. The pain usually starts suddenly and moves downwards as the pain intensifies. You may also experience nausea, vomiting, fever, constipation, or diarrhea. Appendicitis is difficult to diagnose because Crohn's disease, pelvic inflammatory disease, bowel obstruction, and colitis can have similar symptoms. A diagnosis of appendicitis requires a physical examination and imaging studies.
4. Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland in the neck produces excessive amounts of thyroxine. You may experience nervousness, anxiety, or irritability. However, these symptoms are similar to those of a mood disorder. Due to the diagnostic challenges associated with this condition, it is crucial to provide the physician with a comprehensive medical history, including all experienced symptoms, such as weight loss, tachycardia, or hyperhidrosis. More specific symptoms, combined with blood tests, can help your doctor make the correct diagnosis.
5. Hypothyroidism
If you experience fatigue and weight gain, these may be indicative of insufficient thyroxine production by the thyroid gland. Hypothyroidism can also manifest as hair loss, altered bowel habits, and increased sensitivity to temperature extremes. Correlation of these clinical findings with blood tests can aid in establishing a diagnosis of hypothyroidism.
6. Sleep apnea
The patient's breathing will stop for a few seconds during sleep and repeat many times. This condition can make you irritable and less alert in the morning, along with dry mouth, sore throat, and headache. However, this could also be a sign of the flu, a cold, or other medical conditions. To be sure about this hard-to-diagnose condition, doctors need to study your sleep, also known as polysomnography. Specifically, technicians will monitor and record brain wave activity, heart rate, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and snoring (if present).
7. Lyme disease
A type of tick transmits the bacteria that cause Lyme disease through its bite. A bull's-eye rash (two concentric red rings resembling a target) is a sign that you have been infected, but this sign does not always appear. Patients may also experience headaches, joint pain, and dizziness, but these symptoms can be caused by many other things. Although early treatment of Lyme disease is very important, signs of the disease do not show up in blood tests for several weeks. Consequently, researchers are actively investigating improved diagnostic modalities for Lyme disease.

8. Fibromyalgia
There are no definitive diagnostic tests for fibromyalgia. Therefore, doctors first need to rule out other causes of pain that are not due to arthritis, lupus, etc. If you have unusual sleep symptoms or mental fogginess, doctors also need to rule out depression or anxiety before making a diagnosis. Once other causes have been ruled out and your symptoms have been closely monitored over time, doctors can then diagnose you with fibromyalgia. This condition is also classified as a condition with an unknown cause.
9. Lupus
Lupus is a condition where the immune system, which is supposed to protect the body, mistakenly attacks its own tissues and joints. Like some forms of arthritis and fibromyalgia, lupus can cause fatigue and pain throughout the body. Doctors can also identify lupus through rashes, but not everyone has this symptom. There is no single test that can confirm you have lupus. Moreover, symptoms can vary from person to person and may disappear for a while and then come back. Physical exams and tests can rule out other conditions, after which doctors will continue to monitor your symptoms before diagnosing lupus. Lupus is also among the hard-to-treat diseases, and those who have it find ways to live with and fight the disease long-term.
10. Parkinson's disease
This condition disrupts the normal function of brain cells. Affected individuals may present with resting tremor, rigidity of the neck musculature, postural instability, and facial masking. However, these can also be signs of stroke, head injury, Alzheimer's disease, and even stress. Currently, there is no standard test or examination to diagnose the disease, so it can take many years to be certain whether someone has Parkinson's disease. Neuroimaging techniques that assess dopaminergic function may provide adjunctive information to aid in the diagnostic process. Similar to lupus, Parkinson's disease is also one of the difficult-to-treat diseases.
11. Multiple sclerosis (MS)
This disease causes your immune system to mistakenly attack the protective covering of nerve fibers. This makes it difficult for the brain to control the body, leading to fatigue, vision problems, weakness, dizziness, depression, etc. However, these symptoms can also suggest other diseases. There is no specific test to confirm MS, but imaging scans or spinal fluid tests can help with diagnosis.

12. Chronic fatigue syndrome
Persistent fatigue lasting six months or longer without an identifiable cause may suggest chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). This condition can also cause sore throat, headache, muscle pain, difficulty sleeping, and difficulty concentrating. However, these are also signs of sleep apnea, insomnia, thyroid disease, anemia, diabetes, and many other conditions. There is no test that can confirm chronic fatigue syndrome, so doctors must rule out other causes before making a diagnosis.
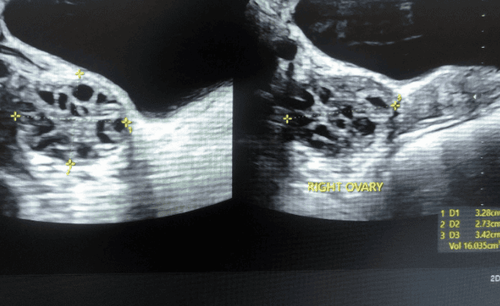
13. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Three symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome include:
- Cysts on one or both ovaries.
- Missed or irregular periods.
- Signs of high androgen hormone levels, such as excess hair growth or acne.
If you have these symptoms, your doctor may do blood tests to rule out other conditions, such as thyroid problems. In addition, your medical history, health, and an ultrasound of your ovaries will be reviewed to accurately diagnose PCOS.
14. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is defined by the presence of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus. Women with this condition will have severe lower abdominal pain and have trouble getting pregnant. Endometriosis can be mistaken for other conditions that also cause pain in this area, such as ovarian cysts or irritable bowel syndrome. The only way to diagnose it is through laparoscopy. In this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin tube with a light and lens through a cut in the abdomen to look inside. Sometimes the doctor also needs to take a tissue sample for testing.
The above information pertains to several diseases that frequently present diagnostic challenges. Please visit Vinmec.com regularly for further updates and valuable health information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com