The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Tran Thi Mai Huong - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Ovarian inflammation is a rare but serious gynecological disease, with the risk of long-term effects on fertility in the future. The most common causative agents are bacteria, especially sexually transmitted strains. The treatment is really simple if detected early and properly intervened in time.
1. What is Ovarian Inflammation?
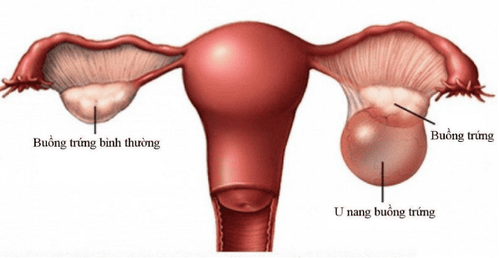
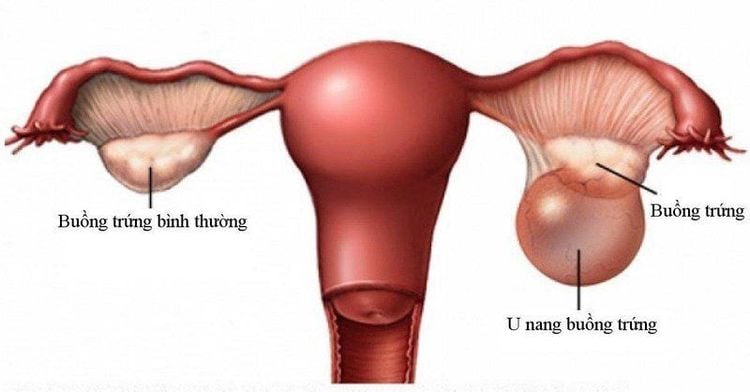
The ovaries are an important part of the female reproductive system. This is a gonadal gland that forms female gametes or eggs and synthesizes the female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone. The ovaries are located in the pelvis and on either side of the uterus, connected via the fallopian tubes - which approach the ovaries during ovulation to receive the released egg. Ovulation in women is when the egg matures around the middle day of the menstrual cycle, leaves the ovary and is ready to be fertilized, because the male gamete is the sperm. A fertilized egg then implants and develops in the uterus. If the egg is not fertilized, the egg will be excreted in the menstrual blood.
Ovarian inflammation is a term that is defined as inflammation occurring in the ovary organs, belonging to the group of pelvic inflammatory disease or upper genital inflammation. This inflammation can affect multiple organs in the pelvis at the same time, including the uterus, endometrium, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and possibly the abdominal wall or peritoneum.
2. Causes of Ovarian Inflammation
The most common cause of ovarian inflammation is two bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria - the causative agent of gonorrhea. These bacteria cause sexually transmitted diseases. The infection spreads from the cervix into the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries and may also enter the peritoneal cavity or abdominal wall.
Risk factors for ovitis are multiple sex partners and unprotected sex without a condom, not incorporating treatment for your partner, a history of purulent cervicitis. or pelvic inflammatory disease...
3. Signs of ovarian inflammation
One of the typical signs of ovarian inflammation is mild to severe spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen. Sometimes the pain will increase or become more obvious with sex, which may be related to bleeding, as well as pain with urination, yellow, green or yellow discharge, or prolonged menstruation. Besides, other accompanying symptoms also deserve attention to assess the patient's overall condition such as fever, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, dizziness, dizziness...
If there is any doubt or The presence of signs of ovarian inflammation, the patient should see a gynecologist as soon as possible. It is important to begin treatment of ovarian inflammation early and thoroughly. When treatment is delayed or inadequate, this condition can lead to the risk of complications, including postinflammatory adhesions, ovarian abscess, or torsion-induced ovarian torsion. If the fallopian tubes are blocked, the woman will face the risk of ectopic pregnancy or infertility.

4. How is ovarian inflammation diagnosed?
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of inflammatory ovary disease are important to minimize the risk of progression to more severe ovarian complications.
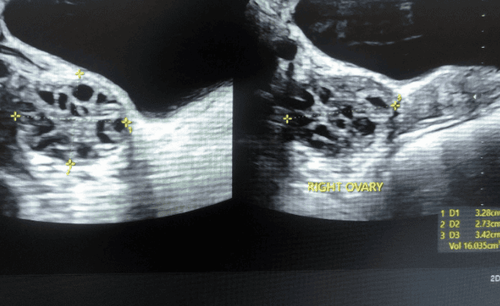
To diagnose ovarian inflammation, the patient needs to lie on the examination table in a gynecological position. The doctor will perform an examination of the appendage by placing a speculum. In addition, the doctor will need blood tests and ultrasound. Today's adnexal ultrasound tool is quite popular, simple and easy to implement, to detect abnormalities on the ovaries as well as other associated complications.
In addition, one of the most important things to take samples. This sample will be sent to the laboratory to determine the inflammatory agents as well as the sensitivity of the bacterial pathogen to antibiotics in order to choose the right drug and achieve the sterilization effect.
5. What is the treatment for ovarian inflammation?
The treatment of ovarian inflammation is mainly based on the indications for the use of antibiotics. The antibiotic chosen initially should be broad-spectrum, including both aerobic and anaerobic. In addition, antibiotic treatment will be adjusted according to the sensitivity to detect the agent. It is important to always adhere to the full day, full dose of antibiotics. Therefore, treatment should be continued even after the symptoms have disappeared, otherwise the causative agent may flare up again.
Besides, supportive treatment measures should also be focused, such as limiting vigorous exercise, but resting in bed, drinking enough water every day and avoiding constipation. In addition, because ovarian inflammation in the early stages will make the patient very painful, the doctor needs to prescribe the use of more pain relievers. Above all, however, it is necessary to encourage treatment of both sexual partners. This is an extremely necessary measure to prevent infection as well as re-infection in the future.
In summary, the signs of ovarian inflammation are not specific, often painful swelling, vaginal bleeding, ... similar to other gynecological diseases. However, the disease can affect a woman's reproductive health, including the risk of infertility. Therefore, recognizing the signs of ovarian inflammation is extremely necessary and every woman needs to raise awareness of protecting her own health.
In order to help customers detect and treat other gynecological diseases early, Vinmec International Hospital has a basic gynecological examination and screening package, helping customers detect early inflammatory diseases Easy, inexpensive treatment. Screening detects gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) early even when there are no symptoms.
Basic gynecological examination and screening package for female customers, has no age limit and may have the following symptoms:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding Having menstrual problems: irregular menstrual cycle, menstrual disorders Abnormal vaginal discharge (smell, different color) Pain, itching in the intimate area Female clients have several risk factors such as poor personal hygiene, Unsafe sex, abortion,... Female customers have other symptoms such as: Abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain in the private area, abnormal vaginal bleeding. If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.