The article was medically reviewed by Dr. Truong Thi Phuong, Specialist in Obstetric and Gynecological Ultrasound, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
There are several causes of abnormally enlarged ovaries. Some are considered functional (non-harmful). During the menstrual cycle, the ovaries enlarge as follicles mature and prepare for ovulation. Enlarged ovaries may also be a sign of ovarian cancer, a malignant condition, though this is not a common cause. Therefore, if you experience any abnormal signs of ovarian enlargement, you should consult a doctor to rule out malignant causes. Below are some reasons for abnormally enlarged ovaries.
1. Ovulation
The ovaries are reproductive organs with two primary functions:
- Recruitment of oocytes to form mature follicles and release eggs for fertilization.
- Production of estrogen and progesterone hormones.
Ovulation occurs when a dominant follicle grows to its maximum size and releases an egg in preparation for fertilization, usually around day 14 of the menstrual cycle.
Just before ovulation, one or two dominant follicles in the ovaries swell with follicular fluid in preparation for egg release. Other signs of ovulation include:
- Increased or altered vaginal discharge.
- Slightly elevated body temperature.
- Abdominal cramping sensations.
No intervention is usually required in this case. Enlarged ovaries during ovulation are normal within the menstrual cycle, and symptoms like cramping or ovarian enlargement typically subside after the egg is released.
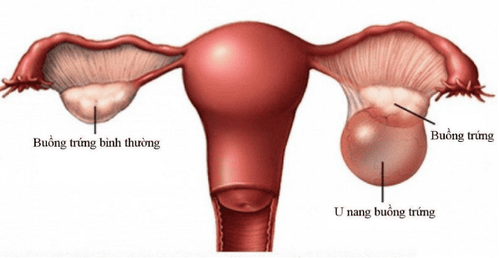
2. Ovarian Cysts
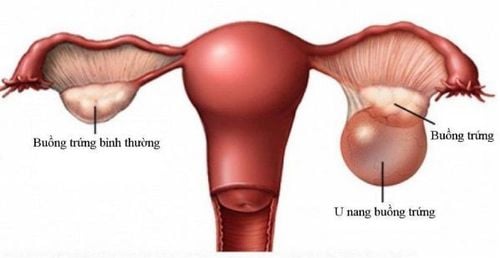
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop within the ovaries. This is a common condition, affecting up to 18% of women of reproductive age.
Ovarian cysts can cause the ovaries to enlarge, especially if the cysts are large or numerous. There are three types of ovarian cysts:
- Corpus luteum cysts
- Dermoid cysts
- Follicular cysts
2.1 Corpus Luteum Cysts
These cysts form after a mature follicle releases an egg. In some cases, the remnants of the follicle fail to regress, and abnormal closure of the follicle causes fluid to accumulate inside, forming a corpus luteum cyst.
2.2 Dermoid Cysts
Dermoid cysts (mature teratomas) originate from ectodermal tissue, which explains why these cysts often contain skin, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, or sweat glands. These tissues may secrete fluids, forming a cyst within the ovary and causing ovarian enlargement.
Dermoid cysts resemble embryonic tissue growth and are usually benign and asymptomatic. Doctors often detect them during ultrasound or surgery for other reasons.
2.3 Follicular Cysts
Follicular cysts develop when a mature follicle fails to release an egg during ovulation and instead continues to grow into a cyst. These cysts are usually asymptomatic and tend to resolve spontaneously.
2.4 What Can You Do About Ovarian Cysts?
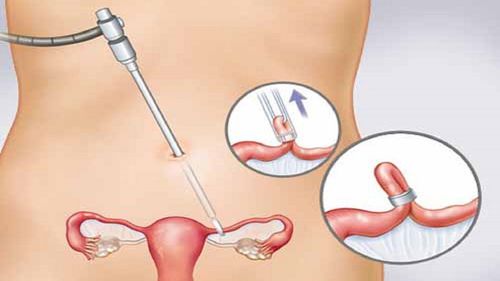
Most ovarian cysts are benign and rarely cause significant complications. They often disappear within a few months without treatment. However, some cysts, such as dermoid cysts, may require surgical removal if indicated. If a cyst becomes large, it can cause symptoms such as pain or bloating, or may rupture. In these cases, surgical removal may be necessary. Doctors may also prescribe birth control pills to prevent future ovarian cysts.
3. Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion occurs when the ovary and part of the fallopian tube twist, cutting off the blood supply and leading to necrosis. This condition often results from ovarian masses or abnormal ovarian growth, which predispose the ovary to torsion.
Ovarian torsion can impact female fertility. Symptoms include:
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain (intermittent cramping or constant).
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
Ovarian torsion is a medical emergency. When torsion occurs, blood flow to the ovary may be cut off, leading to tissue necrosis and infection. Immediate surgical intervention is required to untwist the ovary and remove any mass to preserve ovarian function. Delayed treatment may necessitate removal of the ovary and fallopian tube.

4. Endometriosis
Endometriomas are ovarian cysts that form from endometrial tissue, commonly found in women with endometriosis. Endometriosis occurs when endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, commonly in the uterine muscles, ovaries, or pelvic region.
Endometrial tissue normally grows and sheds with the menstrual cycle. However, displaced tissue in the ovaries cannot exit the body, leading to fluid accumulation and the formation of endometriomas.
According to the Endometriosis Foundation of America, 20–40% of women with endometriosis develop ovarian endometriomas. Symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain.
- Cyclical pelvic pain.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Painful urination or bowel movements.
- Abnormal uterine bleeding.
If untreated, endometriomas can damage ovarian tissue, leading to infertility and increasing the risk of ovarian cancer.
Treatment options include surgical removal of the cyst or the entire ovary, though the latter is typically avoided in women of reproductive age.
5. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
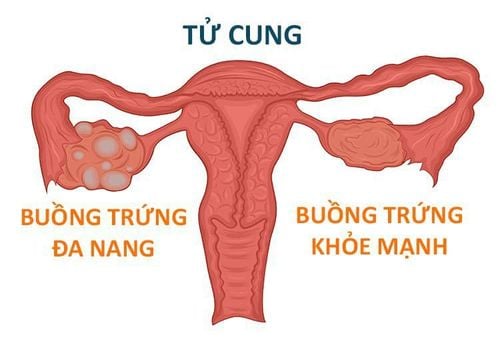
PCOS occurs when women produce elevated levels of androgens (male hormones). Excess androgens can cause multiple follicles to develop in the ovaries, leading to ovarian enlargement.
Symptoms of PCOS, often appearing around puberty, include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles (>35 days).
- Heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Weight gain.
- Pelvic pain.
- Fatigue.
- Hirsutism (excess hair growth) or male-pattern baldness.
- Acne.
- Mood swings.
- Difficulty conceiving.
While there is no cure for PCOS, treatments focus on symptom management, including:
- Birth control pills (estrogen and progestin) to regulate menstrual cycles.
- Ovulation-inducing medications (clomiphene, letrozole, or gonadotropins) to assist with conception.
- Spironolactone or eflornithine to reduce hair growth.
- Weight loss (5–10% of body weight) can help normalize menstrual cycles and improve ovulation. Consult a doctor for personalized weight management strategies.
6. Benign Ovarian Tumors
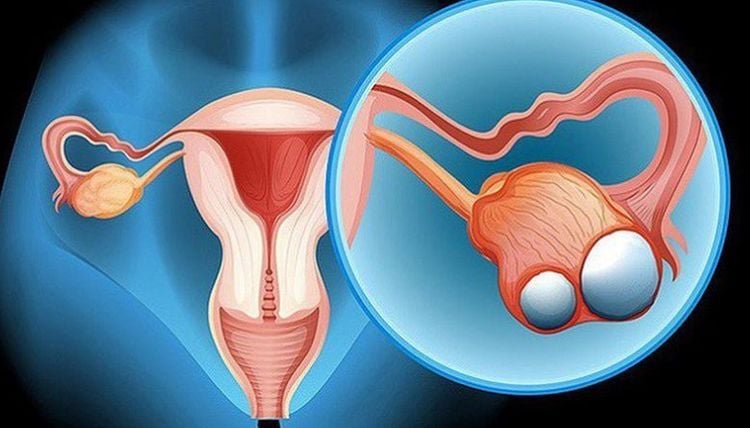
Benign tumors can form inside the ovaries but do not spread beyond the ovary. Fibromas are a type of benign ovarian tumor that develops from connective tissue and grow slowly..
While most benign tumors are asymptomatic, symptoms may include:
- Pelvic pain.
- A sensation of pressure or heaviness.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Fever.
- Nausea or vomiting.
Small tumors may resolve without treatment. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI, can monitor tumor progression. Large tumors may require surgical removal.
7. Signs of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian enlargement may be an early sign of ovarian cancer, though ovarian cancer is rare. According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 22,000 women in the United States are diagnosed annually.
Symptoms often appear in late stages and include:
- Abdominal bloating.
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding.
- Sudden weight changes.
- Frequent or urgent urination.
- Fatigue.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Menstruation change
- Nausea.
- Leg swelling.
Treatment options depend on the cancer type and stage and include:
- Surgery: Removing as much of the tumor as possible, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus if necessary.
- Chemotherapy: Administering drugs to destroy remaining cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy: Reducing hormone-driven tumor growth.
- Targeted therapy: Blocking pathways that support cancer growth.
The main treatments for ovarian cancer are surgery to remove the tumor and chemotherapy. Your doctor may recommend combining two or more treatments for best results.
8. When to See a Doctor

Ovarian enlargement often causes concern. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention. Signs to watch for include:
- Abdominal pain or bloating.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Heavy menstruation.
- Irregular menstruation.
- Unusual vaginal discharge.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for effective treatment. Vinmec International Hospital offers gynecological screening packages to detect and treat gynecological conditions, including ovarian diseases and cancers, even in asymptomatic patients.
The basic gynecological examination and screening package is designed for female clients of all ages who may experience the following symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding.
- Menstrual issues: Prolonged menstrual cycles or irregular periods.
- Unusual vaginal discharge: Discharge with a foul odor or abnormal color.
- Pain or itching in the genital area.
Fmale clients with risk factors such as:
- Poor personal hygiene.
- Unsafe sexual practices.
- History of abortion.
Female clients with other symptoms including:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge.
- Itching or pain in the genital area.
- Irregular or abnormal vaginal bleeding.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
Reference source: healthline.com