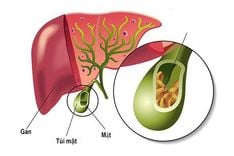
Cirrhosis develops in 4 stages, with each stage becoming more severe and causing more problems for the patient. In stage F4, the liver cells are fully damaged, and the disease has reached its final stage. At this point, the liver no longer works properly.
1. How Dangerous is Cirrhosis?
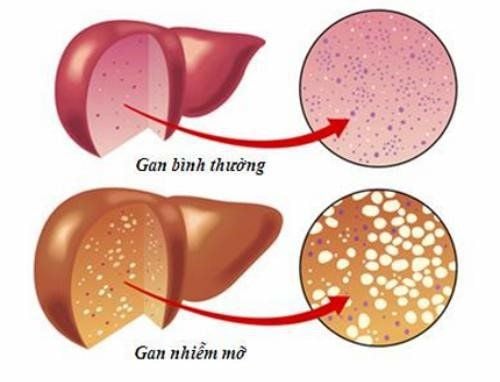
If cirrhosis is not detected and treated in time, it can progress to ascitic cirrhosis. This is the most severe stage of liver damage, where the liver can no longer function properly. The liver loses its ability to process nutrients and toxins, and fluid starts to build up in the abdomen, putting pressure on internal organs. This causes changes to liver cells and leads to scarring (fibrosis). As a result, the liver's ability to filter blood, digest food, and produce bile weakens. This also lowers the patient’s immunity, making them more likely to get infections in the digestive system, urinary tract, lungs, and bile ducts, which can be life-threatening.
Cirrhosis can also cause dangerous complications, such as: Digestive bleeding; Infections; Brain problems (hepatic encephalopathy); Liver cancer
2. What is F4 Cirrhosis? Symptoms of F4 Cirrhosis
Symptoms of F4 Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis has 4 stages, each becoming more severe. In stage F1, liver damage starts but is not very noticeable. In stage F2, liver damage increases, and the liver starts to lose its ability to work, causing toxins to build up. In stage F3, the damage is more severe, and the liver loses most of its function.
F4 cirrhosis, also called cirrhosis ascites or cirrhosis with ascites, is the final stage. At this point, the liver is completely damaged and no longer works. The disease is at its worst, and the patient will face serious complications and worsening symptoms.
Symptoms of F4 Cirrhosis include:
- Jaundice: In the final stage, the skin turns yellow, and the whites of the eyes and nails may also become yellow.
- Loss of appetite and weight loss: Patients with F4 cirrhosis often feel very weak and lose their appetite, which causes weight loss.
- Mental confusion: Because the liver is no longer able to clear toxins from the body, substances like ammonia build up in the blood and affect the brain, causing confusion, changes in behavior and speech, and sleepiness.
- Edema in the limbs and abdomen: Despite losing weight, patients with F4 cirrhosis often have swollen arms and legs due to fluid buildup. Pressing on the swollen areas may leave an indentation that takes a minute or two to disappear. The abdomen may become bloated, the skin stretched and shiny, and blood vessels may become more visible on the stomach.
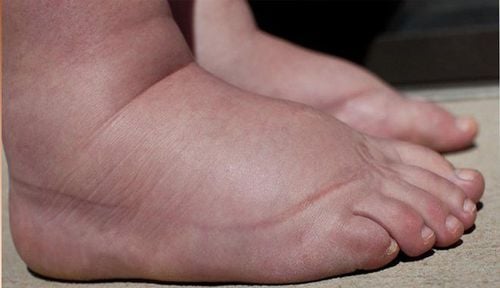
3. Is F4 Cirrhosis Dangerous?
If F4 cirrhosis is not treated in time, it can lead to many dangerous complications that affect the health and life of the patient, such as:
- Gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension : This happens because the scarring in the liver puts pressure on blood vessels, causing increased pressure in the portal vein. This makes the veins more likely to rupture, leading to internal bleeding.
- Hepatic encephalopathy: Also known as brain dysfunction caused by liver failure, this condition occurs because the liver is no longer able to remove toxins from the body.
- The toxins then affect the brain, causing confusion, drowsiness, unconsciousness, and tremors in the limbs.
- Ascites
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
- Hepatorenal syndrome
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome
- Liver cancer
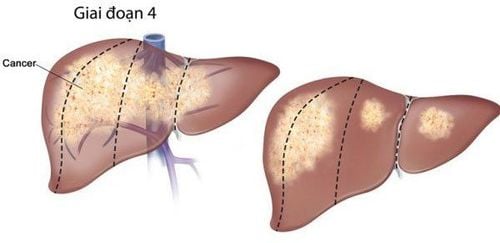
4. Can F4 Cirrhosis Be Cured?
When cirrhosis reaches stage F4, it cannot be fully cured. Treatment at this stage aims to slow the progression of the disease and manage complications rather than cure the condition. F4 cirrhosis is the most severe stage, with significant damage to the liver.

5. Method of Diagnosing Cirrhosis
- Blood Tests: When someone has cirrhosis, the scarring in the liver blocks blood flow. This causes blood to flow backward into the spleen, making it enlarge. The spleen then traps and breaks down blood cells, which lowers the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This condition is called an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly). A blood test that shows a low platelet count can suggest cirrhosis.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound is a simple, fast, and safe test that doesn't harm the patient and can be done multiple times. Today, liver elastography (a special type of ultrasound) is the best way to check for liver damage and how severe the cirrhosis is. The advantage of this test is that it is non-invasive, can be done on overweight patients or those with fluid buildup in the abdomen, and can be used on various organs.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.