This article has been reviewed by Dr. Le Duc Tuyen, Specialist in Pediatrics and Neonatology, Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Hepatitis B is primarily transmitted through blood, sexual contact, and from mother to child. While vaccination is an effective preventive measure, it does not provide absolute protection. So, can a person who is fully vaccinated still contract hepatitis B, especially through sexual contact?
1. What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a dangerous infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which can lead to both acute and chronic liver damage. It is a global health concern on par with cancer and other non-communicable diseases.
Globally, 2 billion people have been infected with HBV at some point, and nearly 400 million currently are living with chronic hepatitis B. Around 1 million people die annually due to complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
In Vietnam, the prevalence of hepatitis B is relatively high, with about 9 million people infected (approximately 9% of women and 12% of men). It is a leading cause of liver cancer and cirrhosis in the country.
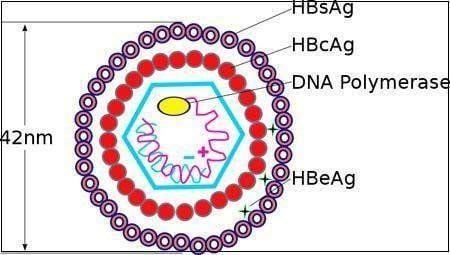
2. How is Hepatitis B Transmitted?
The hepatitis B virus is highly concentrated in blood and bodily fluids such as semen and vaginal secretions. It is also present in other fluids, like saliva, tears, breast milk, and urine, but in quantities too small for transmission. There are three main routes of HBV transmission:
2.1. Blood Transmission
Hepatitis B can be transmitted through blood when infected blood enters the bloodstream of an uninfected person who is not protected. Common scenarios include:
Receiving a blood transfusion from an infected individual.
Sharing needles or syringes, or direct blood contact through open wounds.
Sharing personal items that may have blood traces, such as toothbrushes or razors, with an infected person.
Undergoing invasive procedures (e.g., dental work, tattoos) with improperly sterilized equipment.
2.2. Mother-to-Child Transmission
An HBV-infected mother can transmit the virus to her child, especially during childbirth. This is the most common route of hepatitis B transmission worldwide, accounting for about half of all cases.
The risk of transmission depends on the viral load (amount of a virus present in a person's blood) in the mother's blood and the presence of the HBeAg antigen, which indicates active viral replication and a high risk of infectivity. If HBeAg is positive, the transmission rate is as high as 90%.
2.3. Sexual Contact
Hepatitis B can spread through sexual contact due to exposure to semen, vaginal secretions, or blood (if there are skin lesions). It is 50–100 times more transmissible through sexual activity than HIV.
The risk is higher in cases of sexual practices that damage mucous membranes or cause bleeding, such as: Oral or anal sex, same-sex male partnerships, having multiple partners or engaging with sex workers.

3. Can Vaccination Fully Prevent Transmission?
Fortunately, hepatitis B can be effectively prevented through complete vaccination.
The hepatitis B vaccine, first introduced in 1982, is now widely used in most countries around the world. In Vietnam, the hepatitis B vaccine has been incorporated into the National Expanded Immunization Program, administered to all newborns. Infants receive four doses of the hepatitis B vaccine: the first dose within 24 hours after birth, and subsequent doses at 2, 3, and 4 months of age as part of the 5-in-1 combination vaccine, which includes protection against hepatitis B. Additionally, for private immunizations, the vaccine may be administered as part of a 6-in-1 combination vaccine (covering diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, polio, pneumonia caused by Hib, and hepatitis B) as a booster between 18–24 months of age.
The hepatitis B vaccine is only effective in preventing infection for individuals who have not already been exposed to the virus. Vaccination triggers the body to produce antibodies that protect against HBV, reducing the risk of future infection. When properly administered, the vaccine is approximately 95% effective in children and adults, and about 90% effective in individuals over 40 years of age. The protective effect typically lasts 15–20 years or longer, depending on the individual.
4. Can a Fully Vaccinated Person Still Contract Hepatitis B Through Sexual Contact?
The effectiveness of hepatitis B vaccination is determined by the concentration of anti-HBs antibodies (anti-HBs or HBsAb) in the vaccinated person's blood. A higher concentration of anti-HBs antibodies indicates stronger protection.
Anti-HBs > 10 mIU/mL: Provides effective protection.
Anti-HBs > 100 mIU/mL: Offers very high immunity.
Anti-HBs < 10 mIU/mL: Insufficient for protection.
Antibody levels gradually decrease, varying by individual, which is why vaccine effectiveness diminishes over time. Periodic testing of HBsAb levels can determine if a booster shot is necessary, especially when the levels drop below 10 mIU/mL.
While the hepatitis B vaccine provides high protection, it is not 100% effective. A fully vaccinated person can still contract hepatitis B through sexual contact under certain conditions:
Unprotected sexual activity with an HBV-infected person, particularly if the infected individual has a high viral load due to active replication.
Low levels of protective antibodies (HBsAb < 10 mIU/mL) in the vaccinated individual.
Conclusion: Even if a person has been fully vaccinated against hepatitis B, additional preventive measures are essential. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding unprotected sexual contact with HBV-infected individuals are critical. In cases of unprotected contact with an infected person, seek immediate medical evaluation, counseling, and monitoring from a specialized healthcare facility.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.