This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Minh Son - Interventional Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General HospitalDiabetes is a disorder of sugar metabolism caused by insulin deficiency or insulin resistance. One of the ways to help patients control blood sugar well is to exercise. Regular exercise helps lower blood sugar levels and increase insulin sensitivity, helping to reduce the complications of hyperglycemia for patients.
1. Importance of Exercise for Diabetics
In patients who have been diagnosed with diabetes, having a scientific and regular exercise regimen according to the doctor's instructions will help lower blood sugar levels and improve the body's ability to use glucose. Besides, exercise helps increase the effect of insulin - this is an important hormone in the body's sugar metabolism. Well controlled sugar levels will help reduce the need for insulin and reduce the complications of medication and diabetes.
In addition, exercise also helps reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by removing bad cholesterol (LDL), and increasing good cholesterol (HDL), keeping blood pressure stable. The performance of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system is enhanced, increasing the ability to transport oxygen, increasing the body's flexibility and endurance. Physical activity also helps balance body weight, increases excess energy consumption (stored in fat cells), thereby helping to lose weight or maintain body weight. Exercise helps patients reduce stress (stress), relax more and will feel less tired. Stress is also one of the factors that contribute to high blood sugar in patients with diabetes.
2. How does exercise lower blood sugar?
Exercise is physical activity, so the body's muscle cells need energy to function. During exercise, muscle cells increase their consumption of sugar for energy, and blood sugar easily passes through cell membranes without insulin to help increase glucose metabolism. The results can help lower blood sugar levels.

Tập luyện thể dục là hoạt động thể lực có thể giúp giảm lượng đường trong máu
The effect of exercise on blood sugar depends on the duration of the activity and many other factors. Physical activity can lower blood sugar for 24 hours or longer after a patient exercises.
3. Lower blood sugar and exercise
Blood glucose levels are not too low, below the threshold of 70 mg/dL or 3.9 mmol/L during or after exercise. Depending on the intensity of exercise, blood sugar levels can fluctuate high or low after exercise. To provide enough energy during exercise, the liver is the body's energy storage organ that releases sugar into the bloodstream. The body needs insulin to move this sugar into the cells for use. Therefore, when overactive or insulin levels are too high, there is a risk of hypoglycemia.
Patients with diabetes on insulin therapy are at risk of hypoglycaemia if the insulin dose or carbohydrate intake is inappropriate for physical activity. Patients should check their blood sugar before exercise because it helps to prevent complications of hypoglycemia.
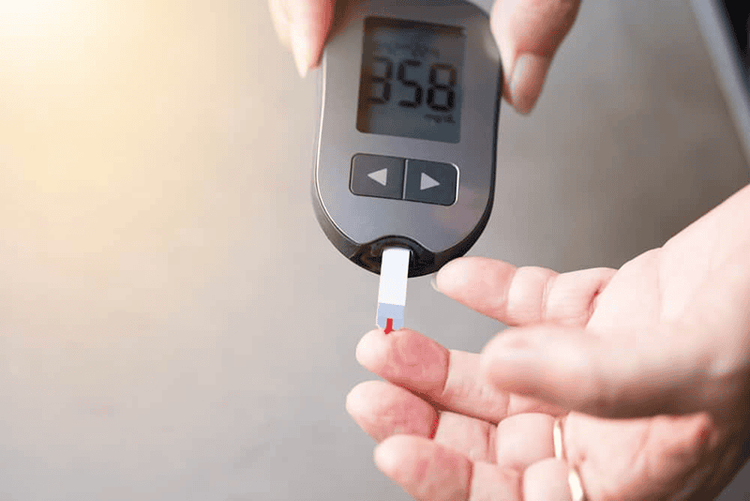
Người bệnh cần kiếm tra đường huyết trước khi tập luyện tránh tình trạng hạ đường huyết
4. Notes on exercise in patients with diabetes
The best time to exercise in patients with diabetes is one to three hours after eating because blood sugar levels tend to rise at this time.
If the patient is on insulin, the blood glucose should be checked before exercise. If the blood glucose level is below 100 mg/dL, the patient can eat a snack that provides about 15 -20g of carbohydrates to increase the blood glucose level. A snack contains 15g of carbohydrates such as: 4 prepackaged sugar tablets (4g in each); or 1/2 cup juice or soda; or a large spoonful of honey or sugar.
Check blood sugar again after 15 minutes and add carbohydrates until blood glucose levels are at least 100mg/dL.
It is recommended to check blood sugar after performing any strenuous physical activity. If the patient is taking insulin, the time when the risk of hypoglycemia is highest is 6 to 12 hours after physical activity.
Patients with too high blood sugar above 250 mg/dL are not recommended by doctors to exercise because after exercise there is a risk of further increases in blood sugar and leading to severe complications of hyperglycemia blood.
Exercise is one of the effective measures to help control blood sugar in patients with diabetes. The choice of exercise form depends on the subject, age, existing complications, comorbidities, and current glucose levels.
Experts recommend that patients with diabetes should walk 30 minutes a day and 3 to 4 days a week is a suitable regimen in most patients. Patients should consult with their doctor and be consulted before planning an exercise program that is safe and effective for themselves.

Bệnh nhân có đái tháo đường nên tập đi bộ với chế độ phù hợp
At Vinmec hospital, we always deploy a screening package for diabetes and dyslipidemia to help detect pre-diabetes early, accurately classify diabetes type, develop a nutritional regimen, and monitor the treatment of diabetes. risks and complications caused by diabetes.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.