This is an automatically translated article.
The most popular drug worldwide to treat diabetes is the drug metformin (Glumetza, Riomet, Glucophage, Fortamet). Metformin helps control high blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes. To make sure it works best, you need to follow the instructions for taking it.
1. What does metformin do?
Metformin is a medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes or prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes in people at high risk of developing it (pre-diabetes). In addition, metformin is also used to treat polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), although this indication is not officially approved. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or the amount of insulin produced cannot work properly, thereby causing high blood sugar.Metformin does not treat the underlying cause of diabetes. The drug only treats the symptoms of the disease by lowering blood sugar through the following mechanisms:
Decreased glucose production in the liver; Reduced absorption of glucose from the intestines; Improves insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues, increases tissue uptake and utilization of glucose. Other effects of metformin:
Lowering lipids, lowering blood triglyceride levels; Reduce LDL- bad cholesterol; Increases HDL - good cholesterol; May reduce appetite leading to mild weight loss. The drug metformin is often prescribed to patients with diabetes when diet and exercise are not enough to control their blood sugar. For women with PCOS, the drug metformin can stimulate ovulation.
Metformin is a medicine used by a doctor's prescription, made in the form of tablets or oral liquid with different strengths: metformin 500mg, metformin 850mg, metformin 1000mg...
MORE: Metformin drug: Note when treating type 2 diabetes
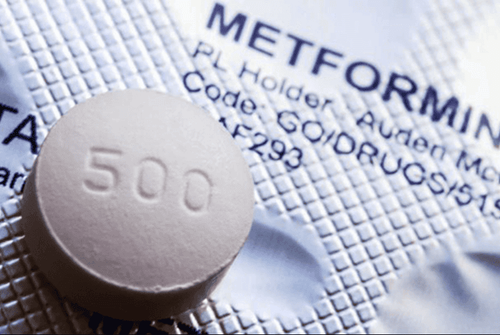
Thuốc Metformin có tác dụng điều trị bệnh tiểu đường type 2
2. Notes when using metformin
Some notes when using metformin are as follows:Metformin works by reducing the amount of sugar that the liver sends back into the blood (glucose production) and making the body respond better to insulin (insulin is the hormone that controls insulin). blood sugar control). It is best to take metformin with meals to reduce side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain and loss of appetite. Metformin does not cause weight gain, unlike some other diabetes drugs, this is an advantage of the drug that is very beneficial for patients.
3. Who can and cannot take metformin?
Metformin is indicated for adults and children 10 years of age and older. Metformin is not suitable for some people, so let your doctor know before you start taking it if you:
Have had an allergic reaction to metformin or other medicines in the past; Patients with uncontrolled diabetes; People with liver or kidney problems; Have a serious infection; Are being treated for heart failure or have recently had a heart attack; People with severe circulation problems or difficulty breathing; People who drink a lot of alcohol. You may need to stop taking metformin before surgery or before having certain medical tests such as X-rays, injecting an iodine-containing contrast agent into your blood...

Người bị suy tim chống chỉ định dùng thuốc metformin
4. How to take metformin
Ideally, patients should take metformin tablets with meals to reduce side effects, swallow metformin tablets whole with a glass of water, do not chew before swallowing. The maximum dose of metformin is 2,000mg a day (eg 4 500mg tablets). Metformin comes in 2 different tablet forms: a standard-release tablet and a delayed-release tablet.Standard release tablets release metformin into the user's body quickly. Users may need to take metformin several times a day depending on the dosage prescribed by the treating doctor. The slow release tablets dissolve slowly, so you don't need to take metformin as often, usually just one dose is enough, it is recommended to take metformin with the evening meal.
5. Increase or decrease the dose of metformin?
Your doctor will check your blood sugar regularly to change your dose of metformin if necessary. When a patient is first taking metformin standard-release tablets, the patient should increase the dose slowly, which reduces the risk of side effects.For example: take 1 metformin 500mg pill with or after breakfast for at least 1 week, then take 1 metformin 500mg pill with or after breakfast and 1 tablet with dinner for at least 1 week. Next take one 500mg metformin tablet with or after breakfast, one with lunch and one with dinner
If you find you can't tolerate the side effects of standard-release metformin, see your doctor. may recommend switching to a delayed-release tablet.
SEE ALSO: People with type 2 diabetes should take Metformin 500 for diarrhea, what should they do?

Dù tăng hay giảm liều thuốc metformin bạn cũng cần tham khảo ý kiến bác sĩ
6. What to do if you forget to take and overdose on metformin?
If you miss a dose of metformin, take your next dose at the usual time, do not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose. An overdose of metformin can cause serious health problems. Serious symptoms will soon appear including:
Abdominal pain; Diarrhea; Rapid or shallow breathing; Feel cold; Unusual drowsiness;

Tiêu chảy báo hiệu tình trạng quá liều thuốc metformin
8. Metformin side effects
Like all medicines, metformin can cause side effects, although not everyone has them. Side effects are more common than 1 in 100 people, tell your doctor if these effects do not go away after 1 week:Feeling nauseous (vomiting); Diarrhea; Stomachache ; Loss of appetite; There is a metallic taste in the mouth. Serious side effects are very rare with the use of the drug, occurring in less than 1 in 10,000 people, call your doctor immediately if you notice the following warning signs:
Irritability accompanied by fatigue severe fatigue, rapid or shallow breathing, coldness and slow heartbeat Yellow skin or whites of the eyes: this could be a sign of liver problems Extreme fatigue, lack of energy, feeling such as pins and needles, pain and red tongue, mouth ulcers, muscle weakness and vision disturbances: these could be signs of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia Skin rash, redness or itching: these could be signs signs of skin disorders. Metformin can cause a life-threatening condition called lactic acidosis. People with lactic acidosis have a build-up of lactic acid in their blood and should not take metformin. This condition is very dangerous and often fatal, but it is a rare side effect, affecting less than 1 in 100,000 people taking metformin. Lactic acidosis is more common in people with kidney disease, so tell your doctor if you have ever had kidney problems.
How to deal with these side effects? If you experience nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, take metformin with food to reduce discomfort or increase the dose slowly over several weeks. Ask your pharmacist or doctor for advice. . In addition, the patient should drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration, take small and frequent sips, notify the medical staff when there are signs of dehydration (urinating less than usual, dark urine, strong odor). ). Do not take any medicine to treat diarrhea or vomiting without consulting your doctor.
If in case of stomach pain, the patient should try to rest and relax, eat slowly and divide into smaller, more frequent meals. Placing a heating pad or hot water bottle on the abdomen can also be helpful in improving pain. If the patient is in a lot of pain talk to the pharmacist or doctor.

Một trong những tác dụng phụ của thuốc metformin là gây chán ăn
9. Warning signs of hypoglycemia when using drugs
The drug metformin does not usually cause hypoglycemia when taken alone, but can cause hypoglycemia when taken with other diabetes medications, such as insulin or gliclazide. Early warning signs of low blood sugar include:Feeling hungry Tremors Sweating Confusion Difficulty concentrating Blood sugar levels can drop too low while sleeping, if this happens it will cause the person to sweat smelly, tired, and confused when waking up. Hypoglycemia can occur if:
Take an overdose of certain diabetes medications; Eating infrequently or skipping meals; Fast; Not following a healthy diet, not getting enough nutrients; Change your diet; Increase physical activity without eating more to compensate; Drinking alcohol, especially after skipping meals; Taking certain other medicines including herbal medicines; Hormonal disorders such as hypothyroidism; Kidney or liver problems.
10. How to prevent hypoglycemia?
To prevent hypoglycemia, it is important to have regular meals, including breakfast, and never miss or delay a meal. If you plan to exercise more than usual, be sure to provide carbohydrates such as bread, pasta, or cereal before, during, or after exercise.Always carry fast-acting carbohydrates with you such as candy, fruit juice or some sweets, in case blood sugar drops low. You may also need to eat starchy carbohydrates like sandwiches or cookies to maintain blood sugar levels longer. If sugar does not help or symptoms subside and then return, contact your doctor or nearest hospital. In addition, make sure friends and family know about the patient's diabetes and the symptoms of hypoglycemia to promptly identify if it occurs.

Người bệnh nên ăn đồ ăn trước khi có ý định tập thể dục để ngăn ngừa hạ đường huyết
11. Metformin for pregnant and lactating women
The drug metformin is generally safe to take during pregnancy, either alone or in combination with insulin. Mothers can take metformin while breastfeeding, which passes into breast milk but in amounts that are too small to affect a nursing baby. However, you should still tell your doctor if you are trying to get pregnant, are pregnant or are breastfeeding.12. Be careful when taking metformin with other medicines
Some medicines interfere with the action of the drug metformin. So if you are taking any of the following medicines, your blood sugar may need to be checked more often and the dose of metformin should be adjusted:Steroids such as prednisolone; diuretics such as furosemide; Medicines to treat heart problems and high blood pressure; Male and female hormones, such as testosterone, estrogen and progesterone; Other diabetes medications; Some women may need an adjustment in the dose of metformin after starting oral contraceptives, because birth control pills can change the way the body processes glucose.
13. What happens when you take metformin for a long time?
Metformin is safe for long-term use, it doesn't make people gain weight, and it can even help with weight loss and keep cholesterol at a healthy level. Your doctor will check the kidney function of a person taking metformin at least once a year. Patients may be more proactive in testing if they are elderly or whose kidney function is not working normally.Metformin can cause vitamin B12 deficiency if taken for a long time. Vitamin B12 deficiency can be treated with oral or injectable vitamin B12 supplements.

Khi dùng thuốc metformin trong thời gian dài có thể gây thiếu hụt vitamin B12
14. When can metformin be stopped?
Metformin can be an integral part of an effective type 2 diabetes treatment plan. But reducing the dose of metformin or stopping it altogether is safe in certain cases if a patient's diabetes is under control. However, if you want to stop taking diabetes medication, you need to be prescribed by your doctor.All people with diabetes can benefit from making certain lifestyle changes, even those on medication. Losing weight, eating healthy, and exercising are the best ways to lower blood sugar and A1C. If the patient can control blood sugar and A1C through lifestyle changes, the patient can stop taking metformin or other diabetes medications.
According to the experts of the American Diabetes Association, patients need to meet the following criteria before stopping taking diabetes medication:
A1C < 7% Fasting morning blood sugar < 130mg/dL Blood sugar any or postprandial blood glucose < 180 mg/dL. Discontinuing metformin if the patient does not fully meet these criteria is very risky. However, these criteria can change based on age, overall health, and other factors, so it's still important to talk to your doctor before changing your metformin medication plan.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: nhs.uk, healthline.com