This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International Hospital
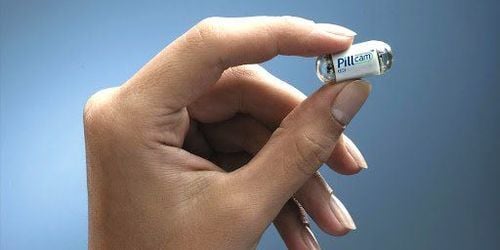
Wireless capsule endoscopy (WCE) allows the physician to examine the gastrointestinal tract by wirelessly transmitting images from a disposable capsule to a data logger. Although WCE is the least invasive endoscopic technique for diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders, interpreting a patient undergoing WCE requires considerable effort and training time.
Image analysis using artificial intelligence, through advances like machine learning or deep learning, is increasingly being applied to medical imaging. There has been considerable interest in using deep learning to detect various gastrointestinal disorders based on WCE imaging.
1. Overview of gastrointestinal endoscopy
Since 1868, endoscopy has been constantly evolving and improving to evaluate the lumen and lining of the gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, colon (colon) and parts of the small intestine. Despite its utility, endoscopic examination of the small intestine is limited by the length and distance from the access holes. This limitation was a contributing factor to the development of wireless capsule endoscopy (WCE).
2. The advent of capsule endoscopy (CE)
Developed in the mid-1990s, WCE uses a miniature swallowable camera that can directly view the esophagus, stomach, entire small intestine and colon without pain, sedation or lack of oxygen. An important clinical application of WCE is the evaluation of gastrointestinal bleeding after high-quality two-way conventional endoscopy and colonoscopy with no identifiable source of bleeding.
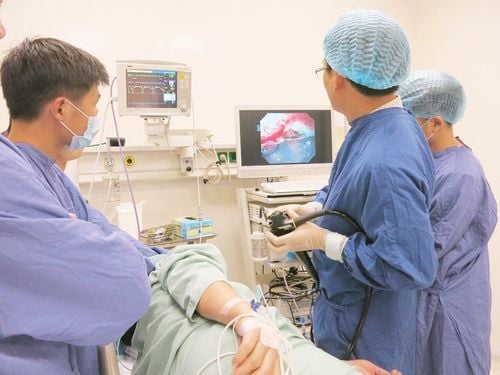
A typical WCE study lasts 8 to 12 hours and produces 50000-10000 images. Reviewing that number of images requires considerable effort and training time. In addition, gastrointestinal abnormalities may be present in only one or two frames of the video that may be missed. A computer-aided automated diagnostic system can assist and assist physicians in the analysis of images obtained by WCE.
3. The birth of artificial intelligence AI
Artificial intelligence (AI), an aspect of computer-aided design, is rapidly expanding and penetrating in academia and industry. AI deals with computer programs that perform functions related to human intelligence. Specific AI features include computer learning and problem solving. AI was first described as the development of computer systems to perform tasks that require human intelligence, which may include decision making and speech recognition. Many techniques of AI have been proposed to facilitate the recognition and prediction of patterns.4. Machine Learning Algorithms (ML) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in AI System
Machine learning (ML) is an application of AI that gives systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without the need for explicit programming. ML can recognize patterns from data sets to generate algorithms and make predictions A huge breakthrough in ML was the development of deep neural networks (also known as deep learning). Deep learning consists of a huge multi-layered artificial neural network that can automatically discover useful features.
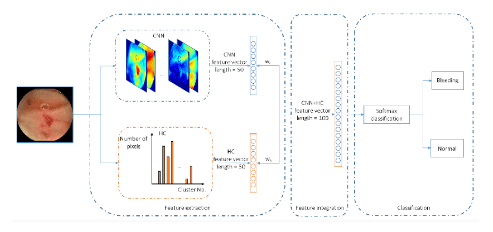
Simply put, deep learning can extract more samples from high dimensional data. Several deep learning models have been reported in the literature and are distinguished by their application. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a type of deep learning, are highly effective in performing image analysis. With CNN's utility in image analysis, applications for CNN have expanded into the medical field, including gastroenterology. The main limitation of deep learning is the long training time. However, advances in graphics processing units have dramatically reduced deep learning training time from days or weeks to hours or days.
5. Application of Machine Learning Algorithms (ML) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in Medicine
ML and CNN are increasingly being explored and applied to diagnostic images in radiology, pathology and dermatology. Likewise, ML and CNN have utility in endoscopy and WCE through image-based interpretation without altering existing procedures. Current applications of ML and CNN in gastroenterology include polyp detection, esophageal cancer diagnosis, and ulcer detection through image-based interpretation from WCE. WCE is one of the leading interests of AI researchers in the digestive field.
Part 2: Capsule endoscopy using artificial intelligence
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.