This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalBy using capsule endoscopy or balloon-assisted small bowel endoscopy, endoscopists can now evaluate the entire small intestine and perform endoscopic therapies in a place that has never been seen before passing through, thereby contributing to accurate diagnosis of the disease condition and effective treatment plan.
1. Balloon-assisted small bowel endoscopy
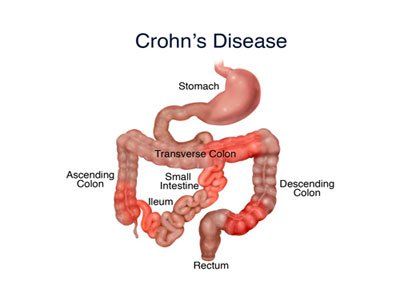
Although standard small bowel endoscopy plays an important role in the management of patients with IBD, its place in the diagnostic and therapeutic algorithm remains poorly defined. The term “balloon-assisted small bowel endoscopy” (BAE) was first proposed by Mönkemüller and colleagues and summarizes three different endoscopic methods for small bowel reconstruction: Double-balloon small bowel endoscopy. (DBE; Fujinon, Tokyo, Japan); single-bulb endoscopy (SBE; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan); NaviAid (Pentax, Tokyo, Japan). All systems allow deep insertion of a colonoscope in the small intestine for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions (eg, for hemostasis, dilation, or biopsy). A combination of oral and anal bronchoscopy is used to examine the entire small intestine.
2. Capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy (CE) was introduced in 2002. Currently, many different capsule systems from different companies are available to examine the esophagus, small intestine and colon. The movement of the cyst is passively pushed through the intestine by peristalsis while simultaneously transmitting a color image of the intestine. CE capsule endoscopy offers the theoretical advantage of visualizing the entire small intestine. However, about 8%-40% of cases cannot reach the cecum. Numerous studies have shown the impact of CE for the diagnosis of Crohn's disease-associated changes such as ulcers, erosions, erythema, abscesses, and intestinal strictures. In the study of Dubcenco et al. CE yielded a sensitivity and specificity of 89.6% and 100%, and a positive predictive value and negative predictive value of 100% and 76.9%, respectively, for the diagnosis of Crohn's disease. small intestine is active. However, none of the studies used definitive gold standards, and the diagnosis of Crohn's was always supported by clinical presentation. Therefore, at present the diagnosis of Crohn's disease cannot be based on CE examination alone.
3. Ambient Laser Endoscopy
Confocal laser endoscopy (CLE) was introduced in 2004 and quickly emerged as a promising method for obtaining real-time in vivo histology during ongoing endoscopy. This technique is based on irradiation of tissue with blue laser light after topical or systemic application of a fluorescent agent. The most commonly used fluorescent agent is fluorescein sodium administered intravenously for systemic tissue staining. Currently, 2 devices are FDA and CE certified. One is integrated into the distal end of the high-resolution endoscope ("integrated", iCLE; Pentax, Tokyo, Japan) and the other represents a stand-alone confocal probe capable of traversing the working channel of most standard endoscopes (“probe-based”, pCLE; Cellvizio, Mauna Kea Technologies, Paris, France).
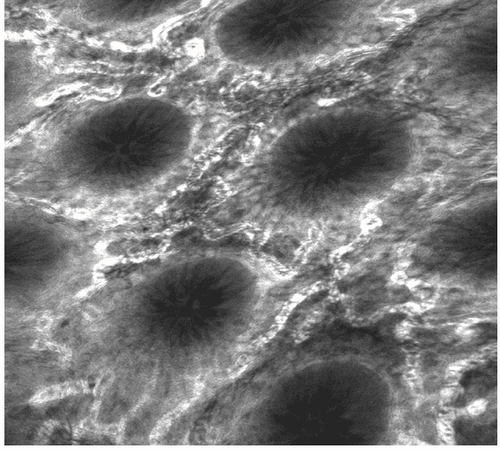
4. Cell endoscopy
Endoscopy cytology (EndoCyto) allows in vivo microscopic imaging with up to 1390x magnification, thus allowing analysis of mucosal structures at the cellular level. EC is based on the principle of contact light microscopy and thus allows visualization of only the very superficial mucosa. This technique has proven to be reliable for examining mucosal surfaces. In addition, EC can predict neoplasms in foci of malformation and can differentiate tumors from non-tumor colorectal lesions. Our team evaluated the value of endoscopy to identify single inflammatory cells during ongoing endoscopy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. EC allows clear visualization of various cellular structures in the intestinal mucosa, including cell size, arrangement and density. Furthermore, the size and shape of the nucleus as well as the ratio between the nucleus and cytoplasm were visualized. According to these changes, one can distinguish in real time neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes by EC.
5. Conclusion
Recent advances in endoscopic imaging now allow endoscopists to obtain real-time in vivo histology during ongoing endoscopy using microscopy or cytoskeletal endoscopy. These emerging imaging modalities allow the endoscope to detect and characterize precancerous and neoplastic lesions and predict mucosal inflammation more accurately than conventional white light endoscopy often. Recent efforts have been made to introduce molecular imaging in inflammatory bowel disease by highlighting inflammatory cells and specific receptors. The results of these trials are highly anticipated and may open new avenues for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in inflammatory bowel disease.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious address trusted by many patients in performing diagnostic techniques for digestive diseases, diseases that cause chronic diarrhea, Crohn's disease... Along with that, at Vinmec Hospital, screening for gastric cancer and gastric polyps is done through gastroscopy with Olympus CV 190 endoscope, with NBI (Narrow Banding Imaging) function for The imaging results of mucosal pathology analysis are clearer than conventional endoscopy, detecting ulcerative colitis lesions, early gastrointestinal cancer lesions... Vinmec Hospital with facilities With modern quality and equipment and a team of experienced experts, always dedicated to medical examination and treatment, customers can rest assured with gastroscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy at Vinmec International General Hospital. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References
Ullman TA, Itzkowitz SH. Intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(6):1807–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Farraye FA, Odze RD, Eaden J, Itzkowitz SH. AGA technical review on the diagnosis and management of colorectal neoplasia in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(2):746–e4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Günther C, Martini E, Wittkopf N, et al. Caspase-8 regulates TNF-alpha , epithelial necroptosis and terminal ileitis. Nature. 2011;477(7364):335–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Neumann H, Vieth M, Langner C, Neurath MF, Mudter J. Cancer risk in IBD: how to diagnose and how to manage DALM and ALM. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2011;17(27):3184–3191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Rutter MD, Saunders BP, Wilkinson KH, et al. Thirty-year analysis of a colonoscopic surveillance program for neoplasia in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(4):1030–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Helmut Neumann, Klaus Mönkemüller. Advanced Endoscopic Imaging for Diagnosis of Crohn's Disease, Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012; 2012: 301541.