This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Gastroenterology - Endoscopy, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Gastroesophageal reflux and Barrett's esophagus are diseases with the same etiology and pathogenesis. In fact, Barrett's esophagus is a complication of gastroesophageal reflux because it is not detected and treated in time.
1. What is Gastroesophageal Reflux?
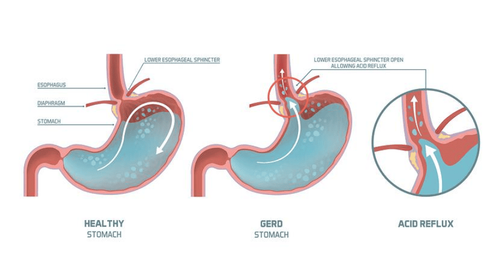
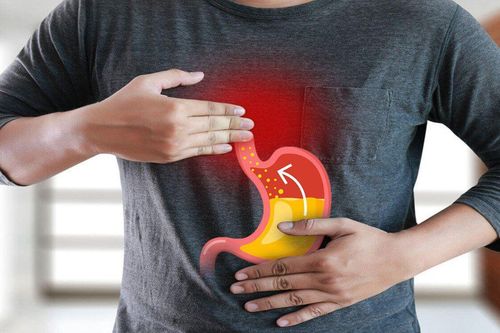
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (also known as reflux esophagitis) is a disease that occurs when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus. This causes heartburn and other specific symptoms.
Reflux episodes normally occur after meals, are short-lived, are not accompanied by other symptoms and rarely occur while the patient is asleep. However, normal episodes of acid reflux can turn into GERD when symptoms occur more often (2-3 times a week) or damage the esophagus.
2. What is Barrett's esophagus?
Barrett's esophagus is a condition characterized by changes in the color and composition of the cells lining the lower esophagus.
The cause of this change is the repeated exposure of the lining of the esophagus to stomach acid. If not treated promptly, the disease can turn into esophageal cancer, threatening the patient's life.
3. Difference between gastroesophageal reflux and Barrett's esophagus
3.1 On the pathogenesis of Gastroesophageal Reflux: Occurs when acid from the stomach back up into the esophagus with a frequency of 2-3 times/week; Barrett's esophagus: Occurs in people with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease. However, not everyone with long-term gastroesophageal reflux disease also has Barrett's esophagus. In fact, only a small percentage of people with GERD progress to Barrett's esophagus. 3.2 About symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease: Ợ gas, nausea in the morning, difficulty swallowing, hiccups, feeling choking when eating, nausea if you eat a lot, phlegm in your throat, frequent coughing, hoarseness, sore throat,...; Barrett's esophagus: Symptoms are more severe than gastroesophageal reflux with manifestations such as heartburn, burning pain in the neck, sour mouth, nausea, chest pain, possibly vomiting blood, black and crushed stools. However, there are cases of Barrett's esophagus but there are no abnormal symptoms until it is discovered through routine physical examination. 3.3 Diagnostic techniques for gastroesophageal reflux disease:
Gastroesophageal endoscopy;
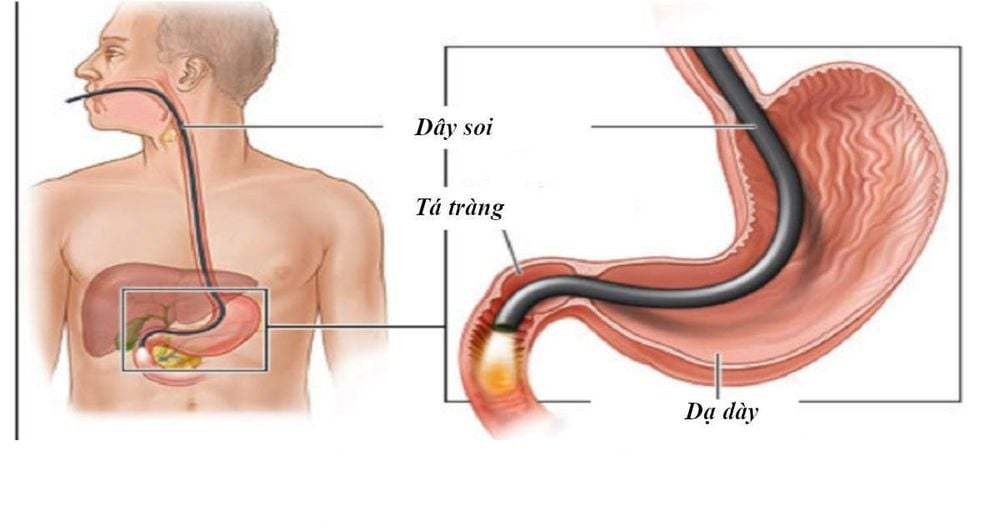
Esophageal manometry; X-ray of stomach - duodenum; Measure the pH of the esophagus within 14 hours; Barrett's esophagus:
Gastroscopy: The color of the lower esophagus lining changes from normal pinkish white to red, which is a sign that Barrett's esophagus is progressing; Biopsy: If the gastroscopy results suggest Barrett's esophagus, the doctor will take a few small tissue samples from the lining of the esophagus during the endoscopy and bring it to the laboratory for examination under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis. 3.4 About treatment methods Gastroesophageal reflux disease: Mainly lifestyle changes and use of acid-reducing drugs such as H2 receptor blockers, proton pump inhibitors. In case of drug resistance, the doctor may recommend performing fundoplication surgery to improve the strength of the lower esophageal sphincter, helping to prevent gastric juice from backing up into the esophagus; Barrett's esophagus: Patients are assigned to use acid-suppressing drugs for life, periodically monitor their disease status, and change their lifestyle. For patients with high-grade dysplasia or esophageal cancer, surgical resection of the esophagus may be indicated. Several new treatments to remove dysplastic cells from the lining of the esophagus through the manipulation channel of the flexible endoscope may also be used to treat the disease. These methods include: Phototherapy, radiofrequency ablation, argon plasma coagulation, endoscopic mucosal resection, etc. Gastroesophageal reflux and Barrett's esophagus can all cause complications. dangerous complications if not treated promptly and aggressively. Therefore, when having symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, sore throat, heartburn, etc., patients should see a gastroenterologist immediately for timely intervention and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.