This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. CKII Phan Phi Tuan - Head of General Surgery Department, Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.Cholelithiasis is a disease that forms stones in the biliary system (including the gallbladder and bile ducts). Gallstone disease, if not treated promptly, can lead to serious complications, even death.
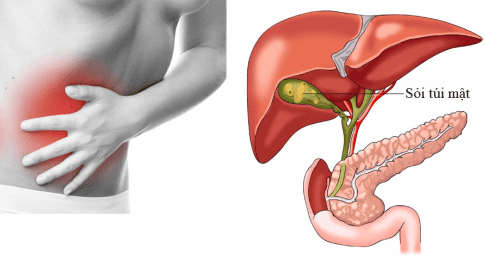
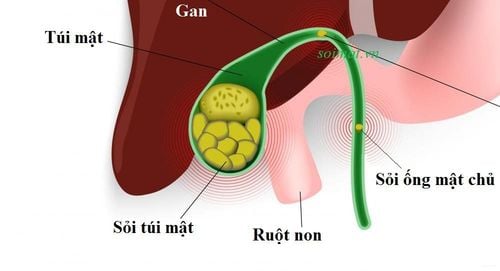
1. Location of gallstones
Gallstones: Base, Body, Funnel, Neck, Gallbladder Extrahepatic bile duct: Common bile duct; Common hepatic duct; Right hepatic duct; Left hepatic duct. Gallstones Intrahepatic: Segmental duct, hyposegmental duct; Smaller ducts (liver parenchyma). Prevalence of sites: Former: Biliary tract > 80%, Gallbladder < 20%, Both about 10%. However, there are now more gallstones than biliary stones due to diet and diagnostic ultrasound.
2. Natural progression
Asymptomatic
Most (>2/3) asymptomatic. Symptomatic risk about 2% per year Complication rate 0.1% per year Treatment not necessary (except in patients with diabetes or valvular heart disease requiring surgery). Symptomatic
If symptomatic episode resolves: 35% risk of symptom recurrence over 5 years; Complications 1% per year. Treat all (with few exceptions). Symptomatic gallstones but refused surgery (150 patients - Sweden). After 2 years, 27% had emergency surgery.
3. Clinical Manifestations
Gallstones (>85%); biliary colic; Acute cholecystitis ; Gallstones ; Cholestasis ; Acute pancreatitis
3.1. Biliary colic Pain Clinical features: Cramping pain in the epigastrium, right lower flank; Pain or discomfort of increasing severity may persist for several hours and may awaken the patient.
Treatment
Symptoms (if acute) Cholecystectomy: Laparoscopic or open surgery; Lithotripsy outside the body, using drugs to dissolve stones. 3.2. Acute cholecystitis Clinical features: Usually epigastric pain, right lower quadrant can spread to the right shoulder, below the shoulder blade. Right lower quadrant pain, Murphy's sign, abdominal wall spasticity, fever, rapid pulse, possibly chills.
4. Gallstone treatment
Non-surgical treatment Lithotripsy (CDCA & UDCA) Litholysis 7% (CDCA) - 30% (UDCA) after 1 year for stones Cholesterol 10% recurrence/year after drug discontinuation Extracorporeal lithotripsy Lithotripsy percutaneous (MTBE) Endoscopic stone removal. Laparoscopic surgery to treat gallstones Laparoscopic surgery to treat gallstones is indicated in the following cases:
Gallstones with complications: acute cholecystitis, gallbladder necrosis, cholecystitis.. Pain. Long-term: Severe pain, painful gallbladder pressure Severe digestive disorders, dyspepsia. Treatment of extrahepatic bile duct stones Indications:
Indication for surgery is mandatory because stones can block the sphincter of Oddi, common bile duct, common hepatic duct Complicated stones: Emergency surgery or delayed emergency Stones Uncomplicated: Scheduled elective surgery. Methods:
Treatment of gallstones by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Surgery to open the common bile duct to remove stones (open surgery or laparoscopic surgery). Treatment of intrahepatic bile duct stones Indications:
Generally indicated when opening the common bile duct to remove extrahepatic bile duct stones or when the patient has severe symptoms such as severe pain or fever.
Method:
This type of surgery is very difficult to remove all stones because the biliary tract is crooked and narrow, so it often requires lithotripsy because the stone is molded into the bile duct.
Gallstone removal through endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is indicated in the following cases:
Gallstones are not too many, not too large Gallstones are not or have been opened to remove stones Choledolithiasis with stones gallbladder is indicated for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Treatment of stones left after surgery Early stage: Still wearing Kehr tube
Wash biliary tract through Kehr duct Every day, for the first 1-2 weeks after surgery, use solutions to dissolve stones combined with biliary lavage to make small stones drift out The stone is taken through the Kehr tunnel after dilation, carried out in the X-ray room until the stones are gone in the biliary tract. The results are usually very good. Late stage
When the Kehr tunnel is blocked, the treatment is the same as before surgery. Open the common bile duct to remove stones (open surgery or laparoscopic surgery) Remove stones through the Kehr tunnel Indications for placing Kehr tube: Kehr tube is placed in most common bile duct open surgery Kehr tube placement is mandatory when stone removal is not complete or there is suspicion of residual stone after surgery.

5. Prevent gallstones with diet
5.1. Limiting saturated fat helps prevent gallstones A diet high in saturated fat raises blood cholesterol levels, increasing cholesterol in the liver and bile. Some foods you should limit include: Red meat like beef, sausage and bacon, whole milk products, butter and lard, fried foods,...
5.2 Add fat sources Good in the diet Choose good fats from foods such as: Olive oil, avocados, nuts such as: Pumpkin, sunflower and sesame seeds, nuts, seeds such as walnuts and Certain fish such as salmon and tuna reduce the risk of stones.
5.3 Eat a lot of fiber, limit carbohydrates to help prevent gallstones Fresh fruits provide a lot of fiber, especially those that eat whole seeds such as raspberries, strawberries, strawberries, green vegetables, etc. cereal...can avoid gallstone disease. Drinking plenty of water helps prevent gallstones Drinking alcohol and coffee in moderation helps prevent gallstones Exercise regularly Avoid sudden weight loss Avoid skipping meals, especially breakfast.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.