Prostatic calcification is a condition with a relatively high prevalence among middle-aged men. If not promptly diagnosed and treated, the disease can progress and lead to complications such as prostatitis, urinary obstruction, and other issues, significantly impacting the patient's quality of life and sexual health.
1. What Is Prostatic Calcification?
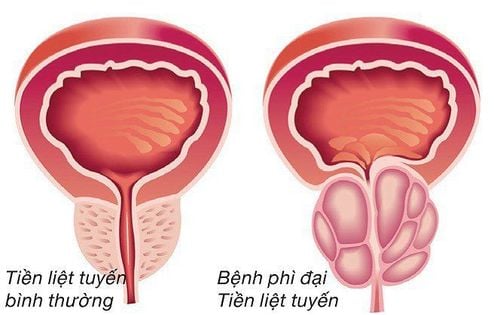
Prostatic calcification, also known as prostate stones, is the deposition of calcium in the prostate gland. This condition can block small ducts that secrete fluids into the urethra, causing fluid retention, leading to infections and calcium precipitation. The disease is common in middle-aged men and is generally considered benign since the stones in the prostate usually do not significantly affect health. However, if left untreated, the stones can lead to prostatitis, complicating treatment and adversely affecting men's health.
2. Causes of Prostatic Calcification
Prostatic calcification can be associated with conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatitis, or prostate cancer. Common causes include:
- Untreated urinary tract infections in men, leading to calcium deposition in the prostate over time and the formation of calcified nodules;
- Underlying medical conditions such as carcinoma, benign prostatic hyperplasia, post-surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia, or post-radiation for prostate cancer;
- Other causes include poor dietary and hygiene habits.
3. Symptoms of Prostatic Calcification
Prostatic calcification is often difficult to detect because it usually does not present with specific symptoms in its early stages. As a result, many cases are incidentally discovered during routine health check-ups. In other instances, symptoms only appear when the disease has progressed significantly.
Common symptoms include:
- Weak urinary stream, difficulty urinating, painful or burning urination, frequent urination, especially at night;
- Sudden and unexplained pain in the abdomen and groin;
- Pain in the perineum, rectum, and penis;
- Discomfort in the penis and testicles;
- Pain during ejaculation, discolored seminal fluid (light yellow), and weak ejaculation force.
Diagnostic methods include ultrasound, X-ray imaging, CT scans, and prostate biopsy.
4. Is Prostatic Calcification Dangerous?
- Increased risk of infertility: The prostate plays a crucial role in nourishing and producing sperm in men. If early symptoms are ignored and treatment is delayed, men may face difficulties with fertility. Specifically, infected calcified nodules can lead to chronic prostatitis. A swollen and inflamed prostate can compress the urethra, impair ejaculation, and cause seminal fluid discoloration (light yellow). These conditions negatively affect fertility, reducing conception rates and increasing the risk of infertility.
- Prone to severe complications: Calcified nodules in the prostate can lead to chronic prostatitis, which may develop into benign prostatic hyperplasia or even progress to prostate cancer and sepsis. Moreover, the condition often requires prolonged treatment and has a high recurrence rate, making it challenging to treat definitively.
5. Treatment Methods for Prostatic Calcification
Calcified nodules in the prostate serve as a haven for bacteria and microorganisms, making them difficult to eliminate completely. In cases where calcifications are not too large or numerous, they may not cause significant problems and often do not require intervention.
In other cases, doctors may recommend the following treatment options:
- Antibiotics: This is a common treatment for cases of prostatic calcification. Acute prostatitis cases are often easily treated with antibiotics. However, antibiotics are less effective for chronic prostatitis, where symptoms may subside during treatment but relapse afterward. High-dose antibiotics may be prescribed but carry risks of liver and kidney toxicity.
- Injections into the Prostate: This is a supplementary treatment to oral antibiotics. Direct injections increase the concentration of medication in the prostate. However, clinical results indicate that injections do not completely eradicate calcifications.
- Herbal remedies: According to traditional medicine, calcifications or prostatitis result from thermal and cold energy blockages in the lower abdomen, leading to congestion of Qi and blood. Herbal treatments to expel cold and heat may improve the condition. For prolonged infections, diuretic herbs can also be helpful. However, this method lacks comprehensive clinical validation.
- Physical Therapy: Techniques such as ultrasound to increase blood flow to the prostate or prostate massage to relieve obstruction and open ducts can help antibiotics penetrate deeper into tissues. However, this method may increase inflammation and does not eliminate pathogens, making it a supplementary rather than primary treatment.
- Other Methods: Surgery to open blocked or calcified ducts may be necessary to prevent severe complications.
6. Lifestyle and Preventive Measures for Prostatic Calcification
If calcifications are detected but cause no significant symptoms, the following measures can help prevent complications:
- Maintain a regular and healthy sexual life to prevent prostate duct blockages;
- Avoid excessively salty foods or spicy, hot dishes;
- Limit alcohol, avoid smoking, and refrain from using stimulants;
- Drink plenty of water daily to aid in toxin elimination;
- Engage in regular exercise and physical activities for overall health. Exercises like walking or yoga that target the pelvic area are particularly beneficial;
- Maintain proper hygiene of the genital area to prevent infections.
Prostatic calcification can affect fertility and lead to complications such as prostate cancer. Therefore, men should undergo regular health check-ups and consult a doctor immediately if warning signs appear to facilitate early detection and effective treatment.
Regular health check-ups help detect diseases early, thereby creating a treatment plan with optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has General Health Check-up packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy.
The patient's examination results will be returned to their home. After receiving the results of the general health check-up, if any diseases that require specialized examination and treatment are detected, you can use services from other specialties right at the Hospital with outstanding treatment quality and customer service.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.