This article is professionally consulted by Le Phuc Lien, MSc, MD - Urology Surgeon - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. The doctor has over 12 years of experience in the field of urology and specialized urology.
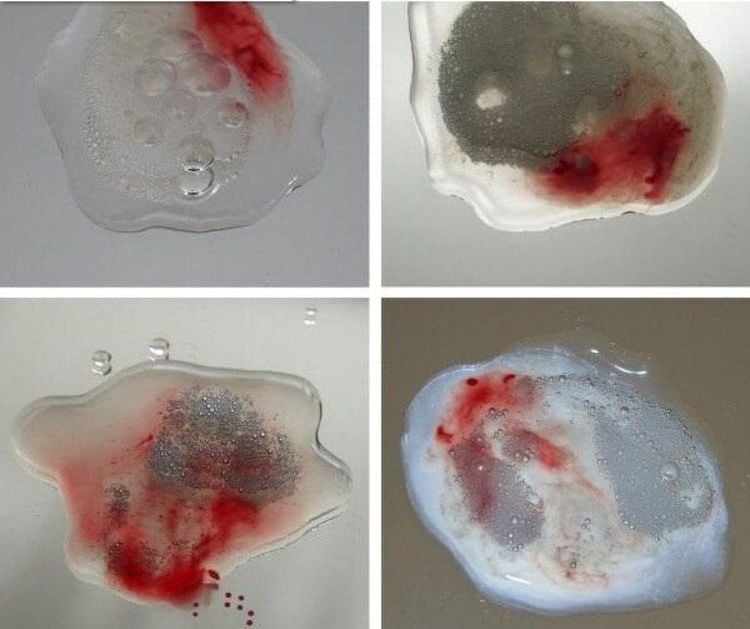
Normal semen is ivory white. If semen turns pink or red, it may indicate the presence of blood. This condition is sometimes harmless and resolves on its own without treatment. However, blood in semen can also be a warning sign of other underlying health issues.
1. What is blood in semen?
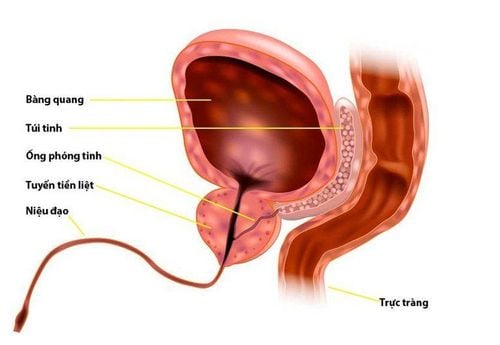
Semen is a product of the male reproductive system. It is produced from various organs, including the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and prostate gland.
The presence of blood during ejaculation is called hematospermia. It is usually a painless, benign, isolated, and self-limiting symptom.
Blood in semen is not uncommon and can affect any male at any age after puberty. The condition is benign and self-resolving but often recurs. However, the most commonly affected age group is men aged 30 to 40. According to epidemiological statistics, up to 9 out of 10 men have experienced blood in their semen without any prior symptoms or abnormalities in the urinary or reproductive systems.
2. Symptoms of Blood in Semen
Blood in semen usually does not cause pain, and the patient only notices blood in the semen. The blood causes the semen to change color from dark brown to bright red. Additionally, the patient may not have any other symptoms.
However, in cases of secondary blood in semen, the patient may have additional symptoms such as pain during ejaculation or a dull ache in the area from the testicles to the perineum. These are considered signs of prostate conditions such as prostatitis. At this point, if the patient has the following factors, they need to be thoroughly examined:
• Age over 40
• Persistent or recurrent symptoms
• Detection of abnormalities during urogenital examination
• Accompanying conditions in other organs
3. Causes of Blood in Semen
3.1. Primary Blood in Semen
In this case, the presence of blood in the semen is the only symptom.
Additionally, it is necessary to rule out the possibility of blood in the urine, either macroscopically or microscopically. The patient has also been examined and there is no evidence of any abnormalities in the structure or function of the urinary system in general. Fortunately, this condition is self-limiting and leaves no sequelae.
In fact, patients with primary blood in semen have been widely studied, and most of these studies show no other related issues.
3.2. Secondary Blood in Semen
The cause of blood in the semen is known or suspected to have a prior origin, such as immediately after a prostate biopsy, urinary tract infection, or cancer.
The following are common causes:
Inflammation and Infection:
Inflammation is one of the most common causes. The inflammatory process stimulates the mucosa, leading to congestion and edema of the ducts, seminal vesicles, prostate, verumontanum, and urethra, causing blood in the semen.
The causes of inflammation include bacterial infection, trauma, seminal vesicle stones, or prostate calcification. Common infections include Enterobacteria (mainly Escherichia coli), Chlamydia, Gram-positive bacteria, tuberculosis bacilli, and some viruses.
Seminal Vesicle Obstruction and Seminal Vesicle Cysts:
Causes of prolonged distension and dilation of the seminal vesicles can rupture submucosal blood vessels.
Cancer:
Common cancers include prostate cancer, seminal duct cancer, testicular cancer, and lymphoma.
Systemic Diseases:
Common systemic diseases include coagulation disorders, hemophilia, cirrhosis, and hypertension.
Local Invasive Procedures:
Prostate biopsy through the rectum, urethral instrumentation, radiation therapy for prostate cancer, post-vasectomy, post-orchiectomy, etc.
Urethral Varices:
In this case, the semen usually does not contain blood, but the patient notices a large amount of blood in the urine after an erection or bleeding from the urethra after an erection without ejaculation.

4. Diagnostic Approach for Blood in Semen
Whenever blood is detected in semen, men should see a doctor for both local and general examinations. The doctor will examine the external genital organs as well as the prostate to detect any underlying conditions.
Additionally, the doctor may order other tests, including:
• Urinalysis to check for infections
• PSA blood test to screen for prostate cancer
• Microbiological tests to diagnose sexually transmitted infections
• Ultrasound of the groin and urinary tract, transrectal ultrasound
• Advanced diagnostic procedures such as CT scans, MRI, or urethroscopy and cystoscopy, seminal vesicle endoscopy
5. How to Treat Blood in Semen
In general, blood in semen sometimes does not require any treatment as the condition often resolves on its own. This is usually true for primary blood in semen, meaning there is no known cause.
Conversely, patients over 40 years old with prolonged blood in semen, especially with other symptoms, need to be examined by a urology specialist. In such cases, treatment will depend on the underlying cause:
• Bacterial infections from common bacteria: Use antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and oral hemostatic agents.
• Genitourinary tuberculosis: Treat according to the tuberculosis treatment regimen.
• Surgical treatment depends on the specific case with indications for open surgery or endoscopy through the urethra or abdomen in cases of seminal vesicle obstruction, seminal vesicle cysts, or seminal vesicle stones; prostate cancer, seminal duct cancer, and testicular cancer, urethral varices.
In summary, blood in semen may sound alarming, but most cases resolve on their own. However, it should not be taken lightly. Instead, men should proactively visit a specialist in andrology, actively monitor, and adhere to treatment to eliminate underlying conditions and alleviate worries, confidently enjoying a happy life.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.