This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Bui Tien Dat - Emergency Medicine - Cardiology - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 12 years of experience in the field of emergency resuscitation - cardiology.1. What is the carotid artery?
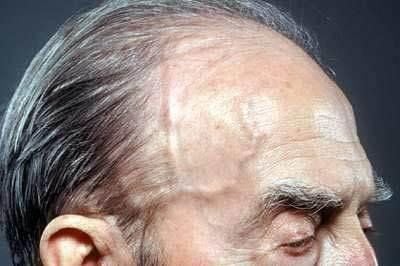
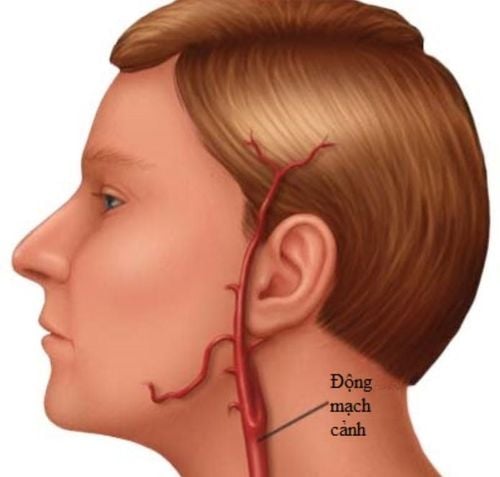
The carotid artery is a large branch that originates from the thoracic aorta and branches upward to feed the brain. The human body has two carotid arteries on either side, with a symmetrical path through the midline. The carotid artery branches at the cervical region, above the thyroid cartilage, at the level of the 4th cervical vertebra, the wall of the internal carotid artery, and the external carotid artery. The carotid artery is clinically palpable and is used in the evaluation of the patient in the context of shock, and the peripheral pulse is not palpable.Carotid artery disease is a fairly common disease in clinical practice, especially in the elderly group at high risk. Patients over 80 years old account for about 10% of all cases, while patients over 50 years old account for only 1%. Atherosclerotic carotid stenosis is the most common cause of carotid artery disease. A serious complication in patients with carotid artery disease is stroke. Patients may face neurological, motor and language sequelae that impair long-term quality of life.
Carotid artery disease develops silently over a long period of time. Sometimes the first sign of the disease is a stroke or transient ischemic attack. However, carotid artery disease is a disease that can be prevented or slowed down by detecting and modifying risk factors. Treatment of carotid artery disease requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and surgical treatment in some cases.
2. Causes of carotid artery disease
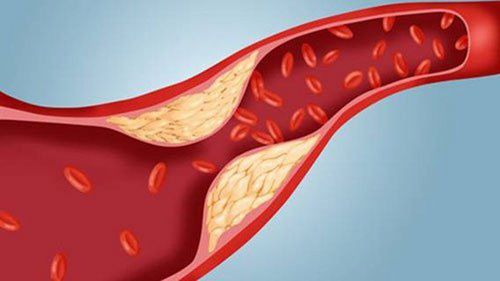
In healthy individuals, the carotid artery has a smooth inner wall, is lined with intact endothelial cells, and ensures a constant supply of blood to the brain and head structures. Carotid artery disease occurs when there is a deposition of cholesterol, fibrous tissue, calcium, and other tissues that form plaques inside the arteries. Over time, the plaques gradually increase in size, occupying the entire vessel lumen and reducing blood flow to the brain. Atherosclerosis causes the artery walls to become stiff and narrow. The drop in oxygen and nutrients in the blood affects the functioning of important brain structures slowly or possibly suddenly in the setting of a stroke.Trắc nghiệm: Huyết áp của bạn có đang thực sự tốt?
Huyết áp cao hay thấp đều ảnh hưởng đến tình trạng sức khỏe con người. Để biết tình trạng huyết áp của bạn có thực sự tốt không, hãy làm bài trắc nghiệm sau đây để đánh giá.3. Risk factors for carotid artery disease
The risk factor, although not a direct cause of the disease, increases the likelihood of carotid artery disease many times over. Some risk factors for carotid artery disease include:High blood pressure: High pressure exerted on the artery wall for a long time causes damage to the vessel wall. Smoking: The active substance nicotine in cigarettes irritates and damages the endothelium of the carotid artery. Smoking also causes an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. Diabetes: Diabetes makes fat metabolism ineffective, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis, including carotid atherosclerosis. Hyperlipidemia: High levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides facilitate the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques. Family history of close relatives with atherosclerosis or carotid artery disease. Age: The carotid artery becomes less flexible and vulnerable in older people. Obesity: Excess weight increases the risk of many different diseases, including hypertension, atherosclerosis, and diabetes. Sleep apnea: Increases the risk of stroke. Sedentary, sedentary lifestyle: Increased risk of arterial damage from hypertension, diabetes, and obesity.

4. Signs of carotid artery disease
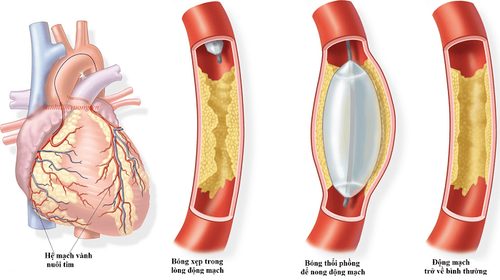
Carotid artery disease in the early stages is difficult to detect because there are no clinical symptoms. Carotid artery disease will progress slowly and silently until it causes a lack of blood to the brain, causing a transient ischemic attack or a stroke with the following symptoms:Sudden weakness, paralysis of the limbs or facial muscles, often only found on one side of the body. Sudden abnormalities in speech and language comprehension. Sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes. Dizziness, loss of balance. Severe headache of unknown cause. Diagnostic imaging modalities are indicated to clarify the diagnosis of carotid artery disease and assess its extent. Carotid ultrasound examines the blood flow and pressure of the carotid arteries. Computed tomography or cranial magnetic resonance imaging detects cerebral infarction or cerebral hemorrhage. Internal carotid angiography is adjunct to ultrasound in the assessment of flow and degree of stenosis of the carotid artery and associated other arterial systems.
When having one of the above-mentioned signs suggesting a stroke, the patient should be taken to the nearest medical facility with a stroke treatment center for timely treatment in the golden time.
5. Prevention and treatment of carotid artery disease
Fortunately, carotid artery disease is preventable by taking the following measures:Don't smoke: Quitting smoking within a few years reduces the risk of stroke to as low as a non-smoker leaves. Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight is a risk factor for many different cardiovascular diseases. Limit cholesterol and fat in your daily diet. Eat more green vegetables and fruits: Potassium, folate and antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables help protect the body from transient ischemic attack and cerebrovascular accident. Limit salt: According to experts, a healthy adult should consume less than 1.5 grams of salt per day. Regular exercise: helps lower blood pressure, increases HDL-cholesterol, a type of good cholesterol and improves cardiovascular health, weight loss, and good blood sugar control in patients with diabetes. Limit alcoholic beverages Well control chronic conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.

Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.