This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Pham Van Hung - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Arterial thrombosis is a blood clot that develops in an artery. This is very dangerous because it can obstruct or stop the flow of blood to major organs, such as the heart or brain. The main cause of arterial thrombosis is atherosclerosis. Accordingly, the symptoms of arterial thrombosis depend on where the clot forms against the background of intravascular plaque.
1. What is Atherothrombotic Arterial Thrombosis?
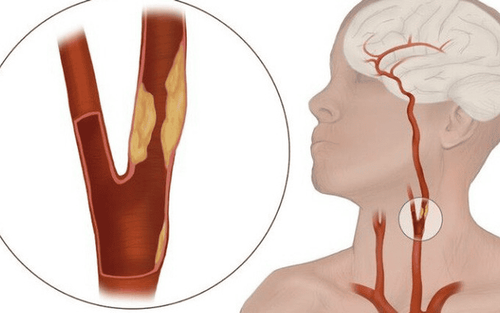
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich and nutrient-rich blood from the heart to the organs. Arterial thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in an artery. Can be viewed similarly to deep vein thrombosis, arterial thrombosis affects only arteries instead of veins. The arteries are usually larger and carry more blood.The most common cause of arterial thrombosis is atherosclerosis. The nature of atherosclerotic plaques is composed of excess fat, calcium and local endothelium metabolic products. As the plaque grows, the vessel lumen becomes narrower. Under high-pressure blood flow, atherosclerotic plaque is sloughed off, carried along with the blood stream, forming arterial thrombosis due to atherosclerosis, causing obstruction of downstream vessels.
Therefore, arterial thrombosis due to atherosclerosis can cause life-threatening events, such as heart attack or stroke, by blocking a blood vessel that feeds the heart, the coronary artery or the blood vessels in the brain. .
2. Symptoms of arterial thrombosis due to atherosclerosis
The symptoms of atherothrombosis are dependent on the location of the blood clot blocking the lumen. Some of the symptoms of a blood clot may include:Pain in one leg Clamping pain when walking Swollen legs or arms Chest tightness Numbness on one side of the body Weakness on one side of the body Changes in consciousness However, many people may experience no symptoms of atherothrombotic disease if the thrombus does not completely occlude the vessel or the occluded area is nourished by collateral circulation. However, the patient always faces the risk of thromboembolism due to atherosclerosis at any location in the future.

3. Complications of arterial thrombosis due to atherosclerosis
Possible complications of atherothrombotic disease include:Myocardial infarction : Symptoms of a heart attack due to myocardial infarction may begin as chest tightness, or chest pain, that spreads to jaw, back or neck, to shortness of breath, dizziness, and collapse. Ischemic stroke: Symptoms of a cerebrovascular accident can be numbness on one side of the body, difficulty walking, partial or complete loss of vision in one eye, double vision, slurred speech, and distorted mouth.
4. Factors that increase the likelihood of atherothrombotic disease
A person's behavioral habits and health conditions can put them at a higher risk of developing thromboembolic disease than other people.Some of the risk factors that can cause blood clots due to atherosclerosis in the arteries include:
Smoking Diabetes High blood pressure High cholesterol Obesity Unbalanced diet Having a family history Arterial thromboembolism Passive lifestyle Elderly.

5. How to diagnose arterial thrombosis due to atherosclerosis?
A history, history with the participation of many risk factors helps the doctor quickly towards a diagnosis of atherothrombotic artery thrombosis. However, the possibility of having a clotting disorder or having risk factors for developing a blood clot is also avoidable.To detect blood clots, doctors often recommend imaging studies to evaluate the arteries. The first commonly used tool is vascular doppler ultrasound because blood clots can change the sound of the arteries.
Besides, the electrocardiogram, which measures the electrical activity of the heart, can also indirectly indicate the flow of blood in the coronary arteries, early detection of the possibility of arterial thrombosis caused by atherosclerosis, leading to to myocardial ischemia.
In some cases, your doctor may recommend more invasive procedures, such as background erasure angiography. The principle of this method is X-ray angiography, which is based on the presence of contrast material in the vessel through the insertion of a catheter into an artery in the thigh, arm or groin of the patient.
6. How to treat arterial thrombosis due to atherosclerosis?
Doctors may recommend the following measures to treat arterial thrombosis:Taking thrombolytics Thrombolytics thin the blood to help dissolve the clot. This indication is usually placed when arterial thrombosis due to atherosclerosis causes acute arterial occlusion, helping to re-circulate blood in time, minimizing the risk of target organ necrosis.
Because fibrinolytics can dissolve blood clots more quickly, they can also cause dangerous bleeding. After that, this indication will be maintained with anticoagulants, helping the possibility of other blood clots in the future.
In the case of atherosclerosis that forms blood clots that cause a stroke or heart attack, the patient may need lifelong treatment.
Surgical intervention Types of procedures or surgery to treat arterial thrombosis due to atherosclerotic coronary artery occlusion include coronary artery bypass surgery and balloon angioplasty combined with stenting.
In coronary artery bypass surgery, the doctor removes a blood vessel from another part of the body to bypass the blocked part.
In the procedure of balloon angioplasty combined with stenting, the doctor only approaches through a small skin incision and performs it with percutaneous endovascular instruments.
Alternatively, carotid endarterectomy may be considered in the case of patients with arterial thromboembolic stroke due to atherosclerosis from the carotid artery.
Lifestyle changes Since the cause of arterial thrombosis in these cases is atherosclerosis, lifestyle modifications such as quitting smoking, good control of blood pressure, blood sugar In patients with diabetes, dyslipidemia, increased physical activity... can help reduce the risk of disease.
At the same time, the medical treatment for the diseases mentioned above should be followed for life with periodic monitoring and evaluation by doctors.
In summary, atherothrombotic arterial thrombosis when obstructing vital blood vessels can be life-threatening. Many people may have latent disease potential, especially those with multiple risk factors, until symptoms or acute events occur. Accordingly, early detection by screening and timely treatment can prevent the unfortunate thromboembolic complications in the future.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical professionals, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: medicalnewstoday.com