Bladder wall thickening can be localized or generalized. Bladder wall thickening can be caused by infection or tumor, then it may cause discomfort, painful urination, frequent urination, hematuria, and even endanger the patient's life.
1. What is the bladder? What is bladder wall thickening?
The bladder is an organ of the urinary system, which stores urine secreted by the kidneys and excretes urine through the urethra. Therefore, they have the role of storing urine for the body. This organ is located in the cavity between the pelvis, when the bladder is full of urine, the bladder wall muscles will relax until urination, the muscles will contract to push the urine out.
The bladder is a hollow organ. The average capacity in adults for men is from 350-750 ml and for women is 250-550 ml. The normal bladder wall is about 3mm thick when the bladder is tense. The bladder wall is composed of 4 layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscle layer and serosa.
2. When is the bladder wall thickened?
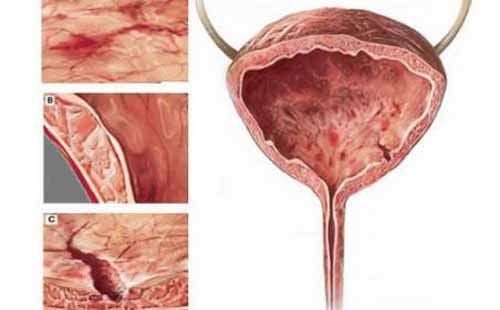
If the bladder wall is not treated early, it can cause bladder infection
Bladder wall thickening occurs when the mucosal layer, submucosa, muscularis mucosae and serosa grow larger than average. If you have frequent urination day and night, you should see a doctor, because this may be a sign of bladder wall thickening.
Lateral thickening of the bladder wall is an abnormal health manifestation due to a disease in the urinary system. The disease can be a bladder infection if not treated early. More dangerously, it can lead to retrograde infection to the ureter and renal pelvis. Because the bladder is located in the body, it cannot be self-examined but must go to a medical facility for examination and treatment of this disease.
3. Signs of bladder wall thickening
- Frequent urination - frequent urination, always feeling the need to urinate urgently
- A burning, stinging sensation when urinating
- Urine is cloudy or has blood in the urine, has a strong odor
- Back pain or mild fever
- For young children, bedwetting at any time during the day is also a sign of bladder-related diseases.
4. Causes of bladder wall thickening
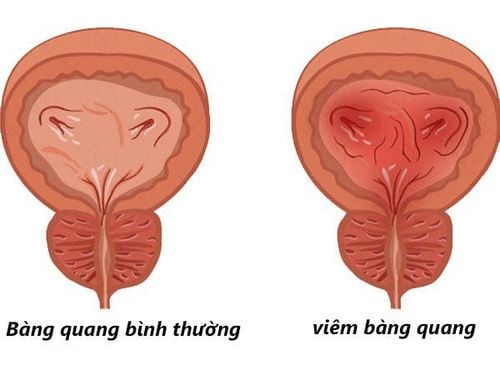
The abnormal growth of cells in the bladder wall can also be related to smoking or exposure to chemicals. Bladder irritation or exposure to radiation can also be the cause of the disease. In addition, the patient does not exclude the following diseases:
Cystitis
This is the most common disease that can occur in both adults and children. The cause is due to frequently holding urine for a long time, unsafe sex or taking strong antibiotics..... In addition, the disease is caused by E.coli bacteria in the bladder or can be due to complications of diseases such as diabetes, kidney stones or prostate enlargement, nerve damage, spinal cord... In many cases, this condition also recurs over a long period of time.
Bladder obstruction
This condition often occurs at the bladder neck, so it is adjacent to the urethra. For men, prostate cancer or prostate enlargement can cause bladder obstruction.
Bladder stones
Cloudy, dark urine, with a layer of film or film on the surface, and constant pain in the lower abdomen or lower abdomen may be due to bladder stones. The cause is holding urine for a long time, drinking unfiltered water, and impaired function of some organs....
5. Methods for diagnosing bladder wall thickening
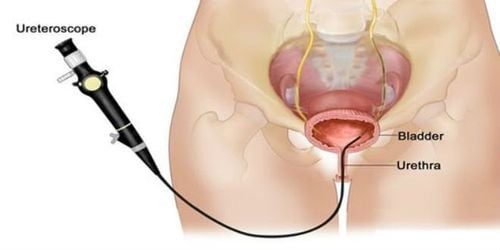
Currently, there are many methods for diagnosing whether a patient has a thickened bladder wall. Some of these methods are widely used by doctors because of their simplicity, speed, and high efficiency:
Bladder ultrasound
This is the most common imaging diagnostic method used when encountering urinary disorders in general and bladder wall thickening in particular. Ultrasound can detect congenital malformations, detect tumors, assess the degree of bladder wall invasion and urinary tract hydronephrosis. Through this, the doctor will determine the problem you are having.
In addition, ultrasound can also detect a number of other diseases such as inflammation, prostate enlargement, stones, blood clots in the bladder, urethra, etc. Bladder ultrasound is a highly effective method, and people with mild illnesses often only need to perform this method.
Cystoscopy
A diagnostic imaging method using a specialized endoscope. The doctor can look directly into the endoscope or through a computer screen. If the doctor detects an abnormality in the bladder, treatment can be performed immediately during the procedure.
Urine test analysis
This helps the doctor determine the proportion of bacteria, blood, and pus in the urine, thereby assessing the level of infection. From there, a reasonable treatment regimen can be given. If the test results show white blood cells, microscopic red blood cells, and polymorphonuclear leukocytes, it proves that the disease has progressed to a severe stage.
Of the three methods above, bladder ultrasound will be the first indication that the doctor asks the patient to perform because it is safe, has the fastest, and most general results. If the patient has other abnormal signs, the doctor will request other tests to determine the patient's condition most accurately.
Depending on the severity, the doctor will have different treatments, including bladder wall thickening, which can also be treated with medication. If abnormal signs appear, you need to go to the nearest medical facility for examination, avoiding leaving it for too long, which will make the condition worse.
Regular health check-ups help detect diseases early, thereby having a treatment plan to achieve optimal results.

To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.