There are many different causes of acute urinary retention; one of these is due to drinking too much beer and alcohol. If acute urinary retention is not promptly catheterized, it can lead to bladder rupture, causing urine and blood to spill into the abdominal cavity, causing acute inflammation, and threatening the patient's life.
1. What is acute urinary retention?
For normal people, urination is a reflex controlled by the will, with a harmonious combination of strong muscle contractions and wide expansion of the bladder neck, under the control of the central nervous system to bring urine from the bladder to the urethra and then out.
Normally, when the bladder contains a certain amount of urine, about 250-300 ml, it will stimulate you to urinate. Urinary retention is when the bladder is full of urine but you cannot urinate. Urinary retention is also known as "Bí đái", which occurs mainly in adults. If not treated promptly, urinary retention can have consequences.
Many different causes can lead to acute urinary retention. If the bladder wall does not contract strongly enough, it can cause urinary retention. The cause of weak bladder contractions is loss of connection with the autonomic nervous system that controls urination or due to spinal trauma, pelvic fractures, or bladder diseases (such as fibrosis of the bladder wall due to chronic inflammation or acute bladder inflammation, chronic inflammation, bladder stones, etc.).
In some cases, bladder stones move to block the opening of the bladder to the urethra, obstructing urine flow or even completely blocking, causing acute urinary retention. Urinary retention can also be caused by chronic urethritis, causing fibrosis and narrowing of the urethra due to infections such as gonorrhea or Chlamydia.
In men, urinary retention can also be caused by prostate disease (such as inflammation, benign prostatic hyperplasia, or benign or malignant tumors) that will compress the bladder neck, causing urinary retention.
Women can also suffer from urinary retention due to the common causes mentioned above. Some cases of acute urinary retention can be psychological, such as traveling in a crowded car, sitting in a meeting for a long time, etc., and having to hold urine for a long time, leading to urinary retention.

2. Why is acute urinary retention caused by alcohol?
In addition to the above causes, acute urinary retention can also be caused by drinking a large amount of alcohol. There are many patients with acute urinary retention caused by alcohol.
The mechanism of this condition is that high blood alcohol concentration inhibits the cerebral cortex and some nerve centers involved in controlling urination, causing a disturbance in consciousness, so the person drinking alcohol does not feel the urge to urinate, thereby increasing the bladder capacity beyond the allowable threshold.
3. Symptoms of acute urinary retention
Most people with urinary retention have symptoms of pain, bladder pressure, prepubic area, and prolonged discomfort if not treated (internal medicine) or not catheterized (surgical intervention) in time.
People with acute urinary retention often have a burning sensation and always want to urinate but cannot urinate, which makes them feel more uncomfortable and restless.
Urinary retention feels extremely unwell, painful, and burning in the bladder, especially when accompanied by acute or chronic bladder inflammation. These will significantly affect your daily life as well as your health.
If urinary retention is not treated promptly or recurs several times, it can cause cystitis, even retrograde inflammation, and nephritis and greatly affect kidney function, leading to kidney failure.
The bladder is like a rubber ball that can stretch to hold urine. When full, the bladder wall will become thinner and more vulnerable than an empty bladder or one that contains little water.
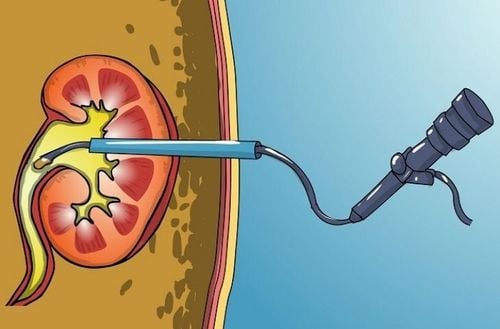
In cases of acute urinary retention, if not promptly catheterized, the bladder can rupture, causing urine and blood to spill into the abdominal cavity, causing acute inflammation. This case, if not treated promptly, can lead to death.

4. How to treat acute urinary retention due to alcohol consumption?
Acute urinary retention requires a medical examination as soon as possible to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Urinary catheterization must be performed with absolutely sterile medical instruments; otherwise, it can cause hospital-acquired urinary tract infections. In cases of acute urinary retention accompanied by cystitis, prostate disease in men, spinal trauma, pelvic trauma, urethral fibrosis, etc., treatment requires persistence under the prescription of medication and advice from a doctor.
In summary, there are many different causes of acute urinary retention, one of which may be due to excessive alcohol consumption. In cases of acute urinary retention, if not promptly catheterized, it can lead to a ruptured bladder, causing urine and blood to spill into the abdominal cavity, causing acute inflammation and affecting the patient's life. Therefore, the best way to prevent acute urinary retention due to alcohol is to avoid or use this beverage reasonably and moderately.