What is the relationship between parents and children's blood groups? Is the child's blood group from the father or mother? Is there a difference in the inheritance of blood groups from parents to children? If so, what problems will occur and how will they be treated?
1. What is blood group?
There are about 4 - 6 liters of blood in the human body. Blood is made up of different types of cells in plasma, including:
- Red blood cells: Deliver oxygen to different tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide.
- White blood cells: Destroy invaders and fight infections.
- Platelets: Help blood clot.
Plasma is made up of proteins and salts. The combination of protein molecules in the blood creates antigens and antibodies, which are what differentiates one person's blood from another. Antigens live on the surface of red blood cells while antibodies are found in plasma. The combination of antigens and antibodies in the blood is the basis for determining blood group.
Although there are at least 33 blood collection systems, only 2 systems are widely used, which are the ABO blood group system and Rh+ (positive) or Rh- (negative). These two groups combine to form 8 basic blood groups, which are: A+, A-, B+, B-, AB+, AB-, O+, O-.
2. The relationship between parent and child blood groups
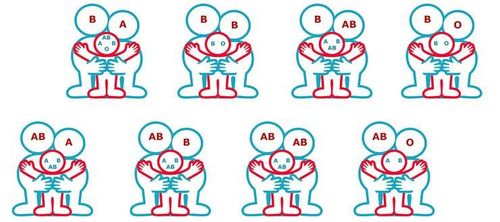
Blood groups are determined by genetics. Each person inherits a gene from their parents, one gene from their mother, and one gene from their father - to create a pair. Therefore, the blood groups of parents and children are closely related to each other.
2.1 Blood group inheritance from parents to children - ABO system
With the ABO system, a person can inherit gene A from one parent and gene B from the other, resulting in blood group AB. It is also possible to receive the B antigen from both parents and create a blood type BB or B.
On the other hand, blood type O does not contain any antigens and does not affect blood types A and B. Therefore, if a child inherits O from one parent and A from the other, the child's blood type will be A. Or both parents have blood types A or B but can still have a child with blood type O if the child carries the O gene.
2.2 Blood type inheritance from parents to children - Rh factor
Blood is also classified according to the Rh factor. This is another antigen found on red blood cells. If the red blood cells have the antigen, it means they are positive for the Rh factor or Rh+, otherwise they are Rh-.
The Rh factor is a genetic protein, so blood type inheritance from parents to children will determine Rh+ or Rh-, but the most common is Rh+.
3. Compatibility of blood types of parents and children during pregnancy?
Rh+ or Rh- usually does not affect health but can affect pregnancy. If the mother's blood type is Rh- but the blood type inherited from parents to children is Rh+, it is necessary to pay attention. Because the blood cells from the Rh+ child will follow the Rh- mother's bloodline to activate the mother's immune response to form antibodies to attack the baby's Rh+ red blood cells. This phenomenon is called blood type incompatibility between mother and child.
Therefore, in the first prenatal visit, the doctor always recommends a blood type and Rh factor screening test. If the mother has Rh- blood type, the doctor will request a blood test again in subsequent prenatal visits to check for antibodies against Rh that have formed in the body. That also means the child has Rh+ blood type.
If the doctor determines that the blood type passed from parent to child is likely to be Rh incompatible, the mother will need to be closely monitored during pregnancy and may even need extra care.
Although the mother's and baby's blood do not normally mix during pregnancy, a small amount of the baby's and mother's blood may come into contact during birth. Therefore, if there is an Rh incompatibility, your body may produce Rh antibodies to counteract the Rh factor.
These antibodies will not cause problems for a baby with Rh+ blood in the first pregnancy. However, they can cause problems in subsequent pregnancies, especially if the baby has Rh+ blood.
If the blood type inherited from the mother to the child is Rh incompatible in the first pregnancy and Rh incompatibility occurs in the second and subsequent pregnancies, the antibodies produced by the mother's body can damage the baby's red blood cells. The baby may then need a red blood cell transfusion while still in the womb or shortly after birth.

4. Treatment of Rh incompatibility between parents and children
If Rh incompatibility has been diagnosed, the doctor may recommend that the mother take Rh immune globulin (RhoGAM) in the seventh month of pregnancy and then repeat within 72 hours after birth if the blood group inheritance from parents to child is confirmed to be Rh+ at birth.
Rh immune globulin contains Rh IgG antibodies, so the mother's body will not react to the child's Rh+ cells and the mother's body will not produce Rh antibodies against them.
In short, the blood groups of parents and children are closely related, the child's blood group is inherited from the parents. Therefore, each person's blood group is determined before birth and cannot be changed after birth.
To schedule an appointment at the hospital, please contact the HOTLINE or book directly HERE. Download the MyVinmec App to manage, track, and schedule appointments conveniently anytime, anywhere.