This article was medically reviewed by Dr. Dong Xuan Ha, a Level I Specialist in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy at the Department of Internal Medicine and General Consultation, Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital, and MSc. Vu Tan Phuc from the Department of Internal Medicine and General Consultation, Vinmec Phu Quoc International Hospital.
The GGT index is commonly used to assess liver and bile duct damage. If this index is elevated, it indicates that the liver is experiencing problems. Therefore, patients should undergo regular check-ups to detect the condition early and prevent dangerous complications in the future. Let’s explore this in detail in the following article.
1. What is the GGT Index in Blood Tests?
The GGT index is one of the essential indicators used by doctors to diagnose the condition of the liver. Combined with AST (SGOT) and ALT (SGPT), GGT is a crucial liver enzyme that helps identify bile stasis in the liver. The GGT enzyme levels will increase when the liver is affected by conditions such as bile stasis, chronic hepatitis, alcohol-induced hepatitis, toxic hepatitis, viral hepatitis, or liver cancer.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.2. What GGT Levels Are Considered Dangerous?
The normal GGT range is below 60 UI/L.
For women, the index typically ranges between 11–50 UI/L.
For men, the index generally ranges between 7–32 UI/L.
The severity of elevated GGT levels is classified into three categories:
- Mild elevation: 1–2 times the normal range.
- Moderate elevation: 2–5 times the normal range.
- Severe elevation: More than 5 times the normal range.
However, because GGT levels can increase due to various liver diseases (e.g., liver cancer, viral hepatitis) and non-liver-related conditions (e.g., acute coronary syndrome), the GGT test alone cannot pinpoint the exact cause of liver damage.
Alcohol consumption can also elevate GGT levels. Chronic heavy drinkers typically have higher GGT levels than individuals who consume 2–3 drinks or less per day. Therefore, the GGT test is often used to evaluate alcohol abuse, both acute and chronic.
3. Causes of Elevated GGT Levels
To reduce the risk of liver damage, it is essential to identify factors that can elevate GGT levels. This is particularly critical for individuals with high liver enzyme levels. The following factors can contribute to increased GGT levels in the blood:
- Obstructive jaundice.
- Acute hepatitis or liver shock.
- Liver cancer or liver tumors.
- Cirrhosis and liver tissue necrosis.
- Use of hepatotoxic drugs such as phenytoin and phenobarbital.
- Chronic alcohol consumption.
- Poor rest habits, which impair liver function.
- Poor nutrition, leading to a weakened liver.
- Diabetes and lung diseases.
- Pancreatic diseases.
- Reduced blood flow to the liver.
- Elevated levels of liver enzymes AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT), and GGT are often observed in individuals with conditions such as malaria, biliary diseases, iron overload, autoimmune hepatitis, and intestinal autoimmune diseases.
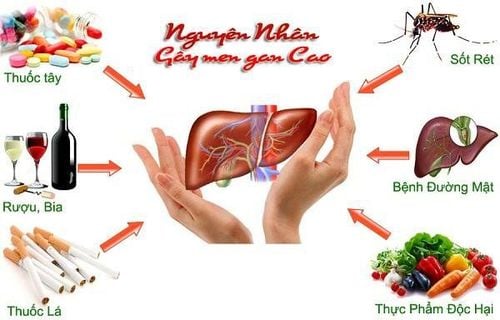
Patients should avoid taking hepatotoxic medications like phenytoin or phenobarbital within 24 hours before a GGT test, as these drugs can artificially raise GGT levels, leading to inaccurate results.
Patients should also refrain from consuming alcohol, tobacco, or any stimulants, as even small amounts can significantly affect test outcomes.
4. How to Control Elevated GGT Levels
If you discover that your GGT levels are elevated, do not panic. With advances in modern medicine, this condition can be managed and treated. Patients should consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and follow their guidance to improve liver health.

Specific recommendations for managing GGT levels include:
- Hepatitis testing: Focus on testing for hepatitis B and C. For hepatitis B, in addition to HBsAg, further tests such as HBeAg, HBsAb, and anti-HBeAg should be conducted. If possible, perform a quantitative DNA test for the virus.
- Address bile duct obstruction: If elevated GGT levels are caused by bile duct obstruction, the root cause must be addressed and treated effectively.
- Alcohol-related hepatitis: Complete abstinence from alcohol and all alcoholic beverages is crucial.
- Reduce alcohol intake to improve liver enzyme levels if alcohol is a contributing factor.
- To monitor liver health and assess disease progression, regular health check-ups are recommended. Patients can register for specialized Liver and Bile Screening Packages at hospitals with experienced specialists, such as Vinmec International Hospital, for early detection and treatment.
- The liver is directly impacted by diet, as it is responsible for processing toxins in the body. A proper diet benefits both internal and external health, while excessive alcohol intake and poor eating habits can lead to liver dysfunction.
- The liver can detoxify harmful substances, such as chemicals and toxins from food. However, prolonged exposure can overwhelm the liver, causing fatigue and silently increasing GGT levels.
- Avoid unverified herbal or traditional remedies, as they can worsen liver conditions if not scientifically validated.
Maintain adequate rest and avoid stressful activities.

We hope this article has provided a clearer understanding of the GGT index, when it becomes elevated, and how to control it. Regular health check-ups and necessary tests are essential for protecting your liver health. If your GGT levels are elevated, consult a doctor immediately to determine the cause and take preventive measures to avoid serious liver damage.
For more health, nutrition, and beauty tips, visit Vinmec International General Hospital to safeguard the health of yourself and your loved ones.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.