This is an automatically translated article.
Plague is a dangerous, highly contagious infectious disease with a high mortality rate. Depending on the type of disease, the incubation period for plague varies, on average 1-7 days.
1. What is the plague?
Plague is an acutely progressive infectious disease with a high rate of spread and high mortality. The disease is caused by the gram-negative bacillus Yersinia pestis of the family Enterobacteriaceae, which circulates in rodents (mainly mice) and the fleas that parasitic on them. From there, the plague spread to humans through infected fleas.
Human plague includes disease forms: lymphatic, pulmonary, bacteremic and meningococcal. In which, the lymph node is the most common, accounting for more than 90% of cases. Plague is a dangerous disease with a mortality rate of up to 30-60% if left untreated.
2. How is the plague transmitted?
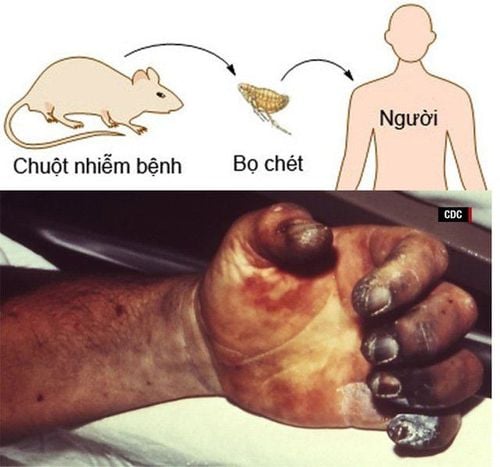
In nature, bubonic plague is transmitted by the following routes:
By fleas, especially Xenopsylla cheopis: The most common route. Accordingly, the fleas feed on the blood of the host (rat), the plague bacteria multiply in the flea's pre-stomach, obstructing digestion. When fleas switch to a new host, bacteria will follow the sting to the new host, causing the spread of plague; Not flea-mediated: By inhalation of airborne bubonic plague bacteria (by contact with a person infected with pneumonic plague or a host who died from plague) and by direct skin penetration of the bubonic plague bacteria ( direct contact with sick animals, bitten or scratched by domestic animals, staff of laboratories for plague bacteria, ..).
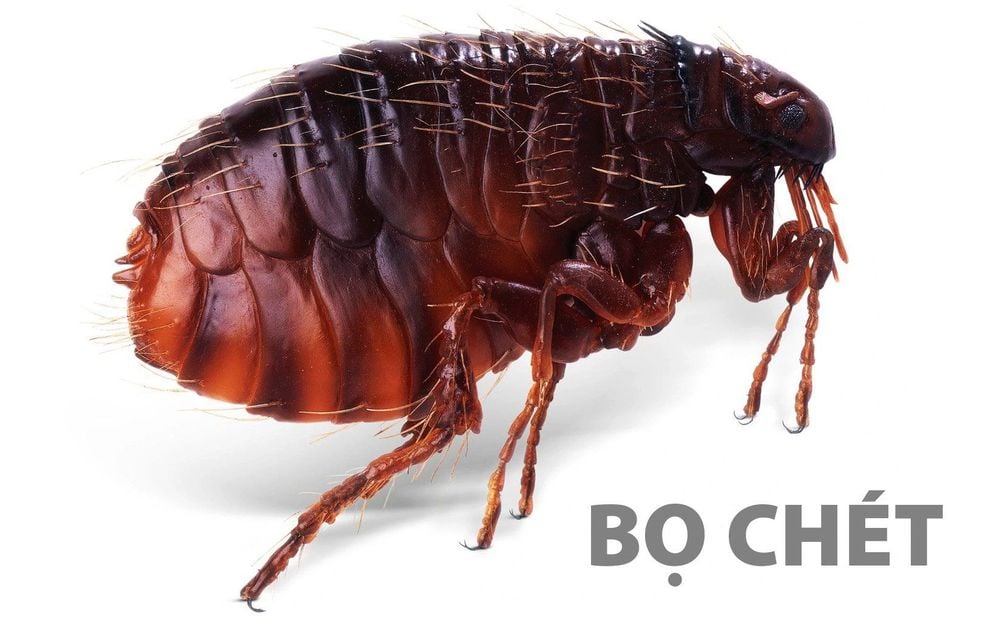

Bệnh dịch hạch lây qua trung gian bọ chét
3. Plague incubation period
The incubation period for bubonic plague lasts an average of 1-7 days, which can be extended by several days in vaccinated individuals. Particularly, primary pneumonic plague usually has a shorter incubation period, averaging 1 - 4 days.
Incubation time, full outbreak of plague types are as follows:
Bubonic plague In the pre-epidemic period, the average incubation period is 2 - 5 days, the shortest incubation period is only a few hours and long The incubation period is about 8-10 days. In the incubation period, the disease has no symptoms. But at the onset, the disease causes many unpleasant symptoms such as headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, high fever, chills, pain all over, a lot of pain in the area about to swell the lymph nodes.
After a few hours or 1-2 days, bubonic plague enters the full-blown stage. When it turns to full-blown stage, it will cause lymphadenitis in the flea bite area, mainly in the groin area, armpit, neck lymph node,... The lymph node is swollen, very painful, purulent, spontaneously bursting, and draining pus. and blood, long wound healing, if the scar wall will shrink. When the whole body is infected, the patient will have symptoms of high fever, rapid pulse, rapid breathing, headache, dizziness, fatigue, nausea, delirium, oliguria, loose stools, mucous membranes. conjunctivitis, red eyes, dry lips,....
Thời gian ủ bệnh dịch hạch trung bình là 2 - 5 ngày
Pneumonic plague Primary pneumonic plague has a very short incubation period, only a few hours, sudden onset, high fever 40 - 41°C with symptoms of chills, rapid pulse, decreased blood pressure, fatigue , headache, discomfort,... After only a few hours to a day, the disease entered a full-blown phase with symptoms of infection, worsening toxicity, respiratory symptoms (chest tightness, shortness of breath, rapid breathing). and shallow, cough with phlegm, cough up blood). If not treated promptly, the disease quickly progresses to acute pulmonary edema, shortness of breath and severe cardiovascular disorders, which are easy to die within 1-2 days.
Secondary pneumonic plague is more common than primary pneumonic plague, often appearing because the patient is not treated or treated late (after 3-4 days). Patients present with high fever, chest pain, cough with bloody sputum, rapidly progressing to acute respiratory failure and possibly death.
Plague with bacteremia With this form, the disease has a sudden, acute onset as soon as the peripheral lymph nodes are not swollen. Very severe infection and intoxication: High fever 40 - 41°C, many chills, mental agitation or lethargy, high fever, loose stools, abdominal distension, cardiovascular and respiratory disorders , bleeding skin, mucous membranes, viscera, can die in 1-2 days.
Secondary septicemic plague usually occurs after the ganglion, the primary pulmonary form is not treated, when the patient's resistance has decreased. Septic bubonic plague is usually severe and has an acute course.
Người bệnh sốt cao kèm cơn rét run
Plague in the skin In the area where Yersinia pestis bacteria invade, it first develops into a burning nodule, then into vesicles, pustules with blood, very painful when pressed. Around the pustules is the congested, infiltrated, raised skin organization compared to the healthy skin. Then, the acne breaks to form sores, the bottom of the ulcer is a yellow infiltrate, the surface of the ulcer is covered with black scales, the ulcer is slow to heal and it takes a long time to heal.
After contracting the plague, everyone is susceptible to the disease. Immunity after recovery is relative and cannot protect against large numbers of bacteria. Therefore, it is necessary to proactively prevent plague by keeping the living environment clean, killing rats, injecting plague vaccines, etc. When there are symptoms of suspected plague such as fever, bubonic plague on people. ... patients need to go to medical facilities for early examination and timely treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
Recommended video:
Health check recurring at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
READ MORE
What is the role of lymph nodes in humans? Tuberculosis: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Sepsis: Dangerous, silent symptoms