This is an automatically translated article.
Plague is a dangerous infectious disease caused by bacteria, they can cause acute symptoms and people can die at a high rate if not detected and treated. The disease has caused a pandemic and the number of deaths is very high, so understanding the disease to help prevent and timely treat when infected is essential.
1. What is the plague?
Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, which circulates in populations of mainly ticks and fleas, of which rats are considered dangerous pathogens. This bacteria is killed at 550C within 30 minutes, at 1000C within 1 minute and killed by commonly used disinfectants.
Plague is a highly contagious and dangerous disease with a high mortality rate of 30-60%. The disease occurs in all ages, both men and women, but mainly in people under 20 years of age, easily occurs in crowded, cramped places, places with poor sanitation (rats are easy to live) or areas with background sandy soil (flea live), which usually occurs in the dry season, is suitable for the growing season of intermediate hosts, rats and fleas.
Trực khuẩn Yersinia Pestis gây ra bệnh dịch hạch
2. How is the plague transmitted?
Plague bacteria Yersinia pestis can enter the human body in many different ways, each path causing disease causes a different disease:
Blood: Yersinia pestis bacillus through the bite of a bug Fleas and lice in humans enter the body. Respiratory tract: Yersinia pestis bacilli follow small saliva droplets shot from the respiratory tract of patients to the respiratory tract of healthy people and cause pneumonic plague. Skin, mucous membranes: Due to direct contact with bacteria-infected objects through the oropharyngeal mucosa, eye conjunctiva or damaged skin areas. Gastrointestinal tract: Contamination of food such as eating sick rats, contaminated water sources
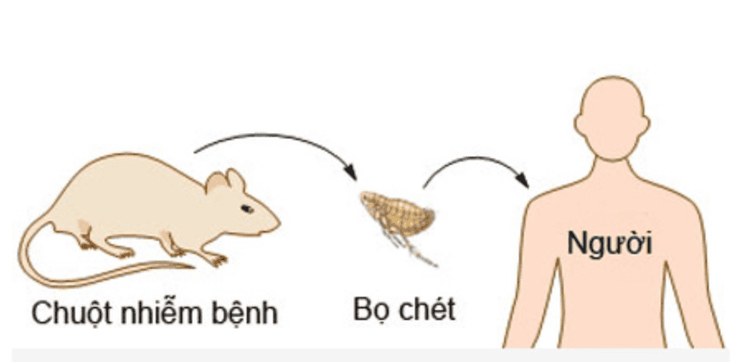
Đường lây bệnh dịch hạch
3. What are the manifestations of the plague?
Plague includes disease forms: bubonic form, bacteremic form, pulmonary form and meningococcal form. In which, the ganglion type is the most common form, up to 90% of cases. After coming into contact with an infectious source, the bacteria enter the body and have an incubation period of 3-7 days. Then appear different symptoms corresponding to each type of disease.
Lymphadenopathy: After the incubation period, flu-like symptoms appear including sudden high fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea. Then there are signs of infection, intoxication and swollen lymph nodes; The lymph node is swollen to the size of a finger or more, very painful, at first it is hard, then it becomes soft and pus. If left untreated, bacteria that thrive in the lymph nodes can enter the bloodstream and cause sepsis, and if it enters the lungs, pneumonic plague. Septic form: The route of entry can be directly into the bloodstream with signs of sepsis even when there are no signs of lymph node swelling or from the lymphatic system if it is not treated. Manifestations of sudden high fever over 40 degrees Celsius, accompanied by chills, low blood pressure, fast, small, struggling pulse, mental confusion, coma, is a very dangerous form, the mortality rate is very high. , usually the patient dies within 3 - 5 days. Pulmonary form: This is a dangerous disease with a high mortality rate due to complications of acute pulmonary edema, caused by direct infection from respiratory secretions of the patient and can be spread into epidemics by respiratory transmission. or in the advanced stage of the ganglion. Symptoms: High fever, over 40 degrees, chills with fatigue, headache, rapid pulse, decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, rapid shallow breathing. Coughing a lot, with sputum and blood, in the patient's sputum contains many bacteria, which is a source of dangerous disease.

Bệnh nhân dịch hạch sốt cao trên 40 độ C
Meningitis: Occurs when bacteria cross the blood-brain barrier to cause disease, after the appearance of the manifestations of bubonic plague, the patient has symptoms such as headache, vomiting, diarrhea. or constipation. Plague has acute manifestations, very dangerous because if not detected and treated promptly, there is a very high risk of death.
4. How to prevent disease?
Methods to prevent plague are promoted due to the dangerous nature of the disease and the ability to spread into a large outbreak. Measures to prevent plague include:
Food safety, food and water must be covered securely and cooked before eating. Regularly clean the environment, ensure cleanliness to avoid mice burrowing and nesting. Implement measures to kill the intermediate host, including: Killing rats, fleas, destroying the breeding grounds of rats. Especially in areas where plague is endemic. Do not kill rats and fleas during outbreaks in rats and in humans. When detecting a patient with plague: Be sure to avoid contact with respiratory secretions from the patient through inhalation or through skin wounds. Vaccines against bubonic plague are widely used, but there is no proven evidence to prevent the disease, so it is only used for high-risk people such as going into epidemic areas or coming into direct contact with the source of the disease.
Vắc-xin phòng bệnh dịch hạch
Plague, if left untreated, can cause death quickly, so early diagnosis and treatment is essential to reduce the risk of death and complications from the disease. Therefore, immediately after coming into contact with the source of the disease, if any suspicious signs appear, it is necessary to go to a medical facility for examination and treatment immediately.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.