This is an automatically translated article.
Plague is a highly contagious, acutely progressive, highly contagious disease with a high mortality rate. What should be done to prevent plague?
1. What is the plague?
Plague is a disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, which causes inflammation of the lymph nodes (inguinal lymph nodes, axillary lymph nodes are common). Diseases with the ability to spread quickly can develop into epidemics and pandemics. The disease is transmitted from rodents to humans through infected fleas or by direct skin-to-skin contact with infected animals, or from person to person through inhalation through coughing. Plague has three main clinical forms: ganglion, bacteremia, and pulmonary disease. In which, the mortality rate in pulmonary form and sepsis form is high.
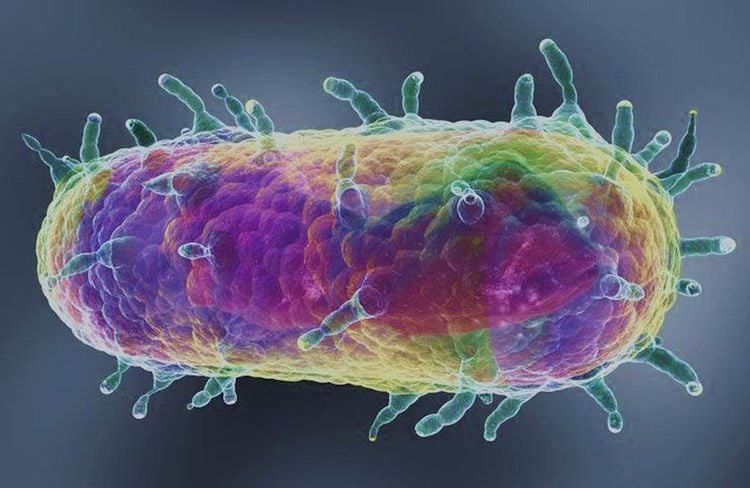
Trực khuẩn Yersinia pestis gây bệnh dịch hạch
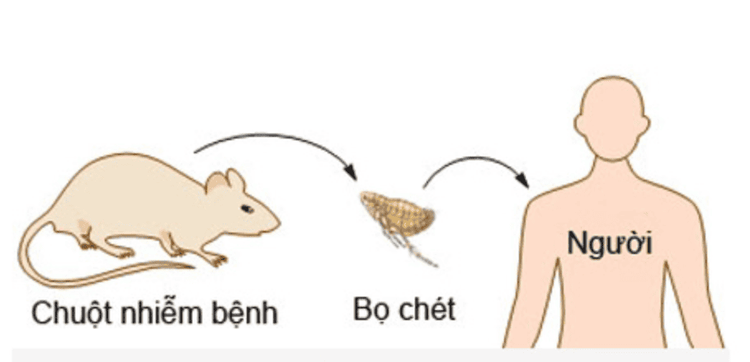
2. How is the plague transmitted?
Fleas are an intermediate host that sucks the blood of a mouse carrying the disease and spreads it to other mice by biting a mouse, the bacteria will follow the bite into the body and spread the disease. Direct person-to-person spread by inhalation of airborne bubonic plague bacteria in contact with a patient with pneumonic plague. Transmitted through the skin. Plague bacteria enter directly through healthy or broken skin, such as by direct hand contact with an infected pet or a cat bite or scratch.
3. Clinical symptoms of plague
Patients with epidemiological characteristics are important signs that need to be carefully explored. Epidemiology of patients living in endemic areas, having close contact with people with pneumonic plague or coming into contact with bodily fluids of plague patients. Incubation: 2 days - 6 days without clinical symptoms. The onset phase is sudden, with fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches, abdominal pain, nausea, and headache. Full-blown stage with symptoms: infection, toxicity and swollen lymph nodes. Characteristics of lymphadenitis in plague + Location: near the flea bite site, common in the groin, armpit...
+ Features: swollen lymph nodes, hot, red, very painful, maybe 1 lymph node or a group of swollen lymph nodes. The skin around the area is congested, edematous. When lymph nodes pus, rupture, exudate, blood, necrotic substances, create fistulas and then form scars. Then the inflammatory lymph node becomes a solid lump.
Bọ chét là trung tâm lây truyền bệnh dịch hạch
If the patient is not treated early, the lymph nodes may suddenly progress to a fulminant infection with a high fever of 40-41 degrees Celsius, then shock symptoms such as decreased blood pressure, rapid and small pulse, and disease. The patient is in a coma, comatose, usually dies within 3 - 5 days. Pneumonic plague has late symptoms such as cough with thin sputum, bloody foam, pleural effusion, and has a high mortality rate. This form is very dangerous due to its great ability to spread. Tests to confirm the diagnosis are as follows: Culture specimens (blood, sputum, plague, cerebrospinal fluid) are positive for Y. Pestis. PCR was positive for plague bacilli. Serological diagnosis: Find the F1 antigen by immunofluorescence or antibody titres by doing ELISA twice.
4. Treatment of the plague
Treatment principles
All confirmed patients must be hospitalized for treatment and isolation Use specific antibiotics Treat symptoms, improve resistance Specific treatment
Antibiotic treatment specificity in 7-10 days. Lymphadenopathy requires only 1 antibiotic. Sepsis or pulmonary type: need to combine 2 antibiotics. Symptomatic treatment with antipyretic, analgesic, fluid resuscitation,...

Bệnh nhân mắc dịch hạch được điều trị bằng kháng sinh theo đơn của bác sĩ
5. Recommendations for plague prevention from the Ministry of Health
When detecting people who are suspected of being infected with plague such as fever, bubonic plague, living in endemic areas, they need to be taken to medical facilities and isolated in time. It is necessary to treat the clothes and utensils of the infected person according to the principle of disinfection. Use the right personal protective equipment to limit disease transmission when in contact with sick people. Strengthen inspection and surveillance of plague on wild animals, focus on monitoring intermediate hosts (rats, fleas) in at-risk areas. Implement good environmental sanitation, ensure that food eaten and drunk is covered and covered securely to prevent mice and fleas from coming into contact. Environmental sanitation. Increase the killing of fleas and rats with a mouse trap or a cat. Prevention of infection at treatment facilities by strictly implementing isolation and treatment of patients, infection control measures, and protection for medical staff and caregivers according to the guidance of the Ministry of Health. economic. Take prophylactic antibiotics in high-risk cases. Vaccines are prescribed for people entering endemic areas and for animal care staff To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System on nationwide, or register online HERE.