This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Xuan Thiep - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.The most common pathology of the arteries supplying blood to the kidneys is renal artery stenosis. This belongs to the group of peripheral artery disease, with the common cause being atherosclerosis, but the incidence is lower than that of the arteries at other sites. However, because of the equally serious consequences that can be caused, renal artery dilation and stenting is a commonly performed intervention to correct this condition.
1. What is renal artery stenosis?
Renal artery stenosis is a narrowing of one or more of the renal arteries (main and accessory renal arteries) reducing blood flow to the kidneys, leading to increased blood pressure, irreversible damage to kidney cells – kidney failure.Renal artery stenosis may not cause any signs or symptoms until it is very advanced. However, renal artery stenosis can also be discovered incidentally during a routine physical exam, or your doctor may suspect the problem if you have unusually high blood pressure, such as sudden or worsening blood pressure. of unknown cause, early-onset hypertension before age 30 or after age 50. As renal artery stenosis progresses, other signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure that is difficult to treat, renal murmur, fluid overload, heart failure...
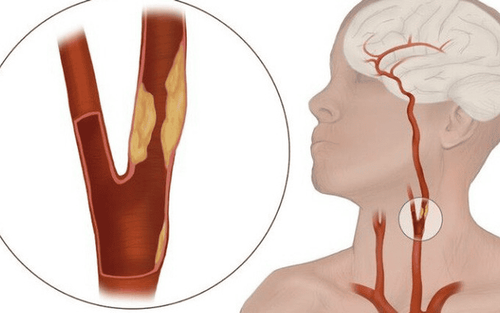
Two major causes of narrowing of the arteries kidney is atherosclerosis and muscular dysplasia. In addition, the renal artery can also be narrowed due to other less common conditions such as vasculitis, neurofibromatosis, or an intra-abdominal mass pressing on the renal artery. Regardless of the cause, when renal artery stenosis has reached a level that causes symptoms, in addition to medical treatment and risk factors control, renal artery revascularization is essential.
Current revascularization interventions to treat renal artery stenosis are renal artery stent dilation and renal artery bypass surgery.

Xơ vữa động mạch thận gây hẹp động mạch thận
2. What is a digital background eraser and angioplasty, renal artery stenting?
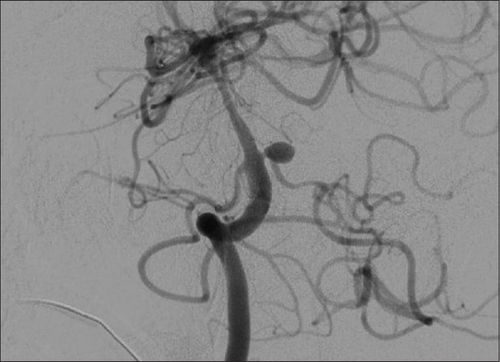
Digital angiography and angioplasty, renal artery stenting is also an endovascular intervention similar to the cases of coronary artery stenosis in the heart or intracranial stenosis.Thanks to the technique of fluoroscopy under the screen and the use of a sufficient amount of contrast medium, the renal artery system will be clearly visible and the location of the narrowing will be determined. From there, the doctor will approach the instrument, inflate the balloon and press the plaque against the vessel wall. As a result, the lumen of the vessel increases, and blood flow to the arteries improves. To maintain this result, a metal support (stent) will be saved. However, because it is a foreign material, there is a risk of embolism, after the intervention of placing the rack, the patient needs to take long-term antiplatelet drugs to stabilize the function of this device.
In summary, the clinical indications for digitized angiography and angioplasty, renal artery stenting are currently applied in cases where there is evidence of renal artery stenosis of more than 50% of all causes and symptoms. clinical symptoms such as hypertension, renal failure. At the same time, the patient does not have contraindications such as allergy to iodine contrast agents, severe renal failure, blood clotting disorders or pregnant women to avoid the risk of radiation exposure to the fetus. However, the above contraindications are relative, especially when renal function is severely impaired, severe hypertension is difficult to control and is responsible for renal artery stenosis.
Bệnh nhân rối loạn đông máu chống chỉ định thực hiện
3. Process of digital imaging to remove background and dilation, install renal artery support
Because it is a delicate technique, patients and their loved ones need to be thoroughly explained about the procedure to be prepared, as well as the risks involved, in order to ask for cooperation. Next, the patient needs to fast, change into appropriate clothes and arrange to lie on his back on the intervention table, place an intravenous line with 0.9% physiological saline solution.Means of monitoring breathing, pulse, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, SpO2 are mounted on the patient and the indicators are displayed on the screen for easy observation. After cleaning the inguinal and genital areas, the doctor will cover the area with a sterile tissue to prepare for the intervention. In case the patient is overstimulated and poorly cooperated, it is necessary to consider appointing a sedative to facilitate the process.
At the intervention site, the doctor will administer local anesthesia on the right femoral artery. When the anesthetic takes effect, the doctor will insert a needle and insert the catheter into the artery. Under the background digitization and contrast screen, the doctor adjusted and guided the catheter to the location of the bifurcation from the abdominal aorta of the renal artery on the side of the injury to the intracranial arterial circulation. Cobra catheters are used to look for narrow passages that are indicated for intervention.
When accessing the location and determining the necessary features of the narrowed renal artery on the DSA, the doctor will proceed to place a catheter into the base of the damaged renal artery. Next, the microcatheter and microwire will be threaded through the narrowing, to the interlobar arteries. Next, the balloon is slowly inflated, and the lumen is widened. Then, when the ball is deflated, a metal support frame will be raised over the narrow spot, unfolding the corresponding bracket to the narrow position.
Finally, the doctor will determine whether the result is satisfactory or not based on the DSA image, the position of the bracket at the narrowed renal artery, the frame is completely open and the lumen is well re-opened. . If the plaque thickness is large, an incomplete narrowing of the lumen may be allowed with the degree of stenosis not exceeding 30%. In addition, the position of the lumen support has the distal end located at least 1cm below the occlusion site, the proximal end convex into the aortic lumen but not more than 3mm. At the same time, the doctor will also check the pulse before, during and after the recirculation is normal, there are no signs of thrombosis or dissection of the vessel wall. The same study was performed on selective angiography of the visceral body, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric angiograms with a Cobra catheter (YASHIRO, liver, RH...)
When all of the above requirements are met, Interventional instruments will be withdrawn. The puncture artery site will be manually compressed for 15 minutes, fixed for 24 hours, or used with angioplasty and compression bandages within 6 hours. During this time, the patient is limited to bed movement.

Trong trường hợp bệnh nhân bị kích động thì cần sử dụng thuốc an thần
4. Complications may be encountered in digitized scanning and dilatation, renal artery stenting
As with any intracranial procedure, digital angiography and stenting for renal artery stenosis may also carry certain risks, including:Arterial perforation Fracture displacement scaffolding Mucosal injury causing arterial dissection Abdominal bleeding Thromboembolism causing renal, mesenteric infarction Complications with anesthesia or contrast media Risk of radiation exposure during DSA .
Bệnh nhân có thể bị nhiễm phóng xạ khi chụp DSA
In summary, when severe renal artery stenosis is symptomatic, revascularization is important, both to control hemodynamics and to preserve renal function. In which, digital scan to erase the background and dilation, placing renal artery bracket is the preferred method to choose compared to bypass surgery, with minimal intervention but still ensuring treatment efficiency.
Dr. Le Xuan Thiep has strengths in performing advanced and difficult magnetic resonance and computed tomography techniques such as: coronary computed tomography, cardiac function, cerebral magnetic resonance, perfusion brain and organs,..
If you notice any unusual health problems, you should visit and consult a specialist
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.