This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Esophageal stricture is a condition in which a section of the esophagus is damaged, causing narrowing of the lumen, leading to obstruction of circulation and transport of food to the stomach. Depending on the cause and severity, the treatment of esophageal stricture will be different, including digital imaging techniques to erase the background.
1. Overview
Esophageal stricture has many causes and is divided into several types such as benign or malignant, intraesophageal or extraesophageal stricture. Specifically:Benign esophageal stenosis due to the formation of scar tissue in the esophagus; Gastroesophageal reflux disease recurs many times, causing irreversible damage to the esophagus and gradually forming scar tissue; Congenital esophageal stricture in the 4th week of pregnancy, possibly genetic; Malignant esophageal stricture due to cancer or malignancy that compresses and narrows the lumen of the esophagus; Esophageal stricture can also be a complication of: Radiation therapy to the chest or neck, esophageal burns, long-term gastric tube retention causing esophageal ulceration, endoscopic trauma, after treatment of esophageal varices, or due to esophageal stricture. Cardiac spasm, ... Currently, the technique of using flexible endoscopic tubes to re-establish esophageal circulation is widely used in the treatment of esophageal strictures. However, it is still a deeply invasive technique, especially in cases where the patient is exhausted or uncooperative, or under general anesthesia. There are even a few cases where the bronchoscope does not pass through the narrow site, so it cannot be performed successfully.
Treatment of re-circulation for the gastrointestinal tract with electroluminescence has been applied in many countries around the world. By definition, the digital background angiography (DSA) system is a diagnostic method that combines X-ray and digital image processing to take angiograms of the body. The outstanding advantages of this method under the guidance of digitizing background removal are:
Minimal intrusiveness; No need for general anesthesia; The necessary tools are very small in size, so it is easy to succeed when going through a narrow place; Few complications; Good support for those who are no longer indicated for surgery or have had surgery.
2. When is it necessary to take digitized photos to remove the background?
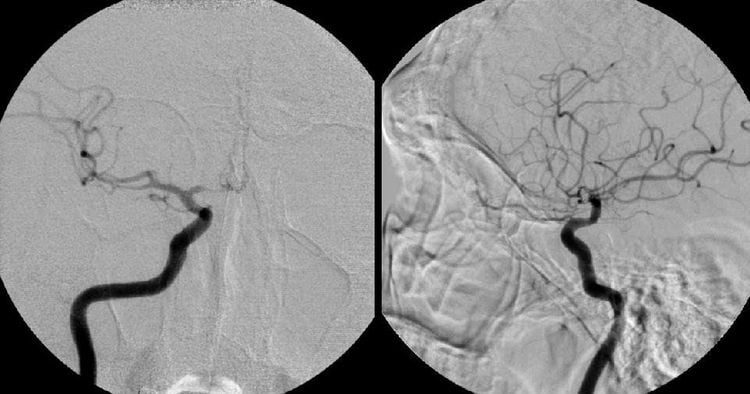
Hình ảnh chụp số hóa xóa nền
3. Prepare
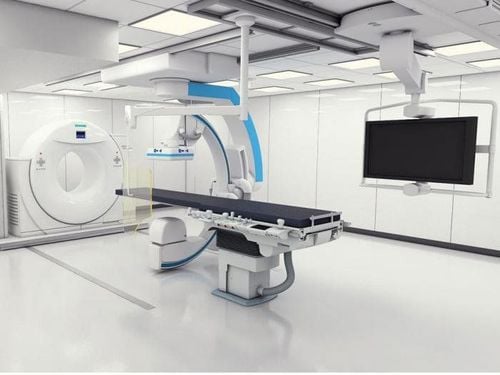
Máy chụp số hóa xóa nền
3.4. General medical supplies
Vật tư y tế thông thường như các bơm tiêm loại 5-10-20ml
Inpatient medical records; Indication sheet for performing the procedure; X-ray film, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (if available).
4. Steps to take
4.1. Evaluation of the site of the stricture Insert the catheter and guide through the mouth - esophagus into the stomach to reach the narrowing site; Withdraw the lead wire; Inject a water-soluble contrast agent to assess the location and extent of the stenosis. 4.2. Narrow approach Approach Continue to guide wire through the narrow site under the guidance of the enhanced X-ray screen; Insert the tube through the narrow position under the guide wire guide; Inject contrast agent through the catheter to determine the extent, location, and length of the stricture. 4.3. Dilatation and stenting at the site of stricture Insertion of rigid wire into the tube through the site of esophageal stricture; Use a narrow position balloon through a rigid conductor; Place and release the stent holder through the rigid lead. 4.4. End of procedure Use contrast agent to check the esophageal circulation down to the stomach; Withdraw all leads and catheters.5. Complications and treatment
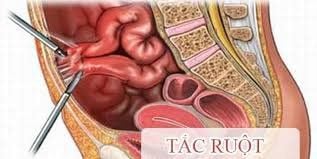
Tắc ruột là một trong số các biến chứng hiếm gặp
Stent slip: Due to the selection of the size of the bracket is not suitable for the degree of narrowing; Intestinal obstruction: Due to the rack sliding downstream or fibrous or undercooked food caught in the stent; Esophageal perforation; Gastrointestinal bleeding: Need to monitor and treat medically. If the bleeding does not stop on its own, endoscopic intervention can be used. In summary, this technique of digital erasure of the background (DSA) will intervene treatment from within the blood vessel, with the advantage of minimally invasive without the need for open surgery. One of the common applications of this method is to guide dilation and stenting of the esophagus, helping to treat esophageal strictures without drugs.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the general hospitals that guarantees the quality of medical examination and treatment expertise, and is famous for its comprehensive medical examination and consulting services, including specialties. Digest. With a team of highly qualified doctors and nurses with many years of experience in the profession, they will provide the best treatment plan as well as advice on the best health for the patient.
Before taking a job at Vinmec Central Park International Hospital from December 2017, Doctor Dang Manh Cuong has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging in Transport Hospitals. Hai Phong, MRI Department of Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital and Diagnostic Imaging Department of Becamex International Hospital.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.