This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thuc Vy - Radiographer - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Renal angiography, also known as renal angiography, uses X-rays to image the blood vessels of the kidney when contrast material is injected into the blood vessels of the kidney. This technique is used to detect signs of a blockage or narrowing of a renal artery or abnormality affecting the kidneys' ability to supply blood. So, specifically, which diseases of the kidney?
1. Why do patients need renal angiography?
After a physical examination, if the doctor suspects that the patient has a problem in the blood vessels of the kidneys, the doctor will order the patient to perform a renal angiogram (English name is renal angiogram), especially the kidney angiogram. complicated diseases such as:
Renal artery aneurysm
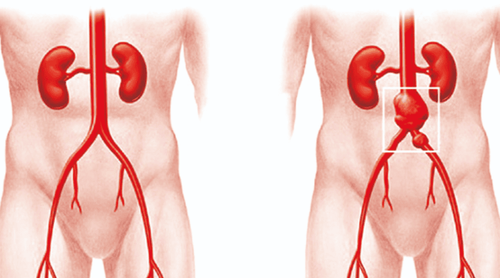
Renal artery stenosis
Renal artery occlusion
Renal artery spasm
Arteriovenous malformation
Blood clot (blood) block )
Kidney tumor
● Kidney cyst
● Bleeding
● Complications due to kidney transplant.
Also, in cases where a CT or MRI scan does not provide enough information to help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis, the patient may also need to use renal angiography.
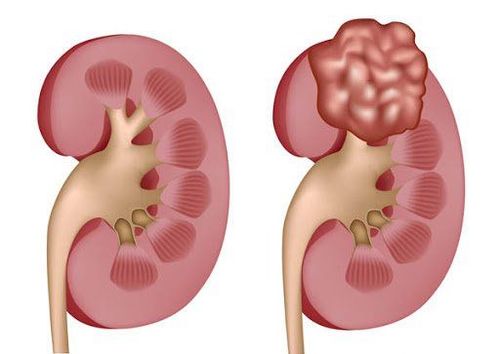
Bệnh nhân có khối u ở thận cần được chỉ định chụp động mạch thận
2. Risks of renal angiography
Before having a renal angiogram, the patient should ask the doctor about the amount of radiation used during the scan and the possible risks. The patient needs to tell the doctor about the history of previous X-rays and any problems such as:
● Are pregnant or the patient thinks she is pregnant. Because radiation exposure during pregnancy can lead to birth defects in the unborn baby
● Are allergic or sensitive to any ingredient of the drug, contrast agent or iodine. Because the contrast agents used in renal angiography have a risk of allergic reactions
● Have kidney failure or other kidney problems. In some cases, contrast agents can cause kidney failure, especially when the patient is taking certain medications for diabetes.
Possible complications of renal angiography include:
Bleeding
Nerve damage
Blood clots
Hematoma
● Infection
● Temporary kidney failure (Temporary) kidney failure)
Damage to an artery or artery wall, which can lead to the formation of a blood clot.
In addition, the patient may face other risks depending on the specific health status of each patient. Therefore, patients should be consulted by their doctor before performing renal angiography.
Some other conditions can make a renal angiogram less accurate such as:
● Contrast is still in the patient's body from a recent imaging scan
● There is gas or stool in the intestines.

Trước khi chụp động mạch thận, người bệnh được bác sĩ tư vấn về một số nguy cơ khi chụp động mạch thận
3. Patients need to prepare before renal angiography?
In general, the doctor will ask the person not to eat or drink anything for about eight hours before the renal angiogram.
Patients need to tell their doctor about all medications they are taking, including herbal preparations and over-the-counter medicines. Even some seemingly innocuous drugs can affect the procedure or your body's response to contrast, like aspirin, which can affect your blood's ability to clot. Your doctor may ask you to temporarily stop some or all of your medications before having a renal angiogram.
In addition, the patient should also tell the doctor if he or she is allergic to:
● Any other medicine
● Latex
● Iodine
Anesthesia
● Contrast .
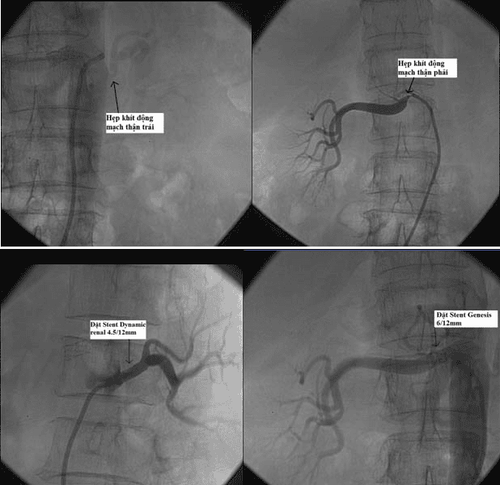
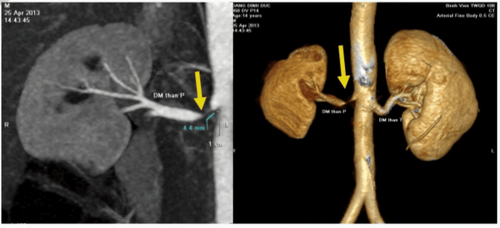
Kết quả chụp cho thấy một số bất thường tại động mạch thận
4. How is renal angiography performed?
Before the renal angiogram, the patient will need to sign a consent form and change into a hospital gown, remove all jewelry.
In most cases, the patient will be sedated before the procedure. This sedative will help the patient relax, but will not put the patient to sleep.
Then, the doctor will then insert a long catheter (catheter) into the patient's artery and inject contrast material through the tube into the body.
Before injecting contrast, the doctor must put the catheter in the correct position. The doctor will insert the catheter into the artery and direct the catheter to the aorta near the renal artery. When the catheter is in the correct position, contrast is injected into the patient's body. Your doctor will take many X-rays as the dye travels through your blood vessels. The dye works to make vessels appear on an X-ray clearer to detect medical problems.
In some cases, the doctor may administer treatment while performing the renal angiogram. For example, if a blood clot or tumor is found, the doctor may inject medication on the spot to treat it.
After the doctor finishes the renal angiogram, the catheter will be removed from the patient's body.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.