Eczema on the penis is a type of skin inflammation. Patients with scrotal eczema exhibit symptoms such as thickened skin in the scrotal area, peeling, itching, and significant discomfort. Scrotal eczema is not a sexually transmitted disease and can be treated. However, if left untreated, the condition can negatively affect the patient's health and quality of life.
1. Overview of Scrotal Eczema
Eczema is a group of inflammatory skin conditions. Nearly 32 million Americans are affected by at least one type of eczema. Eczema causes the skin to become red, itchy, flaky, and cracked. It can appear almost anywhere on the body, including the penis and areas of skin near the genital organs.
Types of eczema that can occur on the penis include:
- Allergic contact dermatitis: This type of eczema appears suddenly as a rash or itchy skin. It can occur in infants without a clear cause.
- Irritant contact dermatitis: This condition is caused by exposure to allergens or chemicals. Irritants can include condoms, underwear, or sports equipment that irritate the penis.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: This type of eczema occurs in areas where the skin produces a lot of sebum. It typically appears on the scalp but can also affect the penis.
2. Symptoms of Genital Eczema
Common symptoms of any type of eczema include:
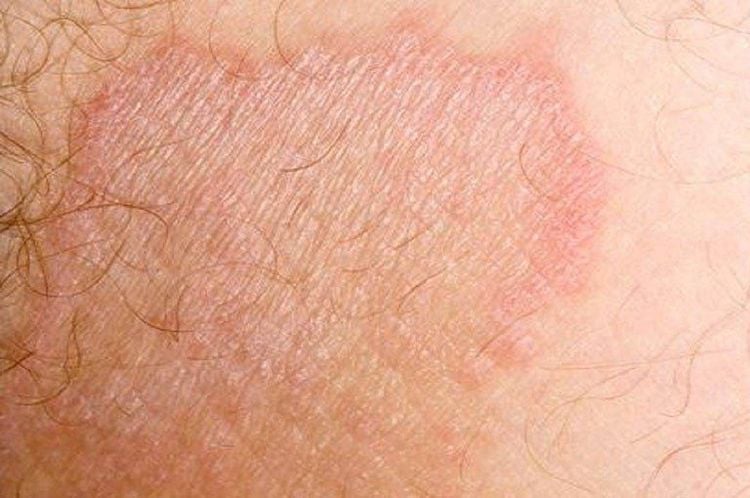
- Rash or redness on the scrotum, raised skin
- Itching or tenderness around the rash
- Dry skin
- Red, brown, or gray patches
- Small blisters that may burst and release fluid
- Thickened or scaly skin
Some symptoms may also occur with sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as genital warts, genital herpes, or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Early STI symptoms may include:
- Unusual discharge from the penis
- Bleeding
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Fever and chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
Eczema only affects the skin and does not cause any other symptoms related to reproduction. If the only symptoms are skin rashes, dry skin, or blisters and no sexual activity has occurred, it is likely a flare-up of eczema. If these symptoms appear after the penis comes into contact with specific substances, you may have irritant contact dermatitis. You should consult a doctor if you notice these symptoms after sexual intercourse or even if you have not had sexual activity, to determine the exact cause.
Test: Is Your Penis Normal?
The health of the penis is a concern for many men. Do you know if your penis is in normal condition? Let’s find out through the following quick tests.
Source: webmd.com
Trắc nghiệm: Dương vật của bạn có bình thường không?
Sức khỏe “cậu nhỏ” là điều được nhiều nam giới chú ý và quan tâm. Liệu bạn đã biết được tình trạng dương vật của mình có đang ở mức bình thường hay không? Hãy cùng tìm hiểu thông qua các câu trắc nghiệm nhanh sau đây nhé.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
3. Causes of Penile Eczema
Penile eczema is caused by genetic and environmental factors. Many people develop eczema because of a gene mutation that produces filaggrin. This protein is responsible for creating a protective barrier for the top layer of skin. If the body does not produce enough filaggrin, the skin will lack moisture, allowing bacteria to enter. Other factors may also trigger eczema development. These triggers include latex, which causes the immune system to create an excessive inflammatory response, leading to eczema flare-ups. Other possible triggers include:
- Chemicals in soap or shampoo

- Fabric materials in clothing, such as polyester or wool
- Antibacterial agents in ointments or wet wipes
- Tobacco smoke
- Metals
- Formaldehyde
4. Is Scrotal Eczema Contagious?
Scrotal eczema is not a contagious disease. It cannot be transmitted through sexual intercourse or contact with the affected area of the penis. However, eczema can cause discomfort during sexual activity. Scratching can lead to open wounds, sores, and blisters, which may become infected.
Penile infections can spread through sexual contact if unprotected. You should use condoms or avoid sexual activity until treatment with antibiotics is completed.
5. Managing Scrotal Eczema at Home
If the symptoms of eczema are mild, you can reduce pain with simple home remedies or over-the-counter (OTC) treatments, including:
- Cold compress: Wet a cloth or towel with cold water. Fold or wrap the towel around the affected area of the penis. Apply as needed for about 20 minutes each time. You can also use an ice pack or a frozen item wrapped in a cloth for the cold compress.
- Oatmeal bath: Add about 1 cup of oatmeal to a warm bath to help reduce itching. You can also apply the oatmeal to the affected area and bandage it.
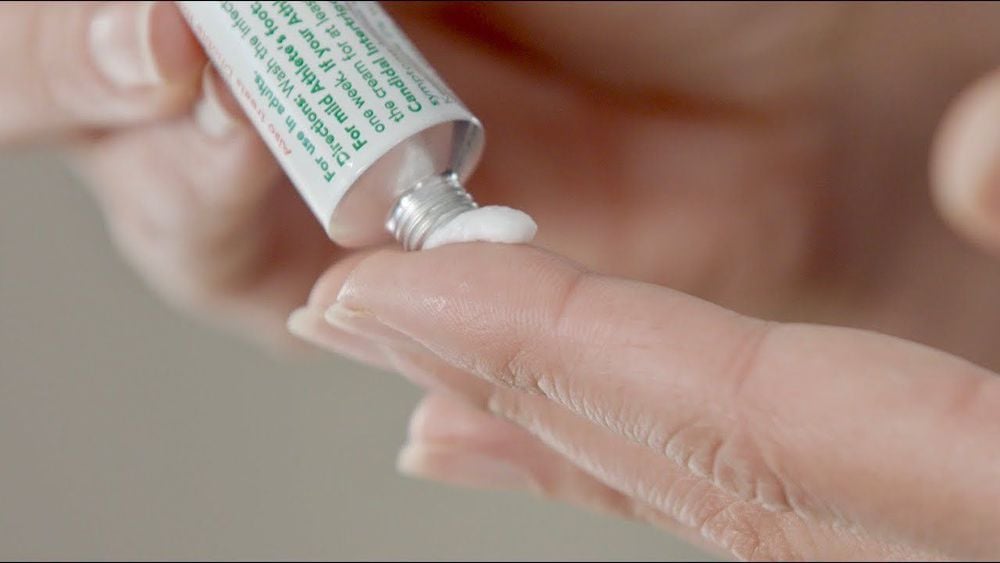
- Itching cream: Apply an OTC cream with at least 1% hydrocortisone to reduce itching. You can also apply the cream to a bandage and wrap it around the itchy area. Do not use hydrocortisone cream for more than seven days unless directed by a doctor.
- OTC antihistamines: Take a mild antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec). These medications are for allergic dermatitis. These medications can cause drowsiness, so do not take them if you need to drive or focus
6. When to Seek for medical attention
Seek medical attention immediately if you notice eczema symptoms combined with the following signs:
- Discharge or pus from the penis
- Fever of 101 °F (38.3 °C) or higher
- Difficulty urinating
- Painful urination
- Lower abdominal pain
- Pain or swelling in the testicles
You should also schedule a doctor's appointment if the symptoms do not improve within a week. The doctor can assess the symptoms and advise the next steps for treatment.
7. Clinical Treatment Options
If you were diagnosed with eczema, the doctor may prescribe one or more of the following medications to help treat eczema flare-ups:
- Calcineurin inhibitors: These medications modify the body's immune response. Common prescriptions include pimecrolimus (Elidel) and tacrolimus (Protopic).
- Anti-inflammatory treatment: Oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone (Deltasone), may be prescribed to help treat inflammation.
- Antibiotics: If the area is painful and infected, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics for about two weeks, such as flucloxacillin (Floxapen) or erythromycin (Ery-Tab).
- Injection treatments: If your skin does not respond to other treatments, the doctor may recommend dupilumab (Dapoxetine). This injectable medication is typically used for severe eczema. It is expensive and is still being tested for long-term use.
- Phototherapy: In severe cases, the doctor may recommend exposing the skin to ultraviolet light to help reduce eczema symptoms.
8. Complications of Genital Eczema
Scratching itchy areas can lead to open wounds or sores, which can increase the risk of infection. One of the infections that may occur is herpes simplex. Other complications of eczema may include:
- Thickened, scaly skin due to continuous scratching
- Chronic asthma
- Fever
9. Preventing Eczema Flare-Ups
Eczema flare-ups typically last for several days before they improve. The flare-up stage can be predictable, and some flare-ups can cause significant discomfort. You can reduce the risk of flare-ups by doing the following:
- Identify triggers: Talk to your doctor about checking for allergens. If you know you're allergic to pollen, mold, chemicals, or other materials, try to avoid them as much as possible.
- Avoid tight-fitting underwear: Wear loose, comfortable underwear and pants to reduce skin irritation. Dress in breathable clothes in the genital area to prevent excessive sweating, which can also irritate the penis.
- Use natural moisturizers or ointments: Apply moisturizer to the penis twice daily to keep the skin hydrated and prevent cracking.
- Avoid harsh soaps or hot water: Take regular baths in warm water, as hot water can dry out the skin. Avoid soaps with fragrances and chemicals, as they can dry out the skin.
- Keep indoor humidity balanced: Use a humidifier to keep the air moist and prevent dry skin.
Scrotal eczema is a form of dermatitis, though not particularly dangerous, it significantly affects the quality of life of the patient. As soon as symptoms appear, it is advisable to visit a reputable healthcare facility for early treatment. Dermatitis is quite common among all ages and genders, and many types of dermatitis can be contagious. Therefore, you should consult a doctor if unusual symptoms appear on your skin.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is an eczema treatment and consultation package to help patients assess their overall condition and provide advice on how to prevent relapse.
When you register for the eczema consultation and treatment package, patients will receive: Dermatology consultation and tests such as IgE quantification, fungal smear, specific IgE quantification for respiratory and food allergens (Panel 1 Vietnam), and Rida Allergy Screen test (panel 1), among others.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com