This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Post-polypectomy electrocautery syndrome is characterized by peritonitis in the absence of perforation occurring after electrocautery polypectomy. An appropriate diagnosis and treatment should be sought to avoid exploratory laparotomy or unnecessary hospitalization.
1.Overview of electrocautery syndrome after polypectomy
Post-polypectomy syndrome (also known as post-polypectomy syndrome or transmural burn syndrome) is characterized by inflammation of the peritoneum in the absence of perforation occurring after electrocautery polypectomy. . This is a rare complication of polypectomy and occurs when the electric current applied during polypectomy enters the muscularis and serosa, resulting in transmural burns at the polypectomy site. Patients often present with abdominal pain and tenderness a few hours to a few days after the procedure but may also have fever, tachycardia, and leukocytosis; Their presentation often mimics colon perforation. Diagnosis and treatment are needed to avoid exploratory laparotomy or unnecessary hospitalization.

2.A clinical case
A 56-year-old man underwent colonoscopy for primary colorectal cancer screening, which revealed an 8mm transverse colon polyp resected with an electric noose and a 6mm transverse colon polyp removed with a noose. cold. The evening after the procedure, he went to the emergency department and spoke of the acute onset of severe, diffuse abdominal pain that began about six hours after the colonoscopy. He presented with diarrhea with no blood in his stools immediately after the endoscopy but had no symptoms of nausea or vomiting. The man was found to be unhealthy and had normal vital signs. Physical examination is notable for moderate right lower abdominal pain without peritoneal signs or abdominal cramping. Tests were significant for leukocytosis 18.0 × 10 9/L with 87% granulocytosis; Liver function tests were within normal limits. Abdominal radiograph results were normal. Abdominal CT with intravenous and oral contrast showed a long segment of circumferential wall thickening extending from the midcolon up to the splenic flexure. The general surgeon and the gastroenterologist were consulted while the patient was in the emergency department. He was diagnosed with electrocautery syndrome after polypectomy and was treated conservatively without antibiotics. His stomach ache was gone for 4 days after that.
3. Causes of electrocautery syndrome after polypectomy
Post-polypectomy electrocautery syndrome is a rare complication of polypectomy occurring in 0.14% to 2% of polypectomy patients. A large retrospective study identified this syndrome as a complication occurring in only 6 of 16,318 endoscopy cases. The syndrome occurs when the electric current applied during polypectomy extends into the muscularis and serosa, resulting in transmural burns at the polypectomy site. Patients typically present with abdominal pain and tenderness within 12 hours of polypectomy, although presentation as late as five days after the procedure has also been reported. These patients may also have fever, tachycardia, and leukocytosis often resembling colonic perforation, a rarer but more serious complication occurring in 0.07% to 0.3% of surgical resection patients. polyp.
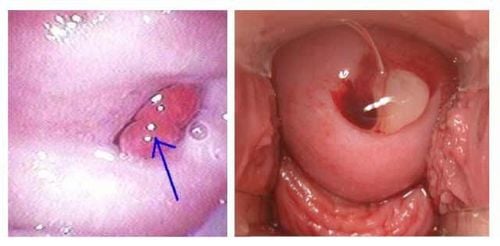
4. Diagnostic methods for electrocautery syndrome after polypectomy
Abdominal radiograph and baseline blood count including complete blood cell count are part of routine evaluation in patients presenting with abdominal pain after laparoscopy. Patients who have undergone electromechanical polypectomy and have evaluation-relevant findings such as fever, leukocytosis, or peritoneal signs but no evidence of perforation on radiographs should be evaluated by radiographic examination. Additional imaging such as contrast-enhanced CT. In patients with intestinal wall thickening consistent with electrocoagulation syndrome after polypectomy, treatment includes supportive care including monitoring, analgesia, IV fluids, bowel rest, and possibly antiretroviral therapy. born . The decision to treat with antibiotics is based on the patient's overall clinical presentation.
Post-polypectomy syndrome may present with symptoms similar to those of colonoscopy perforation. Post-polypectomy syndrome should be considered in patients with abdominal pain, fever, leukocytosis, and/or signs of peritonitis following electrocautery polypectomy. Differentiation from colonic perforation should be assessed by radiographic assessment, preferably by abdominal CT. This syndrome should be treated conservatively with intravenous fluids, avoidance of oral fluids, bed rest, and possibly antibiotics. Moderate cases, such as this one, can be managed without hospitalization.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.