This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, monoclonal antibody drugs are a commonly used immunotherapy in cancer treatment. These drugs may be used in combination with other cancer treatments, such as hormone therapy or chemotherapy. Before deciding to use a monoclonal antibody drug to treat cancer, you need to carefully consider the benefits and potential side effects that the drug may bring.1. How does the body's immune system fight cancer?
The human immune system is a complex network of proteins, special cells, tissues and organs that detects and destroys pathogens, such as viruses. or bacteria. In addition, the immune system helps eliminate damaged or abnormal cells, which include cancer-causing cells.
One of the important elements of the immune system are antibodies. An antibody will bind itself to the specific molecule (antigen) on the surface of a problem cell. They then act as a "flag" to attract disease-fighting molecules or play a role in triggering and promoting cell destruction by other processes in the immune system.
However, cancer cells are extremely sophisticated, able to bypass the immune system undetected or even suppress the functioning of the immune system in the body.
2. What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are molecules produced in vitro that act as surrogate antibodies that can restore, enhance, or mimic the immune system's attack on cancer cells. . Monoclonal antibodies designed to bind to antigens are often more abundant on the surface of cancer cells than on healthy cells.
Currently, monoclonal antibodies are commonly used in the treatment of tumors and inflammatory disorders. The types of monoclonal antibodies currently being applied in clinical practice include:
Murine monoclonal antibodies. Mosaic monoclonal antibody. Human monoclonal antibody. Completely human monoclonal antibody.
Các loại thuốc kháng thể đơn dòng điều trị ung thư hoạt động theo nhiều cách khác nhau.
3. How do cancer monoclonal antibodies work?
Cancer treatment monoclonal antibody drugs work in different ways. The following are important roles of monoclonal antibody drugs in supporting the immune system to fight cancer, including:
Assist in the identification of cancer cells: Certain cells of the immune system Translation depends on antibodies to locate the target site of the "attack". Cancer cells are covered in monoclonal antibodies, which make it easier for the immune system to detect and target them. Triggers cell membrane destruction: Some cancer monoclonal antibody drugs can trigger an immune system response to destroy the outer wall (membrane) of cancer cells. Preventing the growth of cancer cells: Cancer drugs such as monoclonal antibodies have the ability to block the connection of cancer cells to proteins, promoting their growth in the body. . This association is an important activity that helps cancer cells grow and maintain tumor survival. Prevents blood vessel growth: For a cancerous tumor to survive and grow, they will need an adequate blood supply. Some monoclonal antibody drugs used in the treatment of internal tumors can block the interaction of cancer cells and proteins needed for the growth of new blood vessels, thereby cutting off the tumor. blood supply to the tumor. Blocking substances that suppress the immune system: Certain proteins bind to cells of the immune system, known as regulators, to help suppress the body's immune system. overactive. The use of certain cancer drugs, such as monoclonal antibodies, can help them bind to cells of the immune system, giving the cancer-fighting cells a chance to work with less suppression. . Attacks cancer cells directly: Certain monoclonal antibody drugs can attack cancer cells directly. When certain monoclonal antibodies attach to cancer cells, they can cause them to self-destruct. Support for radiation therapy: Due to the strong ability of monoclonal antibodies to bind to cancer cells, they have become an effective vehicle for other cancer treatments. When a monoclonal antibody is attached to a small radioactive particle, it delivers radiation treatment directly to cancer cells and minimizes the effects of radiation on healthy cells. in the body. This variant is also known as radioimmunotherapy in cancer treatment. Supportive chemotherapy: Monoclonal antibody drugs can also support some chemotherapy drugs to directly kill cancer-causing cells and avoid affecting healthy cells. Linking Cancer Cells and Immune Cells: Some cancer drugs combine two monoclonal antibodies, one that attaches to cancer cells and the other to specific immune cells. This association may promote immune system attacks on cancer-causing cells.
4. What cancers can be treated with monoclonal antibody drugs?
Cancer treatments with monoclonal antibodies have been applied to certain types of cancer, including:
Breast cancer . Colorectal cancer. Brain cancer. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Head and neck cancer. Lung cancer . Liver Cancer . Malignant tumor. Non-hodgkin lymphoma. Stomach cancer . Prostate cancer.
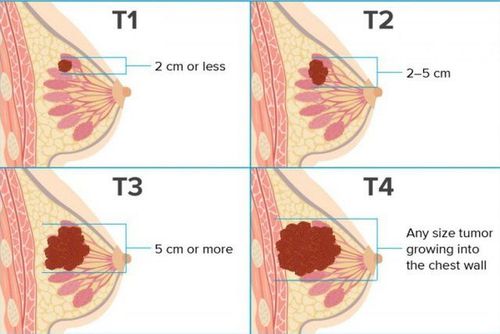
Có thể sử dụng thuốc kháng thể đơn dòng điều trị ung thư vú.
5. How are monoclonal antibodies used in cancer treatment?
Monoclonal anti-cancer drugs are usually given through a vein (intravenously). The frequency of monoclonal antibody treatment will depend on the type of cancer as well as the medications you are taking. Some monoclonal antibody drugs can be used in combination with other cancer treatments, such as hormone therapy and chemotherapy.
6. Side effects of monoclonal antibody drugs
In general, cancer treatments with monoclonal antibodies tend to have fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy treatments. However, the use of monoclonal anti-cancer drugs when causing side effects can be very serious.
Common side effects of monoclonal antibody drugs include:
Allergic reactions, such as itching or skin rash. Have flu-like symptoms, including fatigue, fever, chills, and muscle aches. Diarrhea . Feeling nauseous or vomiting. Low blood pressure . Skin inflammation. Serious (rare) side effects of monoclonal antibody drugs include:
Infusion reactions: Occurs like a serious allergic condition, possibly leading to death. Cancer patients may be given drugs to suppress allergic reactions before starting monoclonal antibody therapy. Infusion reactions often occur while treatment is being carried out or shortly after, so patients should be closely monitored for prompt action when a reaction occurs. Low blood cell counts: Monoclonal antibodies deliver radioactive particles or chemotherapy drugs that can severely lower blood cell counts. Lung and heart problems: Some cancer monoclonal antibody drugs can increase your risk of pneumonia and heart disease (heart attack, high blood pressure, or congestive heart failure). Skin problems: The medicine may lead to infection of sores or skin rashes in rare cases. Increased risk of bleeding: Monoclonal anti-cancer drugs may increase the risk of serious internal bleeding.
7. Notes when using monoclonal antibodies to treat cancer
Before deciding to use monoclonal antibodies to treat cancer, you need to discuss carefully with your oncologist to weigh the benefits and risks that this treatment method may bring. back to yourself. Some questions you can discuss with your doctor about monoclonal antibody treatment for cancer include:
Is my tumor a good fit for monoclonal antibody drug therapy or not? Do monoclonal antibody drugs really help slow cancer growth? Does it reduce the size of the tumor? Are monoclonal antibody drugs the first line of treatment or the treatment after other measures have failed? What are the possible side effects of using monoclonal antibodies to treat cancer? Do the potential effects conflict with the benefits of the drug? How much does monoclonal antibody treatment cost? Is monoclonal antibody cancer treatment available in clinical trials? In summary, monoclonal antibody drugs are an immunotherapy in cancer treatment. Before deciding to use monoclonal antibodies to treat cancer, you need to carefully consider the benefits and potential side effects that the drug may bring.
Currently, early cancer screening is considered the perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Reduce the cost of treatment and especially reduce the mortality rate in patients. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys and introduces to customers the Early Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec - Peace of mind to live well to help with gene testing, imaging, testing of biomarkers to detect tumors you early.
Choosing the Early Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec - Peace of mind at Vinmec, customers will get:
Only one gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women ( lung cancer , colorectal cancer , breast cancer , pancreatic cancer , cervical cancer , stomach cancer , prostate cancer ,.....) Early detection of early signs of cancer cancer through imaging, endoscopy, and ultrasound. The operation is simple, careful and accurate. A team of well-trained specialists, especially in oncology, are capable of handling cancer cases. With a system of facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of doctors with deep expertise and experience, it will help the examination and treatment process of patients at Vinmec become faster with High efficiency, save cost and time.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Mayoclinic.org