Article of Dr. Le Van Quang - Otolaryngologist, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Nha Trang International Hospital.
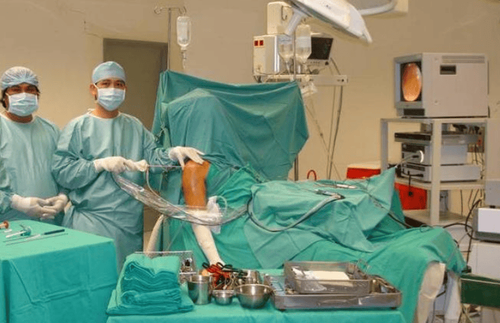
On November 18, 2019, Mr. Le Van Hai (55 years old) was brought into Vinmec Nha Trang in a state of irritation, suddenly having difficulty breathing and swallowing, which progressed very quickly. Previously, Mr. Hai had a sore throat, fever for about 3 days, bought self-medication but the symptoms did not reduce. Mr. Hai was diagnosed with acute pharyngitis, a complication of epiglottitis, which was timely handled and performed emergency surgery by the Doctor's team.
During the surgery, the Doctors discovered that the patient also had necrosis of a portion of the epiglottis. The debridement, timely drainage of the abscess, significantly improved the recovery rate and reduced dangerous complications. After surgery, Mr. Hai is now stable and recovering well.
Acute epiglottitis is a dangerous, rapidly progressive infection that causes obstruction and acute respiratory failure with the cause of usually infection, infectious agents possibly caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi... commonly Haemophilus influenzae type B (HIB) infection, non-infectious agents such as respiratory burns or allergies oropharyngeal object.
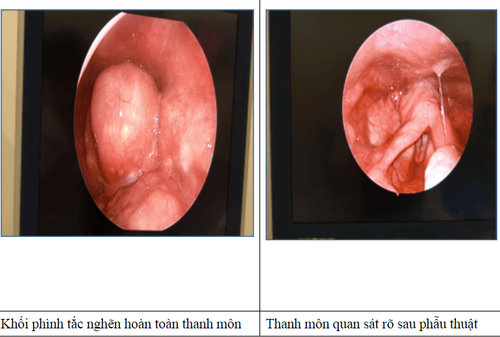
The disease is more common in children than adults, due to differences in anatomical structure and immunological properties. One of the complications of acute epiglottitis is epiglottitis - a rare and dangerous complication that accounts for about 4% and very rare cases reported in the literature to date.
Obsessive glottisitis can progress very rapidly within 12-24 hours with symptoms of irritation, malaise, painful swallowing, dysphagia, hoarseness, dyspnea, stridor, and may be more complex that causes edema, obstruction or constriction of the airways leading to asphyxia and rapid respiratory failure. Patients can die if not diagnosed and treated promptly. The mortality rate from this condition worldwide is 3-7%.
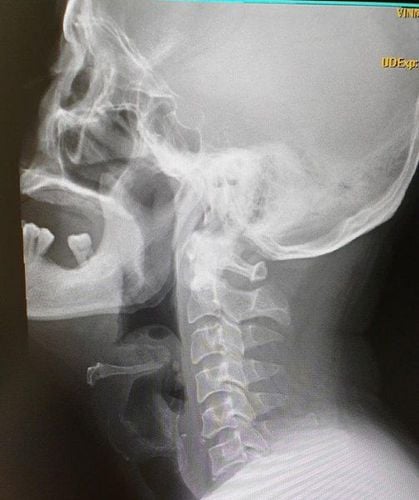
The most important criterion during treatment is to ensure that there is no acute respiratory failure, because when that happens, endotracheal intubation (*) is very difficult, because the entire glottis is compressed and edema. At that time, Doctors must be ready for tracheostomy (**) to secure the patient's airway.
Patients should be examined with an otolaryngologist in case of suspected acute epiglottitis for proper diagnosis and treatment, minimizing dangerous complications.
Children who are fully vaccinated with the HIB vaccine have a lower risk of acute epiglottitis than those who are not fully vaccinated. When examining children with rapid respiratory infections, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, special attention should be paid to the risk of children having laryngitis.
Note:
(*) An endotracheal tube is a tube-shaped device, used to support active respiration, which is placed directly into the larynx through the mouth or nose.
(**) Tracheostomy is a procedure that places a breathing tube directly into the larynx through an incision in the skin from the outside of the neck.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.