Pomelo is a rich source of potassium and vitamin C, both of which are essential nutrients for good health. However, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warns against consuming pomelo or pomelo juice while taking certain medications. This article explores whether pomelo interacts with metformin and provides important considerations for using metformin.
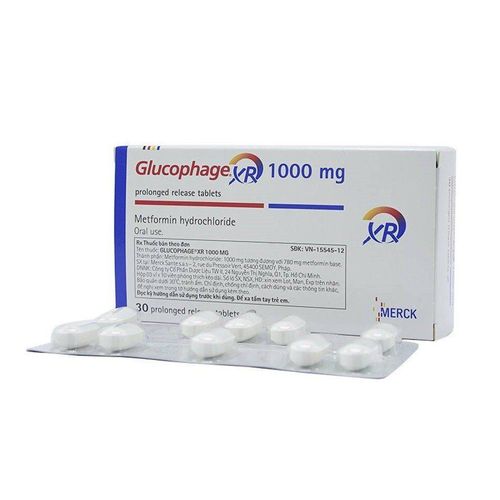
1. What is Metformin?
Metformin is a prescription medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. People with type 2 diabetes cannot use insulin effectively, meaning they are unable to regulate their blood sugar levels. Metformin helps individuals with type 2 diabetes control their blood sugar in several ways, including reducing the amount of sugar the body absorbs from food, decreasing the amount of sugar produced by the liver, and enhancing the body's response to the insulin it naturally produces.
Although rare, metformin can cause a severe, life-threatening condition called lactic acidosis. Therefore, individuals with liver, kidney, or heart problems should avoid taking metformin.
Metformin is often prescribed as a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes. It is also sometimes recommended for individuals with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Certain medications may interact with metformin, potentially reducing its effectiveness or increasing adverse effects. These include:
- Oral contraceptives.
- Diuretics and thiazides.
- Corticosteroids.
- Phenytoin.
- Nicotinic acid.
- Sympathomimetic drugs.
- Phenothiazines.
- Glyburide.
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Antiepileptics like topiramate.
- Thyroid medications.
- Isoniazid.
- Nifedipine.
- Furosemide.
Patients must inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking before starting metformin. Additionally, alcohol consumption while on metformin increases the risk of low blood sugar and should be avoided or minimized.
2. Drug Interactions with pomelo
More than 85 medications are known to interact with pomelo, including 43 that are affected by all forms of pomelo products (e.g., fresh juice, frozen concentrate).
Certain compounds in pomelo can bind to and deactivate an enzyme in the gut and liver that helps metabolize medications. Typically, when a medication is taken orally, this enzyme partially breaks it down before it enters the bloodstream. As a result, less of the drug reaches the blood than the initial dose. However, pomelo compounds can inhibit this enzyme, allowing more of the drug to enter the bloodstream, which may increase the risk of overdose.
Pomelo contains compounds called furanocoumarins, which inhibit the function of CYP3A4, an enzyme responsible for metabolizing around 50% of all drugs.
Inhibiting this enzyme means certain medications remain in the body longer than usual, leading to accumulation in the blood. This raises the risk of adverse effects and, in severe cases, can be life-threatening.
The effect of furanocoumarins on CYP3A4 is irreversible, and it can take the body about three days to produce new CYP3A4 enzymes. As little as 200 ml of pomelo juice—less than one cup—may be enough to trigger this interaction.
Pomelo also contains flavonoids, such as naringin and hesperidin, which can block a protein called organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP). OATP helps transport drugs into cells. This means consuming pomelo may reduce the absorption of certain drugs, making them less effective. However, this interaction is temporary, lasting about four hours. Individuals taking medications that rely on OATP for absorption can consume pomelo if they allow a four-hour gap between the two.
3. How Does Pomelo Affect Metformin?
It is important to note that metformin is not metabolized by the same enzymes as some other medications. Instead, it is excreted from the body unchanged via urine.
Currently, there is limited information on whether consuming pomelo while taking metformin impacts individuals with type 2 diabetes.

A 2009 study investigated the effects of pomelo and metformin on non-diabetic mice. Some mice were given both pomelo juice and metformin, while others received only metformin. The researchers found increased production of lactic acid in the mice exposed to both pomelo juice and metformin. The study suggested that pomelo juice increased metformin accumulation in the liver, leading to heightened lactic acid production. The researchers concluded that consuming pomelo juice might increase the risk of lactic acidosis in individuals taking metformin. However, these findings were observed in non-diabetic mice and not in humans with type 2 diabetes. To date, no human studies have demonstrated that taking metformin with pomelo juice leads to lactic acidosis.
4. Effects of pomelo on Diabetes
Interestingly, pomelo juice may offer potential benefits for individuals with diabetes. An animal study found that pomelo juice consumption reduced fasting blood sugar levels and slowed weight gain. However, no enhanced effects were observed when pomelo and metformin were used together. These findings were based on diabetic mouse models.
A review of pomelo's role in diets and drug interactions indicated that pomelo consumption is associated with weight loss and improved insulin resistance. A compound in pomelo juice, naringin, has been shown to improve hyperglycemia and high cholesterol in animal models of type 2 diabetes.
While pomelo is a nutritious fruit, its compounds can affect how certain medications function. However, there is no evidence that pomelo consumption interferes with metformin use.
Despite containing natural sugars, pomelo may offer some benefits for individuals with diabetes. Researchers hypothesize that compounds in pomelo might help lower blood sugar levels.
A 2014 study examined the effects of sweetened pomelo juice on healthy mice following high-fat or low-fat diets. Mice on high-fat diets that consumed pomelo juice showed reduced fasting blood sugar, lower fasting insulin levels, and less weight gain compared to mice that did not consume pomelo juice. Mice on low-fat diets only experienced a reduction in fasting insulin levels. The researchers attributed these findings to compounds in pomelo that inhibited glucose production in the liver.
Although these studies suggest potential benefits of Pomelo juice for individuals with diabetes, further research is needed to confirm these findings in humans.

Pomelo can interact negatively with certain medications. However, no clinical studies have indicated adverse effects when consuming pomelo while taking metformin. Experimental studies suggest pomelo might aid weight loss and reduce fasting blood sugar levels, but more research is needed to validate these benefits in humans. If you are taking metformin and have concerns about potential food-drug interactions, consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
References: healthline.com, medicalnewstoday.com, nhs.uk