The article was professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyễn Thị Hường - Neurologist - Faculty of General Internal Medicine, Vinmec Times City International Hospital.
Brain infarction has been on the rise, largely due to the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.The disease reduces blood flow to the brain, causes cerebral vascular occlusion, or general hypotension.
1. What is cerebral infarction?
Cerebral infarction is a pathological process that reduces blood flow to a region of the brain due to narrowing, blockage of cerebral blood vessels, or hypotension. Cerebral ischemia is a condition where a part of the brain is deprived of blood supply. If the lack of blood supply is not remedied, that part of the brain will undergo tissue death (aka necrosis) due to prolonged deprivation of oxygen and glucose. The area of the brain that undergoes necrosis due to lack of blood supply is called a cerebral infarction.
Cerebral infarction accounts for about 80% of brain strokes, while the remaining 20% are due to cerebral hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The annual incidence rate of cerebral infarction is relatively high, approximately 130 per 100,000 people per year.
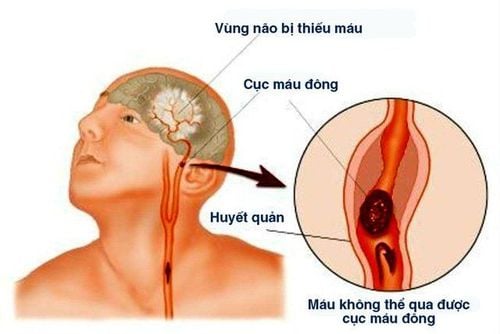
2. Causes of cerebral infarction
Common causes of cerebral infarction are:
- Atherosclerosis of large arteries: This accounts for 50% of cases, with 45% involving extracranial arteries and 5% affecting intracranial arteries.
- Cardiac causes: Conditions such as heart valve regurgitation, atrial fibrillation, arrhythmias, and heart failure lead to the formation of blood clots that travel to the brain, accounting for 20% of cases.
- Small vessel blockages in the brain: Commonly seen in individuals with hypertension or diabetes, these account for 25% of cases.
- Non-atherosclerotic artery diseases: These account for less than 5%.
- Blood disorders: Such as clotting disorders, blood cell diseases, and congenital vascular abnormalities, contributing to less than 5% of cases.
3. Diagnosis of cerebral infarction
The symptoms of a cerebral infarction usually occur suddenly, often while the patient is resting. Typical symptoms include paralysis to one side of the body, numbness, difficulty speaking, and facial drooping. There may be loss of consciousness if the patient has extensive cerebral infarction, affecting both cerebral hemispheres or the brainstem.
Paraclinical diagnosis
CT scan of the brain: In the hyperacute phase 3-6 hours after the onset of the disease, the changes on brain CT images are very subtle, mainly caused by fluid retention in the ischemic area of the brain
Early signs of cerebral infarction on a CT scan of the brain include loss of the gray-white matter junction, obscured sulci, narrowed Sylvian fissure, loss of the insular ribbon, narrowed ventricles and basal cisterns, and increased density of blood vessels in the Willis polygon area due to a thrombus, particularly in the middle cerebral artery.
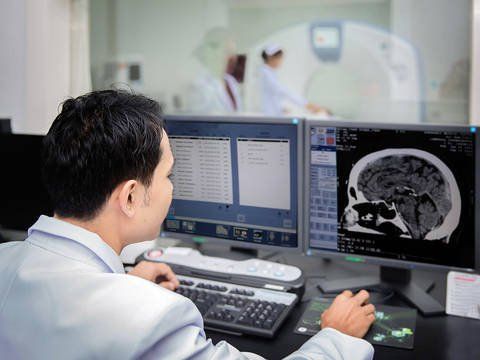
Computed tomography (CT) of the skull is used to diagnose cerebral infarction. In the later stages, after the infarct has formed, the CT images show areas of decreased density in the cortical region, subcortical region, or white matter; deep gray matter in areas supplied by the artery.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the brain: The advantage of MRI of the brain compared to Computed Tomography (CT) in the acute phase of cerebral infarction is that MRI has specialized sequences such as DWI, ADC, FLAIR, MRA that accurately assess the acute nature of the lesion, allowing for an intervention to be planned, as well as a preliminary evaluation of major blood vessels for occlusion in the brain without the need for contrast injection. The disadvantage of MRI is that it takes longer to perform than a CT scan, so it is not the ideal tool for emergency stroke intervention.
Digital subtraction angiography: Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is an invasive technique aimed at accurately diagnosing cerebral vascular occlusive diseases and simultaneously providing emergency treatment to remove blood clots via an intravascular route: after detecting the site of occlusion through cerebral angiography and, specialized instruments are inserted to suction the blood clot out (using a suction device or catheter).
4. Signs of a stroke
When you see a patient showing FAST symptoms (an acronym for stroke assessments): F (face) drooping, A (arm) weakness, S (speech) slurred speech, T (time) immediate hospital transfer is needed.
Some other warning symptoms of a stroke include dizziness, headache, numbness and weakness in the limbs, facial drooping, slurred speech, coma, and seizures... When these signs are detected, the patient should be taken to the hospital immediately for treatment. The golden window for treatment is the first 6 hours from the onset of symptoms, ideally within 4.5 hours, and the diamond window is the first hour from the onset of symptoms. If the treatment window is missed, the patient may suffer severe disabilities due to the lack of timely treatment.
5. Preventing Stroke Recurrence

- Monitoring and managing risk factors: like hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and dyslipidemia can help prevent recurrence.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet (low-fat, low-salt for hypertension, reduced sugar for diabetes), increased vegetable intake, daily exercise, and avoidance of smoking, alcohol, and obesity are crucial.
- Follow-up care: Adhere to regular medical appointments and the treatment plan provided by your healthcare provider.
- If any symptoms of brain infarction arise, seek medical attention immediately.
When there are symptoms suggesting a stroke such as weakness on one side of the body, facial drooping, difficulty speaking, etc., the patient needs to seek emergency medical services immediately, do not attempt to resolve this condition at home. The patient should be diagnosed early and accurately so that the doctors can choose the most appropriate treatment. The sooner you get to the hospital, especially within the first 6 hours after the first symptom apperance, the higher the chance of recovery.
Currently, Magnetic Resonance Imaging - MRI/MRA is considered the "gold standard" for screening strokes. MRI is used to examine the condition of most organs in the body, particularly valuable for detailed imaging of the brain or spinal nerves. Due to its high resolution and contrast, MRI images allow for the detection of abnormalities hidden behind layers of bone that other imaging methods may find difficult to scan. MRI can provide more accurate results than X-ray techniques (except for the DSA technique used to evaluate blood vessels) in diagnosing brain, cardiovascular, and stroke-related diseases, among others. Moreover, the MRI scanning process does not cause side effects like those in X-ray or computed tomography scans. (CT).
Vinmec International Hospital currently owns a 3.0 Tesla MRI system equipped with advanced technology from GE Healthcare (USA), providing high-quality images that allow for comprehensive evaluation without missing any lesions while reducing the scanning time. The Silent technology helps minimize noise, creating comfort and reducing stress for patients during the scan, resulting in better image quality and shorter scan times.With a state-of-the-art MRI system and the application of modern neurovascular intervention methods, a team of experienced and well-trained imaging and neurology specialists, Vinmec is a trusted facility for stroke risk screening and examination
Recently, Vinmec has successfully provided emergency care and treatment for many stroke cases without leaving any sequelae: Saving a patient who suffered two consecutive strokes; Rescuing a foreign female tourist from the brink of death due to a stroke;...
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.