Nội dung bạn đang tìm kiếm không có phiên bản tiếng Việt.
Vui lòng chọn tiếp tục để xem nội dung tiếng Anh hoặc đi đến trang chủ Tiếng Việt.
Rất xin lỗi về sự bất tiện này.

Home
Tag Intestinal microbiota
Articles in Intestinal microbiota

Role of nourishing probiotics in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
Disturbances in the gut microbiota disrupt mucosal homeostasis and are strongly associated with human IBD and murine colitis. Therefore, preventing or correcting microbiome imbalance can be considered as a new prevention or treatment strategy for IBD.
Xem thêm
Regulating the gut microbiome: A new therapeutic strategy for inflammatory bowel disease
Many microorganisms play a role in gut health; they include bacteria, fungi, and viruses that exist in dynamic equilibrium to maintain mucosal homeostasis. Disturbances in the gut microbiota disrupt mucosal homeostasis and are strongly associated with human IBD and murine colitis. Therefore, preventing or correcting microbiome imbalance can be considered as a new prevention or treatment strategy for IBD.
Xem thêm
Role of bile acids in gut microbiota-mediated cholestatic liver disease
The interaction between bile acids and the gut microbiota is implicated in the pathophysiology of many intestinal and gastrointestinal diseases, especially cholestatic liver disease. In particular, the progression of autoimmune cholestatic liver diseases also affects the composition of the gut microbiota, exacerbating the development of cholestasis in this interactive cycle.
Xem thêm
Role of bile acids in gut microbiota-mediated liver diseases
Recent studies have shown that bile acids act as omnidirectional signaling molecules mediating enteric-hepatic crosstalk. The complex relationship between bile acids and the gut microbiota (depending on and inhibiting each other) plays an important role in the maintenance of mammalian homeostasis.
Xem thêm
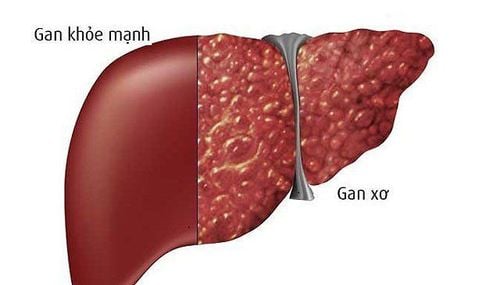
Role of bile acids in gut microbiota-mediated cirrhosis
Previous studies have shown that gut microbiota changes or dysbiosis in patients with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis are often accompanied by a significant decrease in total bile acids and acid ratio. secondary/primary bile acids.
Xem thêm
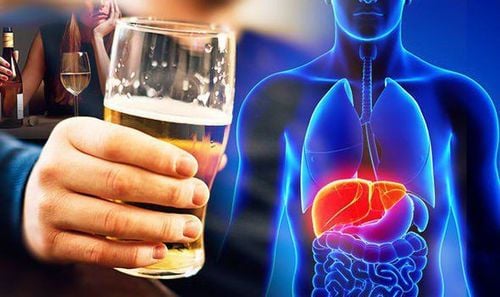
Role of bile acids in alcoholic liver disease mediated by gut microbiota
Alcoholic liver disease is initially characterized by fatty liver, which can then develop into alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and cirrhosis. Alcohol can cause damage to many target organs, especially the brain, intestines, and liver. It should be noted that drinking alcohol can alter the structure of the gut microbiota before liver disease occurs.
Xem thêm

Breastfeeding may benefit your baby's gut
Breast milk is considered the most important and valuable source of nutrition for infants. In addition to providing all the essential nutrients, breast milk also contains a significant amount of beneficial microorganisms that help the baby's digestive system function better. Therefore, breastfeeding is extremely important in the first months of a newborn's life.
Xem thêm
Balancing intestinal microflora in children
The intestinal microflora in children is important for the health of young children. They create protective barriers for the body against risks caused by diseases and external environmental impacts. So what do we need to do to balance the intestinal microflora in young children?
Xem thêm
New therapeutic mechanisms in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which has been listed by the World Health Organization as one of the most difficult diseases to cure, includes ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) and shows a continuously increasing incidence. Although genetic, epigenetic, immunological, microbial and environmental factors are involved in the etiology of IBD, no factor has been identified as a clear and direct cause of IBD.
Xem thêm