This is an automatically translated article.
Breast milk is considered the most important and valuable source of nutrition for infants. In addition to providing a full range of essential nutrients, breast milk also contains a significant amount of beneficial microorganisms that help the baby's digestive system work better. Therefore, breastfeeding is extremely important in the first months of a newborn's life.
1. The role of breast milk in the infant's gut microbiota
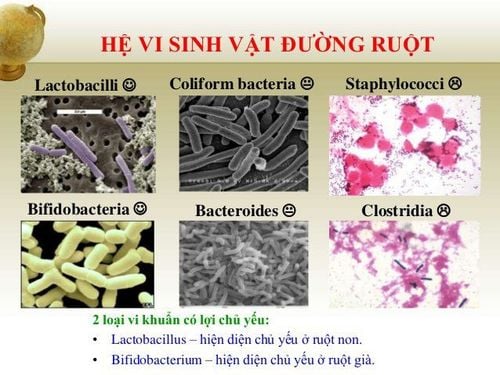
Breastfeeding has many health benefits for babies. Breast milk contains 102-104 viable bacteria per mL of milk. Breast milk can therefore directly influence the microbiome formation in the infant. The microbiota in milk is complex and varies between individuals.
The microbiome in breast milk also develops with breastfeeding. The microbiota in colostrum is more diverse than in mature milk. In colostrum, lactic acid bacteria and Streptococcus are most abundant. After 1 month, the number of Staphylococcus was significantly reduced, while lactic acid bacteria were still abundant.
While many studies have found different types of bacteria in breast milk, breast tissue, and infant stools, researchers have also found that the gut microbiota of breastfed infants has a different immune system. bacteria in breast milk and on the mother's skin than in the samples of the non-breastfeeding women in the study.
This means that the baby will be protected from harmful bacteria by the antibodies present in breast milk. These antibodies are specific to the mother's bacteria, and it is because the microbiota in the gut is similar to that of the breastfed mother that the infant is protected by this passive immune system.
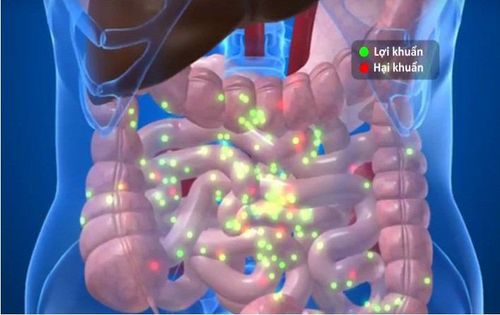
Sữa mẹ chứa nhiều hệ sinh vật tốt cho đường ruột của trẻ sơ sinh
2. The benefits of breastfeeding on the digestive system
Breastfeeding can help babies develop a full range of beneficial and healthy bacteria. In addition to providing a lot of necessary nutrients, protects children from allergies and immunity to many diseases. Several studies suggest that the microbiome has important roles in the digestive system of breastfed infants.
The microbial populations that reside in the infant's gut are influenced by a number of factors, especially by drinking breast milk. The more breast milk a baby gets, the more beneficial bacteria it has from the mother.
Based on laboratory studies of bacteria found in milk, skin, and feces, researchers estimate that babies get a minimum of 75% of their nutrition from breast milk during their first month of life. About 28% of beneficial gut bacteria come from breast milk. These babies also got about 10% of their gut bacteria from their mothers' skin and 62% from unknown sources.
Having a good gut microbiome is important for a child's digestive ability. Babies are less likely to be infected by another foreign bacteria and a healthy microbiome can completely protect them from other gastrointestinal infections.
A study published in the Journal of Pediatrics compared the bacteria in the stomachs of more than 300 infants aged 3 to 6 months who were either breastfed or formula-fed. Researchers have found that breastfed babies tend to have richer and healthier gut bacteria than formula-fed babies.
Besides, pediatricians recommend mothers to exclusively breastfeed their babies until the baby is at least 6 months old; as this has been linked to a reduced risk of ear and respiratory infections, sudden infant death syndrome, allergies, childhood obesity, and diabetes.

Nuôi con bằng sữa mẹ có thể giúp trẻ phát triển đầy đủ các vi khuẩn có lợi và khỏe mạnh
3. Ways to contribute to a healthy gut in babies
Breastfeeding may also help counteract the negative effects on the infant's microbiome from antibiotic exposure during or after labor.
According to Emory University researcher Sara Edwards, other measures you can take to help replenish healthy bacteria include:
Lots of skin-to-skin contact with babies Do not bathe babies immediately after birth Eat probiotic foods such as yogurt, kefir, kombucha, or sauerkraut The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life and continued breastfeeding after birth. when introduced to solid foods until the child is at least 1 year old. Babies who are exclusively breastfed for the first 6 months grow faster and are less likely to be overweight or malnourished, have rickets, and often have better resistance than other babies.

Nên cho trẻ bú mẹ hoàn toàn trong 6 tháng đầu đời
In addition, for infants, especially 6-month-old children, at this time, children's bodies are still weak, their immune systems are not yet fully developed, and they are very susceptible to diseases, especially diseases. respiratory disease. Therefore, parents need to be very careful to protect their children from pathogens.
For children to be healthy and develop well, it is necessary to have a nutritious diet in terms of quantity and quality balance. If children are not provided with adequate and balanced nutrients, it will lead to diseases of excess or lack of nutrients, which adversely affect the comprehensive development of children in terms of physical, mental and motor skills.
Children who do not eat properly are at risk of micro-mineral deficiency causing anorexia, growth retardation, malabsorption,... If they notice the above signs, parents should supplement their children with products. The supplement contains lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, and B vitamins to help fully meet the nutritional needs of children. At the same time, these essential vitamins also support digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, help improve anorexia, and help children eat well.
Parents can learn more:
Signs of zinc deficiency in children
Micronutrient deficiency and failure to gain weight in children
Please regularly visit Vinmec.com website and update useful information to take care of your child. Take care of the baby and the whole family.
Reference source: babycenter.com