This article is written by Dr. Pham Quoc Thanh, MSc, MD - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
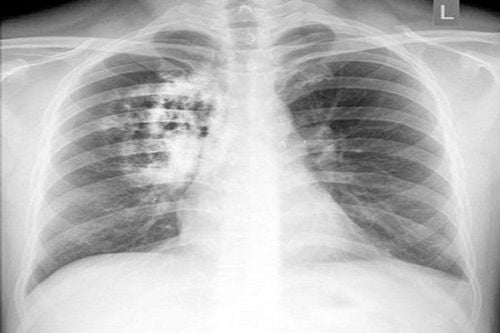
Chest X-ray is indicated as a routine clinical test by clinical doctors to assess abnormalities and pathological lesions of the lungs. Chest X-rays results will be reviewed specifically and in detail by specialist doctors. When the chest X-ray image has blurred spots, it means the lung image is abnormal.
1. What are blurred spots in the lungs?
Through the chest X-ray image, it can not determine the cause of the lung opacities. It could be a scar after the lung parenchyma were infected, or an irritant in the air, lung cancer.
However, lung opacity is quite common, not all are signs of dangerous diseases because half of adults have lung opacities on chest X-ray images.
2. Are chest X-ray showing lung opacities normal or dangerous signs?
A chest X-ray with blurred spots is performed like a regular X-ray. Diagnosis of pulmonary opacities requires comparison of standard upright and lateral X-ray images, compared with previous images.
The lung opacity on a chest X-ray is usually larger than 2cm in diameter. Generally, small nodules do not cause any significant problems. They are too small to cause pain or difficulty breathing.
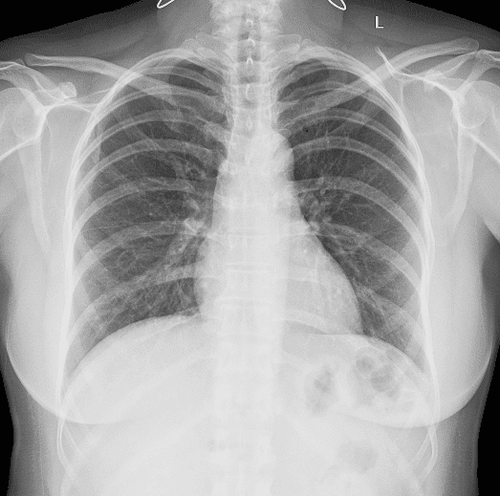
Most lung nodules are not cancerous, but in a few cases, the nodule can represent an early stage cancer.
But if the image has malignant lung opacities, or the lung parenchyma is calcified, be careful with the following dangerous diseases:
- Carcinoma: Lung opacities in peripheral solid carcinoma often appears in the early stages.
- Metastatic tumor nodules: usually have numerous quantities and gather in the lower half of both lungs.
- Pulmonary infarction: Triangular opacities, fading towards the center of the nodule, lying under the pleura.
- Abnormal vascular nodules in the artery - vein: The shape of blurred spots are diverse, with vessels feeding or draining the nodule.
- Other vascular tumors: Triangular opacities located in the path of the pulmonary vascular bed often meet in vasculitis.
- Benign tumors: are usually Harmatoma.
To diagnose the pathological cause of benign lung opacities and eliminate early stage cancers, chest X-rays need to be combined with computerized tomography to help doctor assess:
- Finding calcified lesions and other lesions, if any, and evaluating lung tissue.
- Morphology, structure, properties, size, and density of the blurred spot.
- Evaluating hilar or mediastinal lymph nodes.
- To diagnose accurately, it needs to be combined with CT scans and transthoracic biopsy.
3. Determine and analyze the morphology of lung opacities
When detecting lung opacities, first the doctor needs to determine and analyze the morphology of lung opacities such as: size, border line, shape, ... Then they combine it with medical history, smoking, and job to assess the risk of contracting disease. Cases of lung opacities are as follows:
3.1. Benign lung opacities
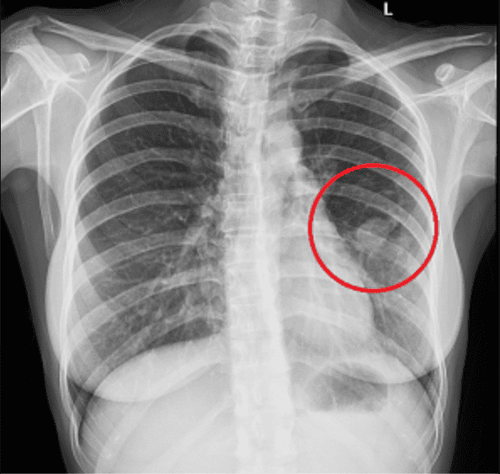
Characteristics of benign lung opacities are as follows:
- Round blurred spot, has diameter less than 3cm.
- Blurred spots have regular borders.
- The lung opacities do not increase in size, for at least 2 years.
In addition, calcified spots can be seen in the center of the lung opacities, these occupy approximately 10% of the volume. Calcified spots often have popcorn-shaped, arranged in layers and clusters.
Benign lung opacities are runned into frequently, they are not dangerous but still need to be monitored periodically, every 3 - 6 months to ensure that this lung opacities do not grow larger or a new lung opacity appears.
Benign lung opacities is common in people under 35 years old, living and working healthily, and not smoking.
3.2. Malignant lung opacities
Characteristics of malignant lung opacities are as follows:
- Diameter of blurred spots more than 3cm.
- Uneven borders and calcified possibility.
- The nodule doubles in a short time (maybe 1 month or longer than 1 - 2 years).
- Calcified blurred nodules are small dot-shaped, accounting for about 10% the volume of the nodule.
Malignant lung opacities is often seen in people over 35 years old, who smoke regularly.
When these signs appear, the patient needs to perform other tests to accurately assess the nature of the lung opacities such as: transthoracic biopsy, bronchoscopy, surgery, etc.
3.3. Calcification of lung parenchyma
Calcification of lung parenchyma has many forms such as:
- Popcorn form
- Benign eccentric form
3.4. Progressive pulmonary fibrosis will have calcification around the fibrous mass
Reticular and dot-shaped forms: Account for 6% of primary lung cancers. Cancer develops on the foundation of old scars, calcium deposits, etc.
Solitary form: Single blurred nodule, located in the center, benign nodule (tuberculous granuloma).
Multiple nodules form: pneumonia, tuberculosis infection hg +.
4. Chest X-ray at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital is currently one of the hospitals in the Vinmec International Hospital system equipped with modern equipment and machinery to serve the medical examination and treatment process.
Patients who have chest X-rays at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital will be clearly instructed by support staff and technical staff on the operations and procedures to minimize exposure to X-rays and reduce the impact on the health of the person being examined, ensuring the diagnostic image.
If your X-ray image has any abnormalities, doctors will promptly advise and propose effective treatment options.
To arrange an appointment, please call … or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.