This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Vu Van Quan - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesia, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Diverticulitis is a disease with one or more inflamed diverticula. Inflammation spreads to surrounding fatty tissue, sometimes perforation of the diverticulum leads to abscess formation or peritonitis. Rarely, a colonic fistula may form with the bladder, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina.
1. What is a colonic diverticulum?
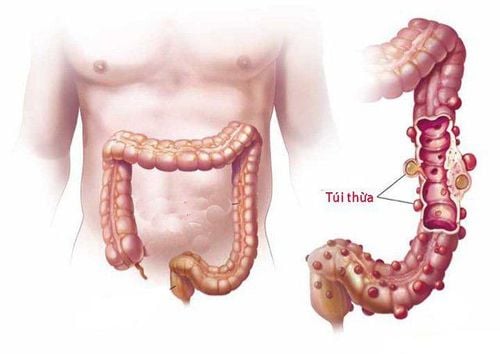
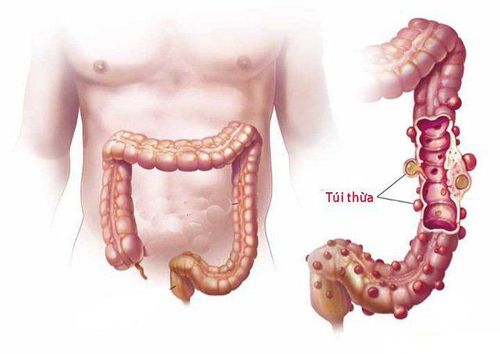
Colonic diverticula are pouch-like structures that develop in the wall of the colon, most commonly in the sigmoid and left colon, but can also involve the entire colon. When these diverticula become inflamed, it causes diverticulitis. Normally, the colonic wall has 4 regular layers and there is no deep depression anywhere. If there is a structure that is deeply recessed into the wall of the colon, it is an image of a diverticulum.
Most diverticula of the gastrointestinal tract occur in the colon, of which 95% are in the sigmoid colon and 5% in the cecum, very rarely in the rest of the colon. When stools are small because of a lack of fiber, for example, stools will be hard and difficult to pass. To be able to expel stool, the colon has to contract more, and the patient also uses a lot of force to push when having a bowel movement, thus increasing pressure in the colon.
The wall of the colon is sometimes uneven in structure, there are places where the wall is weak compared to the surrounding part, and when intestinal pressure increases, the mucosa of those weak areas will be pushed out through the weak intestinal wall and form a small pouch, usually 1-2 cm large, sometimes 5-6 cm large.
Although the exact cause of diverticulitis is still unknown, there are many factors related to the disease such as genetics, race, age, higher incidence, higher fat intake.. Low fiber diet is an important issue, to date many studies show that eating low fiber for a long time leads to constipation and increased pressure in the colon is a risk factor. major cause of colonic diverticulum.
The disease is common in Westerners because the diet is less vegetable and fiber than Asian food. In addition, the sigmoid colon is also smaller in size than other colon segments, so it increases the pressure in the intestine more and thus partly explains why diverticula occur more in this segment of the sigmoid intestine.
In terms of anatomical structure, the diverticulum has the same structure as the colonic wall, but is thinner, consisting of an inner mucosal layer, an outer submucosal layer, then a muscular layer and a peritoneum. The diverticulum may be confined to the wall of the colon, or protrude beyond the peritoneum of the colon, then the muscular layer of the diverticulum may be very thin or absent, so if the diverticulum protrudes, it may rupture easily. or perforated.
2. What is diverticulitis?
When the diverticulum becomes infected, it can cause diverticulitis , which can become inflamed in or around the diverticulum. Colonic diverticulum often contains trapped stool, which gradually solidifies into a fecal stone (fecalith), suffocating the diverticulum and compressing the diverticulum wall, allowing bacteria (often abundant in stool in the colon) to grow. force in the diverticulum causing diverticulitis.
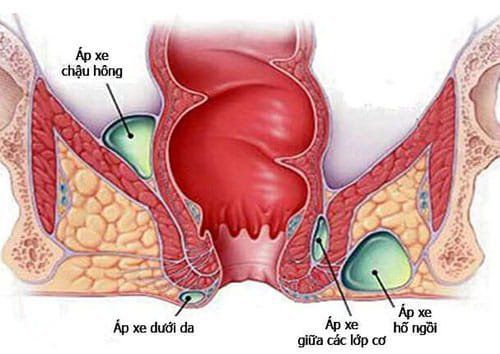
If there is a lot of infection, the diverticulum wall can be destroyed and perforated and the infection spreads beyond the colon wall, forming a local pocket of pus, or causing a very dangerous peritonitis, which can be fatal if left untreated. timely.
3. Why do you have diverticulitis?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing diverticulitis:
Aging. The incidence of diverticulitis increases with age. It is possible that age-related changes, such as a decrease in the firmness and elasticity of your bowel wall, may contribute to diverticulitis. Fat . Being overweight increases the risk of diverticulitis. Smoke. Smokers are more likely to develop diverticulitis than non-smokers. Less exercise. Regular exercise reduces the risk of diverticulitis. Diet high in animal fat and low in fiber. A low-fiber diet combined with a high intake of animal fat is associated with an increased risk, although the role of low fiber intake is still unclear. Certain medications Certain medications have been linked to an increased risk of diverticulitis, including steroids, opioids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve) .
4. Prevention of colonic diverticulitis
To help prevent diverticulitis, the following can be done:
Exercise regularly. Exercise promotes normal bowel function and reduces pressure inside the colon. Try to exercise for at least 30 minutes a day. Eat lots of fiber. Using a high-fiber diet reduces the risk of diverticulitis. High-fiber foods, such as fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains, soften stools and help stools pass through the colon more quickly. Eating nuts has not been linked to developing diverticulitis. Drink a lot of water. Fiber works by absorbing water and softening stools, making it easier to pass through the colon. But if you don't drink enough fluids to replace what you've absorbed, the fiber will solidify and lead to possible constipation.
5. Treatment of colonic diverticulitis at Vinmec Hai Phong

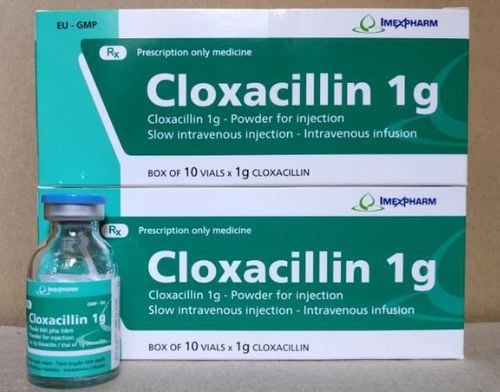
When diverticulitis symptoms - abdominal pain, fever, ... if mild, oral antibiotics are usually sufficient. When pain is worse, a liquid diet to allow the colon and intestines to recover may also be indicated. When the pain gets worse, or when you have a high fever or you can't drink fluids, you may need to stay in the hospital, along with intravenous antibiotics, and not eat or drink for several days.
Diverticulitis unresponsive to medical treatment requiring surgery. Surgery usually involves draining the pus and removing the segment of the colon that contains the diverticulum. Resection of the bleeding diverticulum is necessary for patients with persistent bleeding. Surgery may also be needed for any diverticula that have eroded into the bladder, causing severe, recurrent urinary tract infections and passing gas during urination, and to treat intestinal blockages.
Currently, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital has implemented the method of Laparoscopic Colectomy, whereby doctors will cut the colon with inflamed diverticula that does not respond to endoscopic treatment. Hospital, with many advantages as follows:
Short hospital stay, minimizing the cost of stay, reducing the risk of hospital infections. With cases of lithotripsy, inguinal hernia, customers can always go to work after 1 day of discharge from the hospital. Limit the use of antibiotics, reduce the risk of side effects, save costs, patients do not have to worry, fear when administering antibiotics and follow up after taking the drug. Recovery rate reached 90%, re-hospitalization 0%, postoperative infection 0%. The Early Post-Surgery Care Program provides comprehensive care to patients before, during and after surgery, helping to reduce hospital stay, improve treatment quality and reduce costs; reduce the rate of complications. ERAS has been shown to shorten the average length of stay from 8-10 days to 3-4 days. Insurance: Vinmec signed with many large private insurance partners. When customers are hospitalized, they are guaranteed and compensated at the hospital. Save a lot of customer's time and effort. Other advantages : Modern equipment; Service quality according to international standards; Highly qualified doctor; Patients do not need relatives to take care of them because they are cared for by a dedicated and thoughtful nursing doctor... The doctor who performs the technique is a Master, Doctor Vu Van Quan has more than 10 years of experience working in the hospital. Specializing in General Gastroenterology, specializing in examination and treatment of surgical diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, bile, pancreas and diseases of the abdominal peritoneum and abdominal wall.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.