This is an automatically translated article.
Appendicitis and diverticulitis are two diseases with similar clinical manifestations. It is more difficult to accurately diagnose diverticulitis before surgery than for appendicitis, so most diagnoses are made during surgery.Here are the points that distinguish appendicitis and diverticulitis:
1. Anatomical structure
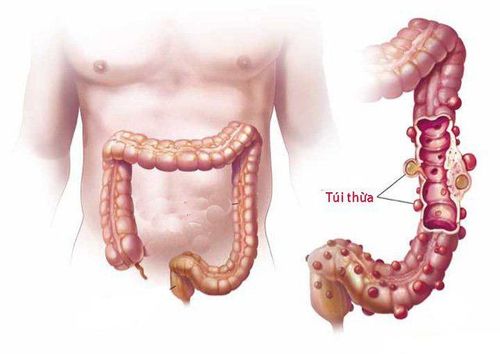
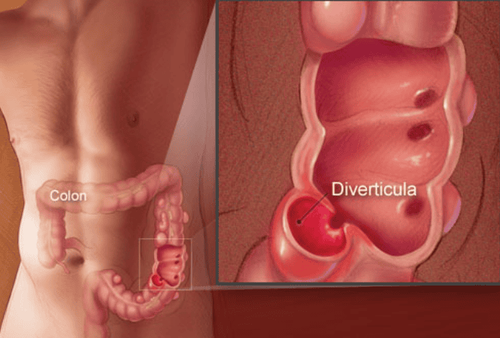
Colonic diverticula:Colonic diverticula are pouch-like structures that develop in the wall of the colon, most commonly in the sigmoid colon and left colon, but may also involve the entire colon. When these diverticula become infected, it causes diverticulitis. The majority of gastrointestinal diverticula occur in the colon, of which 95% are in the sigmoid colon and 5% in the cecum, very rarely in the rest of the colon. When stools are small because of a lack of fiber, for example, stools will be hard and difficult to pass. The wall of the colon is sometimes uneven in structure, there are places where the wall is weak compared to the surrounding part, and when intestinal pressure increases, the mucosa of those weak areas is pushed out through the weak intestinal wall and form a small pouch, usually 1-2 cm large, sometimes 5-6 cm large.
Appendice:
The appendix is the terminal segment of the primitive cecum, initially at the beginning and in the cecum. Due to uneven development (mainly anterior and right) of the cecum as the appendix rotates inward and upward. In adults, the appendix communicates with the cecum via the Gerlach valve (semicircle). Appendiceal size ranges from 1 cm to 20 cm or more, but averages 8-10 cm and averages 4-5 mm in diameter.
2. Causes of appendicitis and diverticulitis
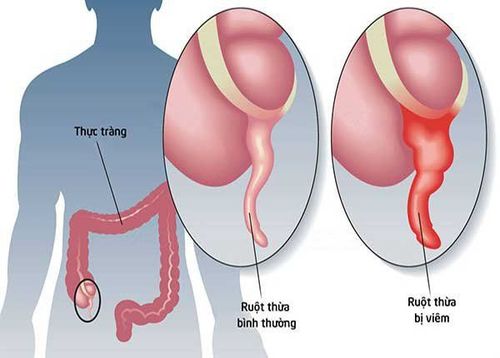
Viêm ruột thừa
A diverticulum is described as a bulge of a round mass of the large intestine (colon). It occurs when the inner lining (mucosa) of the colon weakens and forms one or more pouches (diverticula) through the muscular layers of the colon. When these pouches become inflamed or infected, or if they rupture, the condition is called diverticulitis. Risk factors for diverticulitis include a low-fiber diet high in fats and refined carbohydrates, age, a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and delayed bowel movements. People in the US, Australia, and the UK have a high incidence of diverticulitis and/or diverticulitis (Cunha). Diverticulosis affects 5% of individuals by the time they reach their forties, 33% to 50% of those age 50 and older, and more than 50% of those over the age of 80. Diverticulitis occurs in up to 20% of individuals with diverticula. The disease is not common in Africa and Asia. Both sexes are affected.
3. Symptoms of appendicitis and colonic diverticulitis
3.1 Signs and symptoms of appendicitis may include: Sudden pain that begins in the lower right abdomen Pain that begins around the belly button and often moves to the lower right abdomen Pain that gets worse worse when the sick person coughs, walks Nausea and vomiting Loss of appetite Mild fever may get worse as the illness progresses Constipation or diarrhea Stomach bloating Farting The location of your pain may vary, depending on the patient. on the age and location of the appendix. During pregnancy, the pain comes from the upper abdomen because the appendix is pushed higher during pregnancy. 3.2. Signs and symptoms of diverticulitis include: Pain, which may be constant and last for several days. The lower left side of the abdomen is a common site of pain. However, sometimes, the right side of the abdomen also hurts, especially in people of Asian descent. Nausea and vomiting. Fever. Abdominal tenderness Constipation or diarrhea, but less commonly.
Buồn nôn và ói mửa là dấu hiệu của viêm túi thừa
4. Complications of appendicitis and diverticulitis
4.1. Appendicitis can cause serious complications, such as: Most commonly, generalized peritonitis caused by an inflamed and ruptured appendix (perforation), the patient will have a syndrome of infection, toxicity ( high fever, chills, tachycardia, low blood pressure, bowel obstruction, abdominal distention due to paralytic ileus, abdominal wall reaction is very typical (touching any part of the abdomen hurts) This is the most serious complication if If the patient's life is not detected early and the patient's life is not promptly treated, the patient's life will be threatened by toxic infection 36 hours before the first symptoms (right iliac fossa pain, low fever, nausea) , vomiting...) occurs, the risk of appendicitis perforation is as low as 15%. Therefore, once appendicitis is diagnosed, surgery should be performed, avoiding unnecessary delays. Good adhesions and adhesions of the bowel loops and good mesentery may form a mass of the appendix.In this case, fever and pain may be reduced and the right iliac fossa will appear as a firm, non-motile mass with little tenderness. If considering Blood tests may show that the white blood cells are not as high as at the beginning, even normal. The mass can also progress in either direction, either dissolving or forming an appendix abscess.4.2. About 25% of people with acute diverticulitis develop complications, which can include: Abscess, which occurs when pus builds up in the diverticulum. Causes a blockage in the colon or small intestine due to scarring. Creates a fistula between parts of the intestines or intestines and the bladder. Peritonitis, which can occur if the pouch becomes infected or ruptures, spilling intestinal contents into the patient's abdominal cavity causing peritonitis, which is a surgical emergency and requires immediate care. .
5. Treatment
5.1. Appendicitis Surgery to remove the appendix is one of the main treatments for appendicitis. Traditional surgery: Open surgery with a small incision in the lower right abdomen and through which the appendix is removed. Recently, laparoscopic surgery method has been applied in the diagnosis and treatment of appendicitis with the advantages of observing the whole abdomen, reducing postoperative pain, and early recovery time.If the inflamed appendix is not ruptured at the time of surgery, the patient is usually discharged within 1-2 days. If the appendix ruptures, the hospital stay can be from 4 to 7 days, depending on the severity of the disease and the child's fitness. If it is acute appendicitis (initiated inflammation), appendicitis has not ruptured, the possibility of postoperative complications is very low. But for cases of appendicitis peritonitis, the risk of postoperative intestinal obstruction is very high.
5.2. Diverticulitis Treatment depends on the severity of the patient's signs and symptoms.
Uncomplicated diverticulitis
If symptoms are mild, the person can be treated at home. Your doctor may prescribe the following:
Antibiotics to treat infections, although the new guidelines say that in very mild cases they may not be needed.

Nếu các triệu chứng nhẹ, người bệnh có thể được điều trị tại nhà bằng thuốc kháng sinh
If you have severe symptoms or have other health problems, you may need to be hospitalized. Treatment usually includes:
Intravenous antibiotics Insertion of a tube to drain the abdominal abscess Surgery The patient will likely need surgery to treat diverticulitis if:
There is a complication, such as pressure bowel obstruction, fistula or obstruction, or perforation of the bowel wall Patients with multiple episodes of uncomplicated diverticulitis Patients with weakened immune systems
6. Why should you choose to treat colonic diverticulum at Vinmec?
Currently, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital has implemented the method of laparoscopic right colectomy and lymph node dissection. Accordingly, the doctors will cut the inflamed colonic diverticulum with many advantages as follows:No visual restriction like traditional, optimal image quality with higher accuracy. Less pain after surgery. Colon function recovers quickly. Small surgical scar. Minimize the risk of wound infection. Guaranteed aesthetics. Fast postoperative recovery, short hospital stay. Quickly return to normal activities. The system of modern equipment such as the modern endoscope system Olympus CV 180 allows to detect very small lesions (only a few millimeters) and accurately locate the lesions, endoscopic methods with frequency range Narrow light (NBI) has made a breakthrough for the screening and diagnosis of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum and colon and rectum) at early and very advanced stages. Soon. The level of anesthesia, anesthesia and postoperative analgesia is very good, leading in the application of the world's leading anesthetic-anesthesia methods. The doctor performing the technique is a Master, Doctor Vu Van Quan has more than 10 years of experience working in the field of General Gastroenterology, specializing in examination and treatment of surgical pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, bile, pancreas and pathologies of the abdominal peritoneum, abdominal wall.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.