This is an automatically translated article.
Calcium plays an important role in the formation of strong bones and teeth as well as participates in a number of other metabolic processes. Hypocalcemia occurs when the total plasma calcium concentration is low, causing the patient to have many health problems, even life-threatening. So how much total plasma calcium is considered hypocalcaemia?
1. The role of calcium in the body
In the human body, calcium exists in two forms, inside the bones and outside the bones. The calcium inside the bones accounts for 99% of the body's calcium, the remaining 1% is in the extracellular fluid.Calcium has an important role in human health, this is the main substance that makes up bones and teeth, when calcium combines with phosphorus, it will make bones and teeth stronger and healthier. For adults and children, calcium has certain roles, specifically:
For adults: Helps build strong bones, stable heart muscle, helps the elderly limit mental problems Neurological symptoms such as poor memory, neurasthenia, headaches... For young children: Help develop maximum height, strengthen the immune system, develop the nervous system... Calcium needs of each person in Ages will vary. The older each person is, the more calcium they need to supplement because the amount of calcium absorbed into the body becomes less and less and the amount excreted out increases, leading to a decrease in the total amount of calcium in the body.

Canxi đóng vai trò quan trọng trong cơ thể người
2. What is hypocalcemia?
Almost all metabolic processes taking place inside the human body require calcium, so calcium levels are maintained by a balanced mechanism. The maintenance of calcium stores in the body as well as total plasma calcium concentration depends on the amount of calcium provided through daily food intake, calcium supplements absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and excreted by the kidneys. .
Hypocalcaemia is understood as total plasma calcium concentration falling below 2.1 mmol/l under normal plasma protein conditions and calcium ion concentration less than 1.05 mmol/l.
The main causes of hypocalcemia include: kidney failure, hypoparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, after undergoing surgery, not getting enough calcium through food, using some inhibitory drugs. calcium, hypoalbuminemia or hypomagnesemia, hypophosphataemia.
MORE: Relationship between hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcemia
Patients with acute hypocalcemia often feel numbness around the mouth, numbness around the fingertips or legs, muscle cramps in the back and legs, voice changes. , wheezing, difficulty swallowing when eating and often feeling tired. For people with chronic hypocalcemia, there will be manifestations such as drier hair, brittle and fragile nails, teeth more easily damaged, dry skin, chronic itching and cataracts.
Suy thận là một nguyên nhân gây hạ canxi máu
3. How to diagnose hypocalcemia?
Diagnosis of hypocalcaemia is usually based on clinical and laboratory findings. For the paraclinical examination, the doctor will examine the condition of the patient's hair, skin and muscles, and check for psychological factors such as dementia, hallucinations, confusion. Besides, the doctor also conducts a neurological examination through the trousseau sign, chvostek sign, to check if the patient has impaired consciousness or convulsions.
Although the clinical examination, the doctor finds the symptoms related to hypocalcemia, however, to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will assign the patient to perform some laboratory tests, in which Check the total plasma calcium concentration. This test is crucial in the diagnosis of hypocalcemia. Normally, in healthy people, the mean total plasma calcium concentration is from 2.1 to 2.6 mmol/l, however, if the test results are below the average, it will be concluded as hypocalcaemia.
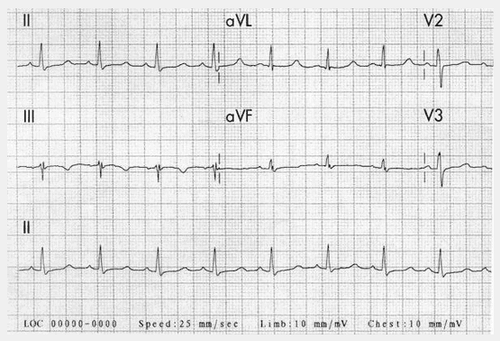
Hình ảnh hạ canxi máu trên điện tâm đồ
4. Treatment of hypocalcaemia
The principle of hypocalcaemia treatment is to supplement the amount of calcium needed by the body, the doctor will base on the patient's condition to choose the most appropriate method of calcium compensation for the patient.
MORE: What to do when hypocalcaemia?
For cases of acute hypocalcemia when the total plasma calcium concentration is less than 1.9 mmol/l, the doctor will prescribe intravenous calcium infusion at a dose of 0.375 mmol/kg, within 4 to 4 days. After 6 hours, the total plasma calcium concentration can increase from 0.5 to 0.75 mmol/l.
A few popular forms of intravenous calcium on the market today are:
Gluconate de calcium Glucoheptate de calcium Chlorure de calcium Globionate de calcium For patients with severe hypocalcemia after complete surgical resection or part of the parathyroid gland needs emergency injections of calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
For chronic blood calcium treatment, calcium is usually supplemented orally. In addition, take vitamin D to improve absorption through the digestive tract. The first dose of calcium used is from 250 - 650 mmol and divided into 3 - 4 oral doses, it is best to drink after eating to improve absorption. Subsequent doses will be adjusted to suit the patient's condition.
Hypocalcemia is a dangerous condition if not treated promptly. Therefore, when there are signs of hypocalcemia, patients should go to medical facilities to examine and prescribe appropriate calcium supplements, avoiding calcium deficiency or excess, both seriously affecting health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.