This article is consulted by Associate Professor, Doctor Le Ngoc Hung, Head of the Laboratory Department, Microbiologist, Laboratory Department, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
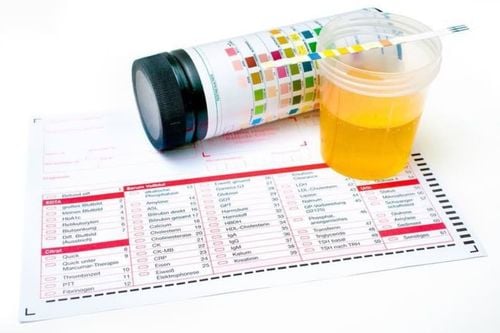
Urine is a sterile fluid produced by the kidneys and excreted from the body through the urethra. It contains various components such as water, salts, and dissolved substances from metabolic processes. Urine tests include a pH level, which indicates the balance of compounds in urine and affects its acidity level. The urine pH test analyzes the acidity or alkalinity of urine.
1. What is the normal pH level of urine?
pH measures the acidity of urine based on the concentration of free H+ ions. The normal pH of urine is around 6.0 but can fluctuate between 4.5 and 8.0 in healthy individuals. A pH below 5.0 indicates acidic urine, while a pH above 8.0 indicates alkaline urine.
2. Significance of abnormal urine pH levels
Kidney stones are small mineral deposits that can form in the kidneys and cause pain by blocking the flow of urine from the kidneys to the ureters. Kidney stones are more likely to form when urine is too acidic or too alkaline. Doctors assess urine pH to determine if you are at risk of developing kidney stones.

One of the primary factors influencing urine pH is food. Consuming excessive amounts of certain foods can lead to abnormal urine pH levels.
- Acidic foods: These include wheat, fish, soda, protein-rich foods, and sugary items.
- Alkaline foods: Nuts, vegetables, and most fruits tend to increase urine pH.
Beyond dietary factors, abnormal urine pH can also be a symptom of underlying medical conditions.
- High Urine pH (above 8.0): This may indicate conditions such as kidney stones, urinary tract infections, kidney dysfunction (like renal tubular acidosis or chronic kidney disease), metabolic alkalosis due to vomiting, respiratory alkalosis due to hyperventilation, gastric lavage, pyloric obstruction, or excessive vomiting.
- Low Urine pH (below 5.0): A more acidic urine pH can be a sign of metabolic acidosis, diabetic ketoacidosis, severe diarrhea or malnutrition, dehydration, or side effects from certain medications.
3. How to collect urine and factors affecting urine pH test
To ensure accurate pH testing, follow these guidelines:
- Thoroughly clean the genital area before collecting the urine sample.
- Collect the urine midstream, avoiding the initial and final portions of urination.
- The sample should be between 30-60ml for optimal testing.

Factors Affecting Test Results:
- Allowing urine to sit for an extended period before testing can lead to the bacterial breakdown of urea into ammonia, causing the urine to become alkaline (increased pH).
- Ammonium chloride acidifies urine.
- Sodium bicarbonate, potassium citrate, and acetazolamide alkalinize urine (increase pH).
- Certain medications can alter urine pH. It is advisable to consult your doctor about stopping these medications before a urine pH test.
- The secretion of stomach acid after meals can cause urine to become alkaline.
Vinmec International General Hospital is renowned for its high-quality medical services, modern equipment, and a team of highly skilled medical professionals. The hospital provides comprehensive, professional examination, consultation, and treatment services in a modern, courteous, and safe environment that adheres to strict sterilization standards. Patients can have complete confidence in the accuracy of their test results when choosing Vinmec.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.