This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Thi Minh Huong - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Glucose comes from the Greek word for "sweet". This is a type of sugar found in food that the body uses for energy. When glucose travels through the bloodstream to cells, it is called blood sugar or blood sugar.
1. What is Glucose?
Glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the key to keeping the body's functions working at its best. When glucose is at its optimum it usually goes unnoticed. But when they deviate from the recommended limits, you will notice unusual effects on your daily activities.Strictly speaking, glucose is the basic unit of carbohydrates, aka a monosaccharide. Not only glucose alone, other monosaccharides include fructose, galactose and ribose.
Like fat, glucose is also a preferred source of fuel by the body in the form of carbohydrates. Humans can get glucose from:
Bread and starches in general; Fruits and vegetables; Dairy products.

Trắc nghiệm: Muối trong thực phẩm, natri, huyết áp và sức khỏe của bạn
Muối, natri là chất khoáng cần thiết cho cơ thể để duy trì hoạt động ổn định. Tuy nhiên, chế độ ăn thừa muối có nguy cơ cao dẫn tới các vấn đề sức khỏe nghiêm trọng. Cùng làm bài trắc nghiệm sau đây để hiểu hơn về những ảnh hưởng của các khoáng chất này tới huyết áp và sức khỏe bạn thế nào nhé.
Nguồn tham khảo: webmd.com
2. How does glucose work?
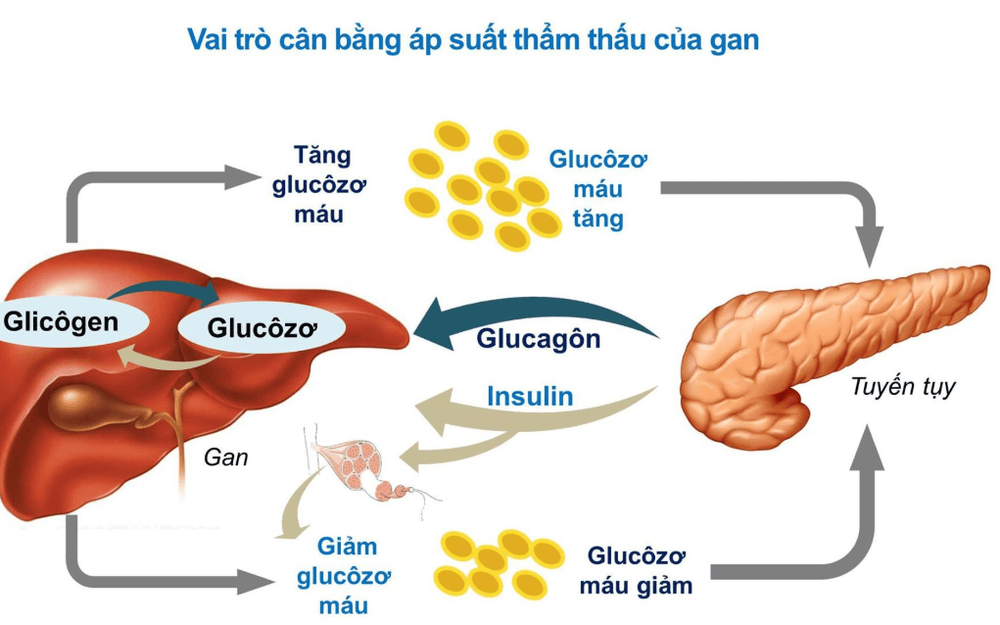
Normally, our bodies have to process glucose several times a day. Specifically, every time you eat, the body will immediately get to work and enzymes start the process of breaking down glucose. The pancreas helps by producing the hormone insulin, which is indispensable for dealing with glucose. In other words, every time we eat, the body directs the pancreas to secrete insulin to deal with rising blood sugar levels.However, some people's pancreas may work the wrong way and not do what it's supposed to do. Diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not produce insulin as it should. In this case, the patient needs external support (eg, insulin injections) to process and regulate the amount of glucose in the body.
Another cause of diabetes is insulin resistance. The liver then fails to recognize the insulin present in the body and continues to produce inappropriate amounts of glucose. The liver is an important organ that helps control sugar, stores glucose, and produces glucose when needed.
If the body does not produce enough insulin, it will release free fatty acids from fat stores. This can lead to a condition called ketoacidosis. Ketones - waste products produced when the liver breaks down fats, can be toxic in large amounts.
3. How to check glucose levels?
Checking glucose levels is especially important for people with diabetes. Most patients have to check their blood sugar as part of their daily routine.The blood test to check glucose at home is now very popular and simple. The patient will use a small needle, called a lancet, to prick the finger, and then put a drop of blood on the test strip. Insert the test strip into the meter according to the instructions to measure your blood sugar. Results are usually displayed on an electronic screen in less than 20 seconds.
3.1. Normal glucose levels Maintaining near-normal glucose levels is an important part of keeping the body functioning efficiently and healthy.
People with diabetes must pay special attention to blood glucose levels. Before eating, the optimal limit is 90 - 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). After the next 1-2 hours, the glycemic index should be below 180 mg/dL.
There are various reasons that trigger blood sugar spikes, such as:
A hearty meal; Stress (stress); Other diseases; Less physical activity; Missed dose of diabetes medication.

3.3. Blood glucose readings too low A glucose level is considered too low when it drops below 70 mg/dL. This condition is also known as hypoglycemia and can be very serious. Hypoglycaemia can occur when:
Diabetics do not take medication as prescribed; Or the average person suddenly eats less than usual and exercises excessively. Supplementing with food or drinking juice can help raise glucose levels. Diabetics also often take glucose-lowering medications, which can be purchased over-the-counter at drugstores. However, the drug also carries the risk of causing extremely low blood sugar levels leading to loss of consciousness. If this happens, the person should seek immediate medical attention.

4. Complications when not controlling blood glucose
If glucose levels are not controlled, a range of long-term consequences can result, including:Neuropathy; Heart disease; Blind; Skin infections Joint and extremity problems, especially the feet; Severe dehydration; Comatose. More serious complications associated with diabetes include:
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA): A condition in which blood ketone levels rise, causing acidosis (also called blood acidosis). May lead to coma, long-term unconsciousness or even death.; Hyperglycemia-induced hyperosmolar state (HHS): Also known as hyperglycemia due to hyperglycemia. Is a syndrome of very high glucose, causing disturbances in consciousness, increased osmolarity, and dehydration of cells with high mortality.

MSc. Le Thi Minh Huong has more than 06 years of experience in examining and treating medical, emergency and emergency resuscitation diseases. In addition, there is the ability to perform catheterization techniques, artificial kidney in patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease, continuous dialysis, plasma exchange.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Reference source: healthline.com; webmd.com