This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Thi Minh Huong - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Glucose is the scientific name of sugar - a substance very familiar and important to the body. Glucose in the blood is the main source of energy for all activities, so we easily feel tired and dizzy when blood sugar drops.
1. Overview of blood glucose
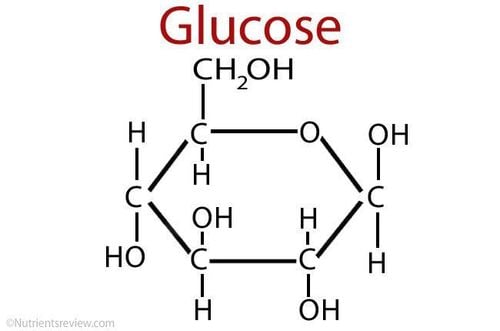
The word “glucose” is of Greek origin, meaning “sweet”. This is a type of sugar found in foods that the body needs to use for energy. When glucose in the blood moves to the cells it is called blood glucose or blood sugar.Glucose is present in the majority of daily food and drink. During digestion, enzymes break down glucose from food, then cells burn glucose for energy along with CO2 and H2O. The liver, pancreas and a number of other hormones also contribute to the regulation of glucose levels in the human body.
Insulin is a hormone that transports glucose from the blood into cells for energy and storage. People with diabetes have higher than normal blood glucose levels. This is because they don't have enough insulin to work or the cells don't respond as well to insulin as they should. High blood sugar levels for a long time can adversely affect the kidneys, eyes and other organs of the body.
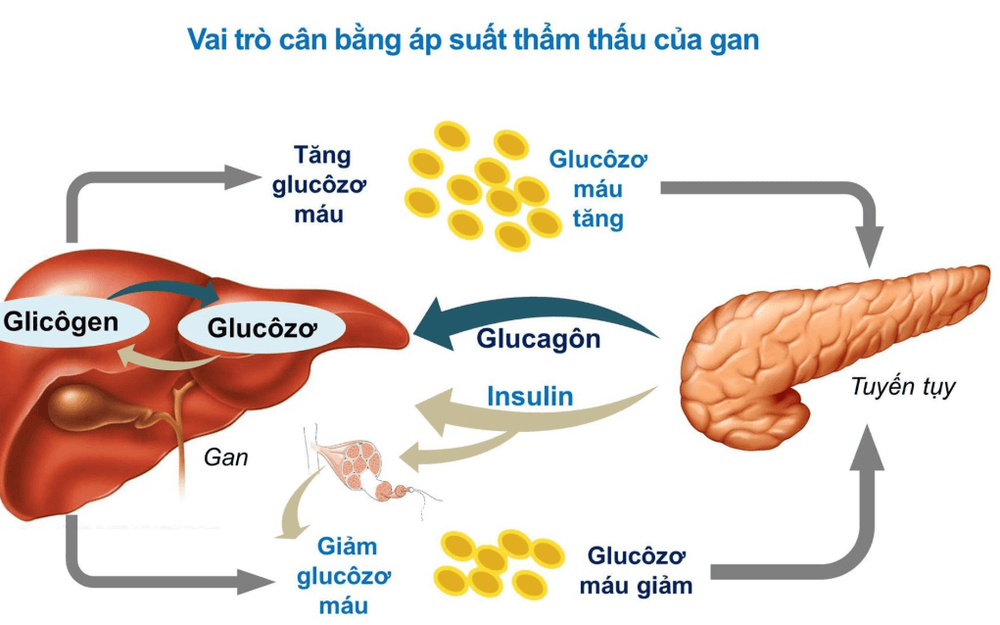
2. How does your body make Glucose?
The main source of blood glucose comes from foods rich in carbohydrates, such as rice, bread, potatoes, and fruit.When you eat, food flows down the esophagus and into the stomach. Here, acids and enzymes break the food mixture into small pieces and glucose is released in the process. The glucose then travels to the intestines and is absorbed into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, insulin helps glucose reach every cell in the body. The body's function is to keep blood glucose levels constant. Beta cells in the pancreas monitor blood sugar levels every few seconds. If your blood sugar rises after eating, the beta cells release insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin acts as a key, unlocking muscle, fat, and liver cells so glucose can move inside.
After the body has used up all the energy it needs, the remaining glucose is stored in secondary sources - called glycogen, in the liver and muscles. Your body will store enough to fuel you to function for about a day.
If you don't eat for several hours, blood sugar levels drop and the pancreas stops secreting insulin. The alpha cells in the pancreas begin to produce another hormone called glucagon. Their role is to signal the liver to break down stored glycogen and convert it back into glucose.
Newly formed glucose enters the bloodstream to replenish your energy source until you eat again. The liver can also make its own glucose using a combination of waste products, amino acids, and fats.
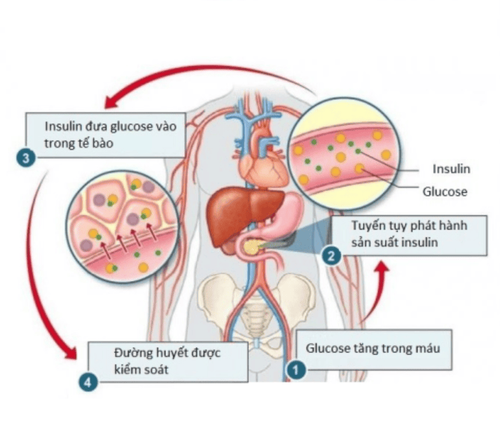
Insulin sẽ giúp glucose đến từng tế bào trong cơ thể
3. What effect does glucose have?
Most cells in the body use glucose along with amino acids (the basic building blocks of protein) and fats for energy. But the main fuel source for the brain is still glucose. Nerve cells and chemical signals need glucose to process information, otherwise the brain won't function properly.In general, glucose is a very valuable nutrient for humans, especially in the elderly and children. Around the question "What does glucose do?", doctors also added that glucose helps:
Provide energy for cells to grow and convert into many other vitamins and minerals needed by the body; Stimulate the production of insulin to help reduce appetite, and at the same time balance hormone levels to make the digestive system work healthier; Becomes a reserve energy source in the form of glycogen and will be used when we start to have an energy deficit.
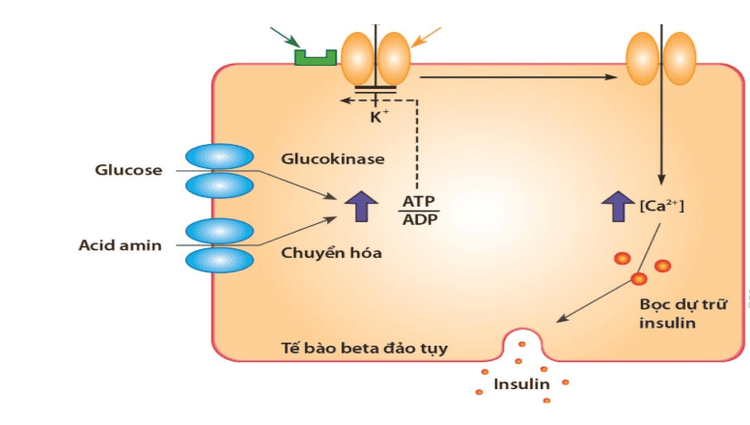
Glucose cung cấp năng lượng cho cơ thế con người
4. Blood glucose levels and diabetes
Blood sugar usually rises after eating, then drops a few hours after insulin moves glucose into cells. Between meals, blood sugar should stay below 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). This is called your fasting blood glucose level.There are two types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes: Your body does not have enough insulin because the immune system attacks and destroys the cells of the pancreas - where insulin is produced. Type 2 diabetes: The cells do not respond to insulin as they should. So the pancreas has to make more and more insulin to move glucose into the cells. Eventually, the pancreas becomes damaged and cannot make enough insulin to meet the body's needs. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot move into cells, while blood glucose levels remain high. A blood glucose reading above 200 mg/dl 2 hours after a meal or above 125 mg/dl when fasting is high, called hyperglycemia.
Bệnh lý tiểu đường
Heart disease, heart attack and stroke; Kidney disease; Nerve damage; Eye disease (retinopathy). People with diabetes need to check their blood sugar regularly. In addition, exercising, maintaining a healthy diet, and taking medications regularly can keep blood sugar levels stable and prevent complications from diabetes.
MSc. Le Thi Minh Huong has more than 06 years of experience in examining and treating medical, emergency and emergency resuscitation diseases. In addition, there is the ability to perform catheterization techniques, artificial kidney in patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease, continuous dialysis, plasma exchange.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Reference source: webmd.com