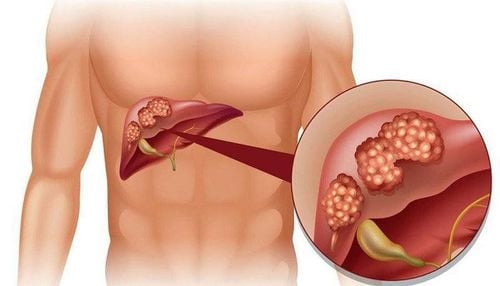
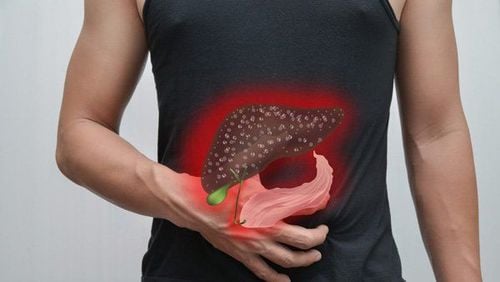
Side effects of excess vitamin K include enlarged liver, pale skin, increased sweating, shortness of breath, muscle stiffness, edema, irregular breathing, decreased movement or activity, swollen eyelids, or red skin. In infants and newborns, vitamin K plays an important role in preventing and controlling bleeding, especially bleeding in the brain and meninges. At the same time, it can combine with calcium to help strengthen bones. However, excess vitamin K can also be very dangerous as it can cause hemolysis, jaundice, and cerebral palsy.
1. What is vitamin K?
Vitamin K is an important component of the liver enzyme system that synthesizes clotting factors such as prothrombin (factor II), factors VII, IX, and X, a group of fat-soluble vitamins, similar in structure and play an important role in regulating blood clotting, necessary for supporting blood clotting. Vitamin K also supports bone metabolism and calcium metabolism in the vascular system. If the body is deficient in vitamin K, the blood will not be able to clot, leading to bleeding and this can be fatal.
2. Types of Vitamin K
There are 2 natural forms of vitamin K: vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, found in natural foods, and vitamin K2, also known as menaquinone, produced by gut microbiota.
There are 3 known synthetic forms of vitamin K: vitamins K3, K4, and K5. While natural vitamins K1 and K2 are non-toxic, the synthetic form K3 (menadione) is toxic.
Vitamin K is commonly found in foods such as broccoli, spinach, celery, asparagus, cucumber, parsley, olive oil, parsley, cloves, eggs, dried fruits, and more.
3. Risks of Vitamin K Deficiency
When the body lacks vitamins and minerals, children can experience stunted growth and develop various health problems. For example, a deficiency in vitamin A can lead to eye diseases, respiratory infections, and digestive disorders; a lack of vitamin B1 can cause edema, inflammation of nerves, and heart failure; a deficiency in vitamin C can easily cause bleeding under the skin and mucous membranes, reducing the body's disease resistance, especially infections; a deficiency in vitamin K can lead to bleeding, particularly in the brain and meninges; a lack of vitamin D and calcium can cause rickets; zinc deficiency can cause skin diseases; a lack of fluoride can lead to dental problems; and iron deficiency can result in anemia...
When the body lacks vitamin K, blood clotting becomes slower (it takes a longer time for blood to clot). This can cause excessive blood loss and increase the risk of death from injuries. Vitamin K deficiency is rare in healthy adults. However, individuals with severe digestive disorders or those undergoing long-term antibiotic treatment are at risk of vitamin K deficiency.
4. Excess vitamin K
An excess of vitamin K usually only occurs when administered via long-term injections, which can lead to hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells) and jaundice.
Side effects of vitamin K overdose include an enlarged liver, pallor, increased sweating, difficulty breathing, muscle stiffness, edema, irregular breathing, decreased movement or activity, swollen eyelids, and red skin.
In infants and newborns, vitamin K plays a crucial role in preventing bleeding, especially hemorrhages in the brain and meninges. Additionally, it can combine with calcium to strengthen bones. However, an excess of vitamin K can also be very dangerous, potentially causing hemolysis, jaundice, and cerebral palsy... The type of vitamin K commonly used for newborns is natural vitamin K1. The reason newborns are given a vitamin K injection immediately after birth is that this vitamin is difficult to transfer across the placenta, so newborns require a vitamin K injection to prevent brain hemorrhages. Furthermore, breastfed babies absorb less vitamin K compared to babies who have Formula Feeding. Therefore, to prevent vitamin K deficiency in their babies, mothers should increase their intake of foods containing this vitamin.
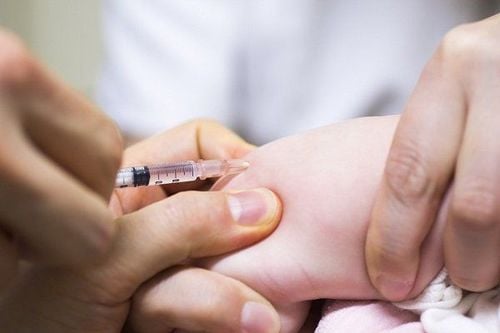
Brain and meningeal hemorrhages are extremely dangerous for newborns, potentially causing death or severe lifelong disabilities. Therefore, to prevent the risk of bleeding in infants and promote their healthy development, healthcare facilities must strictly adhere to the administration of vitamin K, either orally or by injection, according to the dosage and guidelines set by the Ministry of Health.
Anticoagulant medications such as warfarin (Coumadin®) are prescribed to inhibit the normal function of vitamin K in the body. Consuming very large or very small amounts of vitamin K can change the effectiveness of these medications. If you are taking anticoagulants, you should pay attention to the foods you consume, such as spinach and leafy green vegetables, as they contain a high level of vitamin K. It is also important to ensure a consistent daily intake of vitamin K to maintain the drug's efficacy.
Consult your doctor before using supplements like ginkgo biloba and garlic, as these substances can also affect blood clotting.
Master of Medicine, Doctor. Mỹ has over 6 years of experience as an Internal Medicine physician at Central Hue Hospital, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Tam Tri Danang Hospital, and Danang Hospital. Currently, Dr. Mỹ is a General Internal Medicine Physician at Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.