1. What is a septate ovarian cyst?
Ovarian cysts are common benign tumors, however, if these tumors are not detected in time, they will develop and harm the health of the patient, especially reproductive health. Ovarian cysts have an outer shell structure, commonly called a cyst shell, that covers some substances and fluids inside. Ovarian cysts are classified into non-functional cysts and functional cysts (Functional cysts are related to the menstrual cycle and usually go away).
A septate ovarian cyst, also known as a mucinous ovarian cyst, is a type of solid cyst, common in women of reproductive age.
Septate ovarian cysts typically appear on one side of the ovary. However, it is rare for this type of cyst to occur on both sides. They have several main characteristics as follows:
- The outer cyst shell is usually thicker than other types of ovarian cysts, and they are white or slightly yellow.
- Their size is quite large.
- The tumor has multiple septa and may have internal echoes, though at a very low level.
- The mucus inside the tumor is yellow, and if the tumor is left untreated for too long, it can exceed a weight of 10 kg.

2. How dangerous is a septal ovarian cysts?
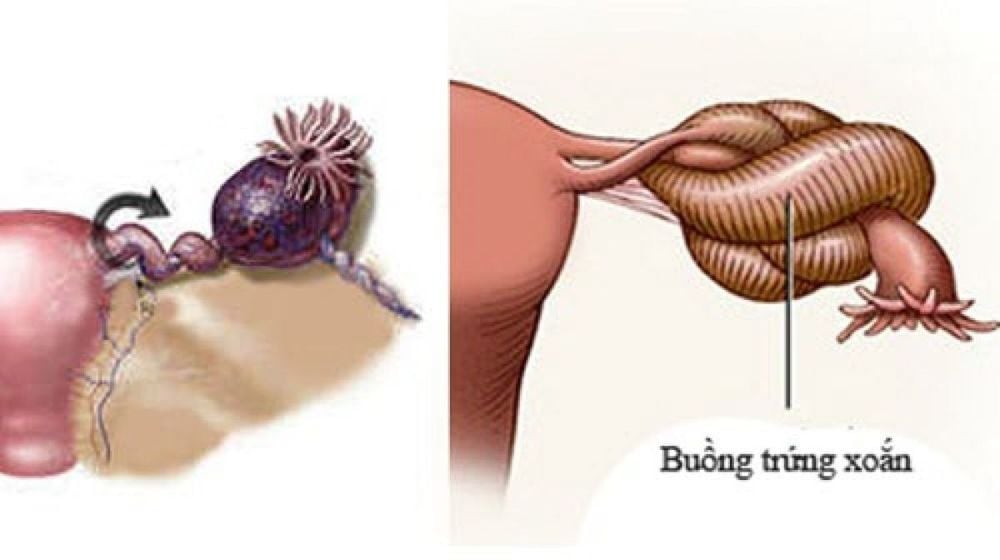
Clinically, a septate ovarian cyst is considered a dangerous type of solid cyst. If not detected and treated early, these cysts can develop and cause several complications, such as cyst torsion, internal organ compression, cyst torsion or transformation into cancer. In addition to potential complications that may arise if septate ovarian cysts are not treated in a timely manner, patients also face issues related to their overall and reproductive health, including the following:
- Menstrual disorders: The impact of ovarian cysts on the ovulation process can cause disorders such as amenorrhea (an absence of a menstrual period), delayed menstruation, changes in the volume and color of menstrual blood, and even vaginal bleeding in the absence of menstrual cycle.
- Reduced fertility rate: Patients with septate ovarian cysts often have more difficulty conceiving than normal individuals due to the disruption in the ovulation process.
- Abdominal and vaginal pain: The significant size and mass of the septate ovarian cyst frequently exert pressure on nearby organs, leading to various types of pain for the patient. This may include persistent or intermittent pain in the pelvic area, pain along the lower back, vaginal pain, and pain during sex... In addition, if the cyst compresses the rectum or vagina, it will make it difficult for the patient to move and defecate.
3. What age group is most likely to have septate ovarian cyst?
Although ovarian cysts can occur at any age from puberty to menopause, the highest rate of ovarian cysts is still in the reproductive age group. In general, ovarian cysts have a fairly high incidence rate, so it's important for people to have regular health check-ups to promptly detect and address any occurrences.
4. How to treat septate ovarian cysts?
Septate ovarian cysts are classified as conditions with a very high chance of recurrence. However, depending on various factors such as the size of the cyst, the age of the patient, and their preferences, the doctor will provide the most appropriate treatment plan.
- For women who do not wish to have children, the doctor may recommend complete removal of the ovary. This is the fastest way to prevent the risk of recurrence.
- For women who are not yet married or still wish to have children, the doctor will try to perform a cystectomy to remove the tumor while preserving as much of the ovary as possible to maintain the patient's reproductive ability.
- Additionally, the size of the tumor will guide the choice of surgical method. There are two surgical methods: open surgery for large tumors and laparoscopic surgery for smaller ones.
- In addition to surgical intervention for tumor resection, depending on the condition of the tumor, patients may not require surgery and can undergo medical treatment and pharmacotherapy as prescribed by the physician.

Ovarian cysts are a common condition in women, and most of them are benign tumors (with a low risk of cancer). Although the prevalence of malignant ovarian cysts and ovarian cancer is not high, this type of cancer has high malignancy and often shows no symptoms in the early stages, it can only be detected during gynecological examinations and ultrasounds. This is why doctors recommend that women undergo regular gynecological check-ups every 4 to 6 months to detect early signs of abnormal ovarian cysts as well as other gynecological diseases.
Along with treatment, Vinmec International Hospital also provides a basic gynecological examination and screening package. This will help patients in the early detection of infectious diseases, facilitating straightforward and cost-effective treatment options. The screening process enables early detection of gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) even when there are no symptoms.
When receiving treatment at Vinmec International Hospital, patients will be attended to by a team of experienced physicians. The procedures are conducted with utmost seriousness, with regular oversight and monitoring. Additionally, the latest global protocols and regulations are consistently updated. Patients will receive attentive care, rest in high-end hospital rooms designed to international hotel standards, and enjoy friendly staff and comfortable amenities that create a homely atmosphere.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.