This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Currently, there is no single test or observation that is sufficiently reliable to diagnose sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, so a combination of clinical and biochemical, radiological, and manometry is required. sphincter force.
1. The role of sphincter of Oddi . pressure measurement
According to Rosch, Koch and Demling 1976, measuring the sphincter of Oddi pressure is very useful in assessing the long-term outcome of endoscopic sphincterotomy. Although some studies have shown that the efficacy of endoscopic sphincterotomy is not predictable (Staritz, Ewe, and Zum Buschenfelde 1986), most studies suggest that pressure measurement is not necessary after endoscopic sphincterotomy. endoscopy if pain does not recur (Ponce 1983, Geenen 1984).
Although sphincter of Oddi is used to evaluate disorders of the bile ducts and pancreas (hepatic duct stones) Toouli 1982; Carr-Locke and Gregg 1984, acute and chronic pancreatitis Johnson, Novis 1985; Okazaki, Yamamoto and Ito 1986, as with other disorders, this technique has only relative diagnostic importance. This technique has an essential role in the diagnosis of papillary muscle stenosis.
2. Different views on the effect of cyclic sphincter of Oddi contraction on biliary drainage There are differing views on the effect of cyclic sphincter of Oddi contraction on biliary drainage. According to some authors, the cyclic sphincter of Oddi activity is peristaltic in nature leading to the expulsion of bile into the duodenum (Toouli and Watts). According to some other authors, it is this activity that slows down the flow of bile and pancreatic juice. People use very small probes to measure the sphincter of Oddi pressure on endoscopically, the pressure value is lower than the pressure value when measured with a plunger pump. Electromyography + pressure showed that the electrical activity of the sphincter of Oddi rhythmically (due to an increase in action potential) corresponds to the ascending phase of the sphincter of Oddi pressure wave (Bortolotti 1985). Touli 1982 reported that there was no difference in sphincter of Oddi pressure between patients with gallbladder intact and patients with cholecystectomy. However, Tanaka, Ikeda and Nakayama 1984 performed the following experiment: Place a super probe into the bile duct in 7 patients before and after cholecystectomy + induce sphincter with Morphine. Before cholecystectomy, morphine did not cause muscle weakness. Adding Carulein (Decapeptide 20 times stronger) contracts the gallbladder and increases bile duct pressure. The basal (baseline) pressure is also elevated after cholecystectomy, which means that the gallbladder has a role as a reservoir in pressure compromise.
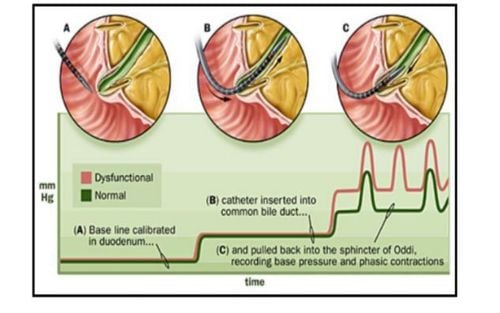
Spasms (Toouli 1984). Increasing frequency has a period (Bar-Meir 1979). Abnormal movement direction of periodic waves (Toouli 1982). Adverse response (Hogan 1982). According to a study by Meshkinpour 1984, abnormal pressure of the sphincter of Oddi in 10 patients with recurrent right upper quadrant pain, intermittent mild elevation of liver enzymes, normal bile duct and pancreatic imaging. The baseline pressure of the sphincter of Oddi was significantly higher than in 9 normal patients, increasing the frequency of the retrograde sphincter, variation, and frequency of the normal sphincter of Oddi. According to a study (Touli 1985) on 38 patients after cholecystectomy (35 women) with intermittent pain and bile duct dilatation or transient elevation of liver enzymes (10 patients) without both of these symptoms (6 patients). The measurement results are clear in 32 patients, 25 patients have abnormal measurement results (compared to control patients), abnormalities include:
Excessive muscle gain in 12 patients. Increased frequency has a cycle of 11 patients. Raised baseline pressure in 8 patients. Paradoxical response in 10 patients. A paradoxical increase in sphincter of Oddi pressure after cholecystokinin or ceruletide was found in 10 to 62 patients with suspected biliary dyskinesia. The authors used a Microtransduser machine to compare 17 patients with post-cholecystectomy pain with 9 controls. Morphine is used to increase sphincter of Oddi contractions continued 30 minutes after Ceruletide is used to relax the sphincter of Oddi. Results 13 patients developed pain in response to morphine with increased biliary pressure. 3 patients had pain but no biliary pressure elevation, and the stimulation test was painless despite increased biliary pressure. Because some patients developed pain at low biliary pressure, the authors conceded that there is a difference in pain thresholds to indicate the degree of sphincter spasm. In the study, patients with post-cholecystectomy syndrome had higher sphincter of Oddi pressures than controls, although there was no typical difference in common bile duct pressure.
4. How to fully diagnose sphincter of Oddi . dysfunction
Currently, there is no single test or observation that is sufficiently reliable to diagnose sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, so a combination of clinical and biochemical, radiographic, and manometry is required. sphincter. Whether mild to moderate or severe inflammation and fibrosis of the sphincter of Oddi can be properly assessed endoscopically is uncertain even in biopsy. To some extent dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi with fibrosis is manifested by the inability to place the catheter and otherwise functional changes that are not endoscopically manifest. In patients with biliary tract and pancreatic duct abnormalities (common bile duct stones) there will be changes in baseline pressure.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References 1. Le Quang Quoc Anh. The basics of sphincterotomy of Oddi and endoscopic gallstone removal. Gastrointestinal diseases. Ho Chi Minh City Digestive Science Conference 1998, 35 - 40. 2. Le Quang Quoc Anh. Role of retrograde endoscopy in biliary-pancreatic pathology. Proceedings of the full text of scientific topics at the Vietnamese surgical conference. Surgical journal. Hue 2002, 61-70. 3. David Fleischer. Endoscopic management of biliary tract obstruction. Techniques in therapeutic endoscopy. Saunders 1992.8.2-8.7. 4. Franklin E. Kasmin, David Cohen, Subash Batra. Needle-knife sphincterotomy in a tertiary referral center: efficacy and complications. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Vol. 44, 1996, 48 - 53.