This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Vater papillary sphincteric stenosis is a clinical syndrome, most patients are middle-aged women, have undergone cholecystectomy, intermittent pain associated with abnormal liver function tests or serum amylase, possibly associated with biliary dilatation.
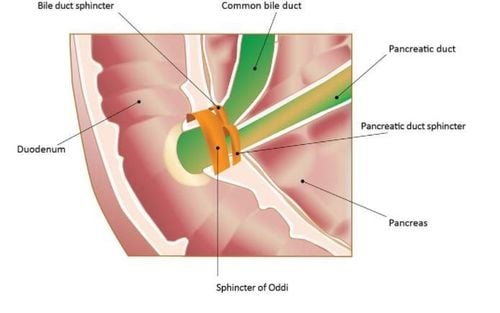
1. What is the histology of the sphincter of Oddi in Vater papillary sphincter?
Histological abnormalities in the majority of duodenal papillae in patients with biliary-pancreatic disorders are variable, with isolated pain that has been recognized for many years. A report of surgical treatment of Vater sphincter stenosis in 92 patients with chronic epigastric pain and sphincter of Oddi stenosis found that 85 of them had abnormalities such as fibrosis or papillary hypertrophy. duodenum, functional stenosis without pathology occurred in 7 cases. Biopsies from the major duodenal papilla in postoperative cholecystectomy patients with abdominal pain and papillary stenosis were compared by Acosta et al., by biopsies from patients without biliary tract disease. The abdominal pain group had higher fibrosis and inflammation than the control group.
2. What do the studies say? Research results on clinical manifestations of the disease are loosely related. Although Acosta and Nardi (1966) did not find inflammation in the control group of 30 patients who underwent large duodenal papillae biopsies. Grage et al (1960) found inflammatory fibrosis in about 5% of biopsies from a control group of 31 patients without biliary tract disease. Grage et al (1960) studied 31 patients and found almost one third no histological changes. In the surgical batch with biopsies found pathological abnormalities in 50-75% of patients. In summary, in patients who were strictly indicated for surgery, a low incidence of related pathology was found.
3. Etiology and pathology of sphincter of Oddi stenosis There is a close relationship between papillary stenosis and biliary stones. Acute inflammation of the great duodenal papilla may be associated with common bile duct stones, which Doubilel and Mulholland from 1956 suggested that distal fibrosis may produce mudstones. Experience has shown that the bile duct itself can produce acute inflammation and muscle hypertrophy.
These observations lead to the hypothesis that the passage of small stones or biliary sludge may cause papillary stenosis. Another hypothesis is that the clinical presentation of papillary stenosis may be explained by dysfunction of the sphincter leading to sphincter spasm or hypertrophy. However, acute or chronic inflammation of the great duodenal papilla occurs in the presence of papillary stenosis but it is difficult to accept that functional spasm may produce pathological changes in the sphincter of Oddi.

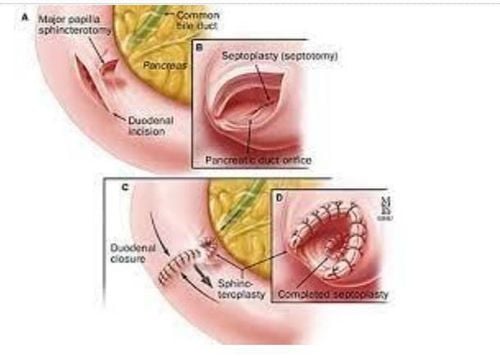
4. Diagnosis of stenosis of the papillary Vater sphincter through surgery
Since 1959, it has been accepted by research as a stenosis of the papillary sphincter of Vater when there is resistance when the rod is inserted through the papillary muscle during surgery. There are also many other authors doing the same work such as Catel and Colcock 1953; Mahorner 1959; Grage et al. 1960; Autio and Parvinen 1965 or Acosta and Nardi 1966.
Although this observation was clearly associated with muscular stenosis, Braseh and Me Cann (1967) measured the normal diameter of the biliary-duodenal junction in 201 cases. , most cases of 3mm dilation will pass without difficulty, while a 6mm dilatation should pass in almost all cases. Various methods of measuring intraoperative bile duct pressure and bile flow with and without operation of the sphincter of Oddi will be used as a test to evaluate papillary stenosis. However, there are many nonsensical factors that affect the large papilla and its constriction during surgery. Sphincter of Oddi function is controlled by physiological conditions and effects challenges.
Stimulation test Sphincter of Oddi function stimulation test was first described in the late 1940s as Knight, Muether and Sommer 1949, Myhre, Nesbitt and Hurley 1949; Snape, Wirts and Friedman 1949, but later research investments show the same sensitivity and specificity as those of Burke, Plummer and Bradford 1950; Wirts and Snape 1951; Dreiling and Richman 1954.
Morphine-Neostigmine stimulation test The Morphine-Neostigmine stimulation test was described in 1965 (Sterkel and Knight). The objectivity of the test is that it produces pain in the patient and increases the serum pancreatic enzyme level in response to the combined action of Morphine-Neostigmine, which reverses the contraction of the sphincter of Oddi and the release of pancreatic juice. . Several studies have found it useful in evaluating papillary muscle stenosis such as Nardi and Acosta 1966; Gregg et al. 1977; Raskin 1978; Broad, Gordon and Vernik 1979; Madura 1981. There are also some other valuable studies such as Steiberg, Salvato and Toskes 1980; Warshaw 1985. Determination of other provoking tests included markers of abnormalities such as serum bile acid measurements (Dolgin and Soloway 1980), liver enzymes (Roberts-Thomson and Toouli 1985) and pancreatic ductal diameter measurements as well. such as bile ducts by ultrasound (Berezny et al. 1985, Warshaw et al. 1985).
There are many ideas given to explain the positive result of Morphine-Neostigmine test:
+ Nardi and Acosta (1966): Increased Amylase or Lipase 4 times, accompanied by pain. + Gregg et al. (1977): Increases Lipase 5 times. + Raskin et al. Madura et al. (1981): Pain and increased enzyme 4 times. + Broad, Gordon and Vernick 1979: Increased enzyme 3 times, with pain.
The above authors all agree that Morphine-Neostigmine is valuable in diagnosing Vater papillary sphincter stenosis (based on the above criteria). In a rather sophisticated study by Robert-Thomson and Toouli (1985) the effectiveness of Morphine-Neostigmine was investigated in 3 groups of patients:
Group 1: 40 patients who had a cholecystectomy with biliary drainage and/or increased transient liver enzymes after pain. Group II: 20 patients had cholecystectomy with pain but no biliary tract dilation or spontaneous elevation of liver enzymes. Group III: 20 patients with gallbladder and no biliary tract disease. Positive test result: Liver enzymes increased 2 times.
Mild to severe pain was found in 81% of patients, 2 patients in the control group had mild pain. However, the frequency of severe pain was significantly different in the first 2 groups of patients compared with the third group, all patients had AST elevations after Morphine-Neostigmine with mild to severe pain. Amylase elevation and no pain/2 patients in group, 5 patients in group II and 2 patients in control group (10 patients without abdominal pain and no history of biliary tract surgery). Positive test results (increased AST + Amylase) were most common in group I.
Correlation between test results and papillary stenosis There is a correlation between test results and surgically confirmed papillary stenosis, but results are more common in Morphin-Neostigmine than in the Secretin test. After intravenous injection of 1 uni/kg Secretin dilated the pancreatic duct, recorded in 10/12 patients on the surgical field with sphincter of Oddi stenosis (in the study group, there were 17 patients with dilated pancreas, 14% of the control group had dilated pancreas). pancreatic duct and these patients did not have major duodenal papillomatosis).
Increased Amylase + pain has no discriminant value. There is a clear correlation between test results and patient response after sphincter of Oddi surgery. Experience with stimulation testing based on changes in pancreatic and bile duct diameters is very limited, some authors did not see changes in pancreatic and bile duct diameters on ultrasound.
Bile duct scintigraphy (cholescintigraphy) Bile duct radiography is used to study functional obstruction of the bile duct (Lee 1985; Roberts-Thomson 1986; Shaffer 1986). Robert-Thomson et al. (1986) performed cholangiography with Te"-di- isopropyl-iminodiacetic acid (DIDA) on cholecystectomy patients, there were 20 asymptomatic patients, 45 patients with gallbladder-type pain, among these some patients had biliary dilatation and elevation of liver enzymes
Result: Asymptomatic patients were compared at the time when Tecsnetium (TCP) reached 50% of the maximum activity in the common hepatic duct (Tso) and compared. at the time the isotope enters the duodenum Patients with bile duct and/or liver enzymes show significant elevations (T50) and increases at the time of duodenal entry. Outcomes of symptomatic patients + no disturbances sphincter dysfunction was not different from the control results.Shaffer et al. (1986) noted that the time to maximal biliary radioactivity was greater in 9 patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. compared with 35 patients who had had a cholecystectomy but had no symptoms, the percentage of radioactive material excreted at 45 min, 60 min, and 90 min was also lower in symptomatic patients and the elimination rate in the bile duct was slower (b) prolonged poop).
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:1. Le Quang Quoc Anh. The basics of sphincterotomy of Oddi and endoscopic gallstone removal. Gastrointestinal diseases. Ho Chi Minh City Digestive Science Conference 1998, 35 - 40.
2. David Fleischer. Endoscopic management of biliary tract obstruction. Techniques in therapeutic endoscopy. Saunders 1992.8.2-8.7.
3. Franklin E.Kasmin, David Cohen, Subash Batra. Needle-knife sphincterotomy in a tertiary referral center: efficacy and complications. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Vol. 44, 1996, 48 - 53.
4. Geenen J.E, Hogan W.J. Sphincter of Oddi. Gastroenterologic Endoscopy, Sivak.