This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Nguyen Xuan Ninh - Emergency Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Tracheal intubation to help ventilate the patient is a technique commonly used in emergency departments. When mechanical ventilation is no longer indicated, the patient will be considered by the doctor to remove the endotracheal tube.
1.When is the patient extubated? Indications for extubation are indicated when:
The patient is breathing well on his own and no longer has respiratory failure. The patient is no longer indicated for mechanical ventilation through an endotracheal tube. The patient had a tracheostomy.
2. When is the patient not extubated? The patient coughs up poorly, unable to protect the airway. The patient is not able to breathe well on his own, and there is a risk of respiratory failure.
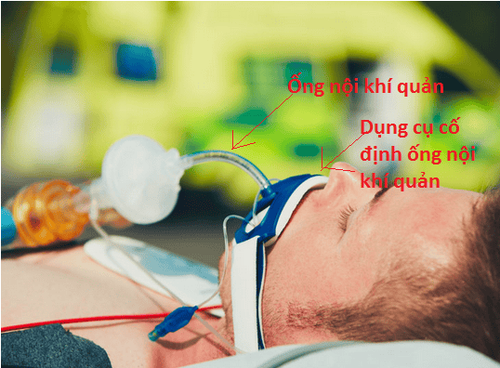
Người bệnh đang được thở máy qua ống nội khí quản (Nguồn hình: https://www.healthline.com)
3. Steps to perform the extubation technique When the doctor has decided to extubate the patient, the doctor will take the following steps:
Step 1: Notice:
Inform the condition of the patient to relatives and the patient, explaining the steps to be taken, the risks and possible complications. Have the patient fast for at least 4 hours. Remove viscous sputum in the endotracheal tube and the nose, mouth, and throat areas. Step 2: Doctors and nurses will prepare necessary tools such as: oxygen line, oxygen mask, ventilator, sputum suction machine, sputum suction tube, syringe, gloves,... Especially, doctor will also prepare the same equipment as when intubation because the patient is at risk of acute respiratory failure and needs to be reintubated.
Step 3: The patient is placed in a lying position 45 - 90 degrees high
Step 4 . The nurse will attach a monitor to the patient. The doctor will re-evaluate the patient's parameters such as consciousness, pulse, blood pressure, breathing rate, SpO2 before extubation
Step 5 . Doctors and nurses will wash their hands with an antiseptic solution under the tap, wear hats, masks, and gloves.
Step 6 . The nurse uses a sputum suction tube connected to the suction machine to conduct aspiration of viscous sputum for the patient.
Step 7. A nurse will remove the endotracheal tube fixator. The nurse will then use a syringe to completely release the air contained in the cuff of the endotracheal tube.
Step 8. The doctor will insert the suction tube into the endotracheal tube. The doctor will ask the patient to take a deep breath while closing the suction valve and slowly withdrawing the endotracheal tube.
Step 9. After that, the patient will be aspirated by a nurse to collect the remaining fluid in the nasopharynx.
Step 10 . A nurse will give the patient oxygen as soon as the endotracheal tube is removed
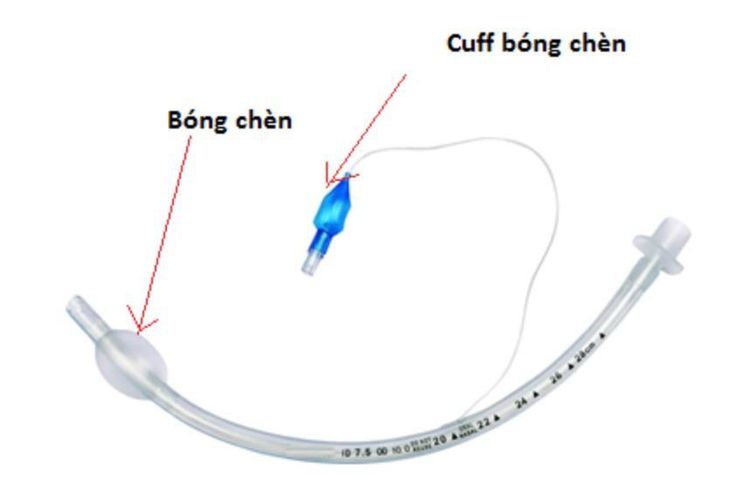
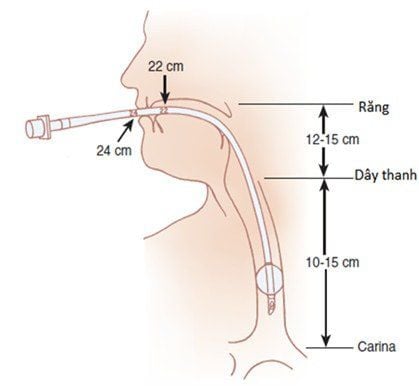
Hình ảnh ống nội khí quản
Step 11. The patient is sprayed with aerosol if indicated.
Step 12 : The medical staff will shake the patient's back if necessary, instruct the patient on how to cough and sputum when there is sputum, and suck sputum in the throat if the patient coughs poorly.
Step 13: Medical staff will clean up equipment, doctors and nurses remove gloves, wash hands.
Step 14: The patient's condition is closely monitored: consciousness, pulse, blood pressure, breathing rate, SpO2, signs of shortness of breath, stridor breathing, labored breathing, respiratory muscle contractions, cough, .
Step 15: After 6 hours of extubation, the doctor will re-evaluate the patient's condition to decide whether to feed the patient again or continue monitoring.
Step 16: The doctor and nurse will record the time of extubation and the patient's condition in the medical record.
4. Complications and how to deal with extubation? After extubation, the patient may have difficulty breathing. There are causes of shortness of breath such as: laryngo-bronchospasm, glottis edema. With this condition, the doctor will give the patient an aerosol bronchodilator, anti-edema drug or possibly non-invasive mechanical ventilation. If the shortness of breath is severe or persistent, or the patient has respiratory muscle fatigue, the doctor will consider re-intubation.
Reflux of fluid from the stomach into the respiratory tract causes aspiration pneumonia. With this complication, the doctor will give prevention by making the patient fast before and after extubation, and aspirate gastric juice before extubation. If aspiration pneumonia occurs, the doctor will consider the use of medication as well as other interventions such as oxygen breathing, re-intubation.
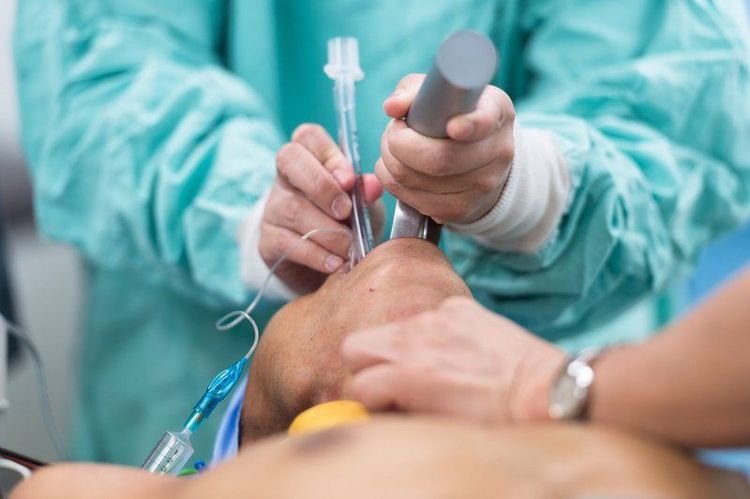
Một số trường hợp người bệnh có thể được đặt lại ống nội khí quản
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
References:
Joseph Varon et al. Handbook of Critical and Intensive Care Medicine Third Edition (2016), Springer, p355-359.