This is an automatically translated article.
Anesthesia has been studied by researchers and plays an important part in medical surgeries to help patients not experience side effects. So what is the anesthetic made of and how does the mechanism of action of the anesthetic?
1. What is an anesthetic?
Anesthesia is a reversible central nervous system depressant when used in a certain dose. The drug has the effect of causing the patient to temporarily lose consciousness, lose sensation and reflexes, but still maintain vital functions such as breathing, circulation, metabolism, excretion,...
Most drugs anesthesia is toxic, so each drug will have its own maximum dose. If the dose is too high, the patient will be poisoned, but if the dose is too low, it will not be enough to anaesthetize the patient. Therefore, the role of anesthesiologist is extremely important, to calculate the dose of anesthetic to suit each patient, each stage of the surgery to ensure enough for the patient to fall into a state of anesthesia. but not drug poisoning.
During the development process, scientists have found many types of anesthetics and clinical applications. There are drugs that have been used so far, but some drugs after a period of use found poor sleep quality, high toxicity, and many side effects, so they were no longer used. . Based on how the anesthetic is introduced into the body, anesthetics are divided into two main groups:
Inhalation anesthetics: gaseous, evaporating liquid. When used for anesthesia, these drugs are introduced into the patient's body through the respiratory tract, the patient inhales the anesthetic vapor, the drug will pass through the alveoli into the bloodstream. Intravenous anesthetics: barbituric group, benzodiazepine group, neuroleptic group (beuroleptic), hypnotic group (hynotic). These drugs are given directly into the bloodstream through an intravenous line.
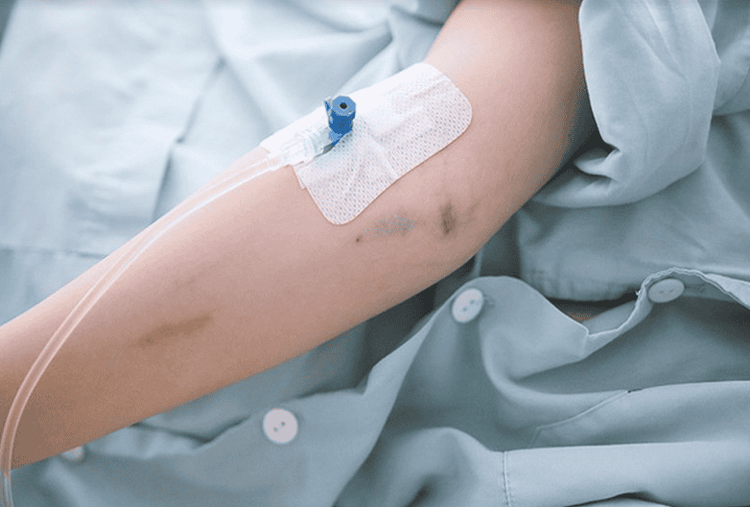
Thuốc mê được đưa vào cơ thể qua đường tĩnh mạch
2. Mechanism of action of anesthetics
No matter how the anesthetic is introduced into the body, it will eventually enter the bloodstream and reach the central nervous system. Anesthesia will cause central nervous system depression in the following order: from the cerebral cortex to the subcortical region, then to the spinal cord and finally to loss of consciousness, inhibiting motor nerves.
Up to now, there have been many studies on the mechanism of action of anesthetics on nerve cells, causing the state of anesthesia. But not all theories can explain the mechanism clearly, most of them can only explain phenomena based on chemical, physical, physiological and neurobiochemical data. The following are the mechanisms that are receiving the most attention:
Physical and chemical mechanisms: Meyer (1899) and Overton (1901) found that anesthetic potency and properties are closely related to lipid solubility of anesthetics. The anesthetic properties are therefore related to the solubility of the drug in biofilms. Anesthesia causes the biofilm to stretch to a limited volume that produces anesthesia. The stretchable biofilm is also caused by the reaction of the anesthetic with the protein. It is possible that such changes in cell membrane structure affect nerve transmission at brain junctions and lead to coma. Physiological and neurochemical mechanisms: Anesthesia has been found to inhibit nerve conduction at the synapses, but it has not been determined whether before or after the synapse. If presynaptic, the cause is related to a decrease in acetylcholine release or to the acetylcholine inhibitory effect of gamma aminobutyric acid. If it is after the junction, it is due to a decrease in sensitivity to acetylcholine or an increase in the polarity of the membrane after the junction. Scientists believe that anesthetics act on mitochondria, reducing intracellular Ca++ uptake leading to decreased neurotransmitter release, destabilizing postsynaptic membranes leading to decreased synaptic neurotransmitters and reduce central nervous system function.
Thuốc mê tác động đến hệ thần kinh trung ương của con người
Under the effect of anesthesia, the patient will go into a coma through the following stages:
Analgesia phase: The patient is still awake, feeling sleepy, responding to analgesia. Excited phase: The patient gradually loses consciousness, inhibits the cerebral cortex, making the patient in a state of aggressive agitation, struggling, salivation, vomiting. Surgical stage: The patient loses consciousness and loses reflexes, skeletal muscle relaxation. The patient's breathing is regular, the eyelid reflex is lost, the eye movement stops, and the breathing becomes shallow. Stage of bulbar paralysis: Respiratory and vasomotor inhibition in the medulla oblongata should cause respiratory paralysis leading to respiratory arrest and cardiac arrest. The patient may die after 3-4 minutes. Thus, if the dose of anesthetic is not calculated and controlled correctly, carefully, it can cause death of the patient. As for the amount of drug just enough for anesthesia, after stopping the drug, the inhibitory effect will disappear, the functions will recover and the patient will gradually wake up.
In fact, until now, the mechanism of action of anesthetics has not been clearly proven, but only hypotheses have been proposed. Among them, there are two most widely accepted hypotheses: the physico-chemical mechanism is the modification of the neuronal membrane and the neurophysiological and biochemical mechanism is the decrease in release or inhibition or decrease in sensitivity. with acetylcholine thereby affecting the process of nerve conduction causing the patient to lose consciousness, lose sensation and movement.
In order to best avoid and treat the side effects caused by anesthetics, it is most important that you share all of your health information with your doctor so that he or she can understand and should follow the instructions given by the doctor.

Người bệnh có tiền sử dị ứng thuốc mê cần thông báo với bác sĩ ngay
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.